Sustainably Growing the Chainlink Network
Chainlink is being developed with the goal of providing a wide variety of decentralized services that smart contracts and Web2 systems need to create a world powered by cryptographic truth. While Chainlink’s unique oracle consensus was initially applied to decentralized data feeds, it is now expanding to include secure off-chain computation and cross-chain interoperability.
Given the evolving functionality of smart contracts and the growing issues around placing trust in established brands and institutions, the potential demand for trust-minimized applications powered by Chainlink decentralized oracle networks (DONs) is rapidly increasing. This demand has already created a large opportunity for node operators to capture fees and eventually stakers to receive rewards by securing Chainlink oracle networks and the applications that use them.
With the upcoming introduction of staking, Chainlink is beginning a new era of sustainable growth, increased transparency, and stronger cryptoeconomic security. Supporting the Chainlink Economics 2.0 era involves the deployment of new and existing strategies designed to accelerate adoption while also continuing to improve the network’s economics. The following post analyzes the total addressable market for trust-minimized applications and the role oracles play, before explaining the growth strategies enabling Chainlink to capture value within this new and expanding economy.
The Growing Total Addressable Market (TAM) of Trust-Minimized Applications
Trust-minimized applications are a transition towards an ideal state, where agreements between counterparties execute exactly as written, without participants being able to manipulate or back out of the pre-agreed upon terms. Realizing trust-minimization at scale can help society alleviate the growing distrust between institutions and users by cryptographically guaranteeing certain parts of their relationships as opposed to relying on good faith or slow-to-act and expensive legal systems. This new type of cryptographic guarantee backed by decentralized infrastructure such as blockchains and oracle networks is generally referred to as cryptographic truth, and forms the backbone of trust-minimized applications.
Trust-minimization builds technologically-enforced assurances directly into key aspects of applications, putting relationships on an even footing by removing asymmetrical advantages. This actively restores user trust in applications, as was evident with instant messaging when failures to protect customers’ privacy led to market demand for end-to-end encryption (E2EE) and the eventual adoption of new messaging apps such as Signal. E2EE provides users a cryptographic guarantee that their privacy is preserved, which is not reliant on a simple unverifiable statement from a communications provider.

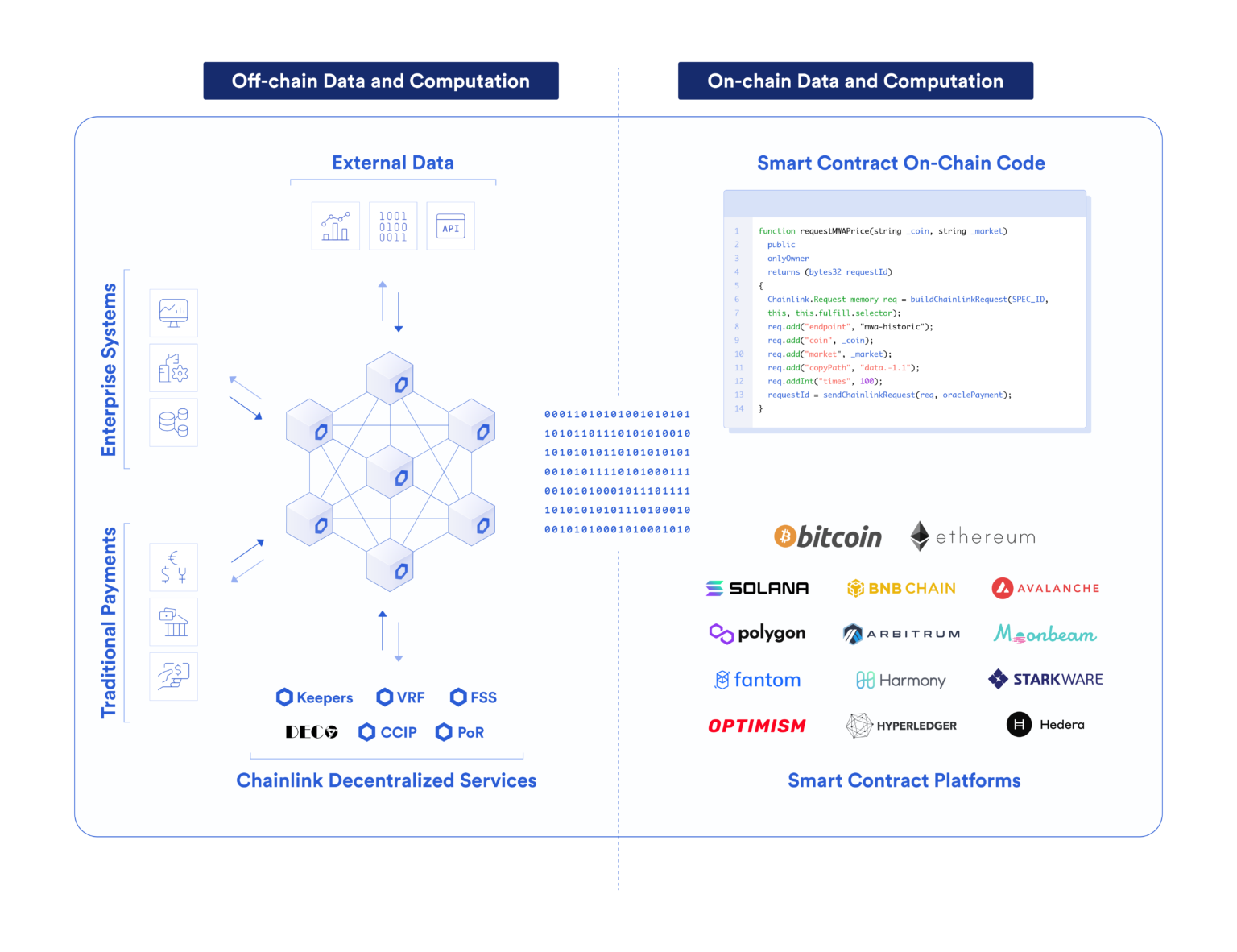
Establishing trust-minimization within more complex digital agreements, such as within the financial industry, often requires the use of hybrid smart contract infrastructure where smart contracts serve as the application layer and oracles act as the services layer. The application layer encapsulates the on-chain logic that defines the conditions of an agreement and therefore how value is exchanged while the services layer accounts for the wide range of connections and external dependencies that make those applications possible.
Chainlink sits at the center of the service infrastructure layer for trust-minimized applications, providing access to key external resources including validated real-world data, off-chain computation, cross-chain interoperability, and much more. These services already collectively secure tens of billions of dollars for hundreds of applications across a dozen blockchain networks, ultimately helping fuel the growth of the hybrid smart contract ecosystem.
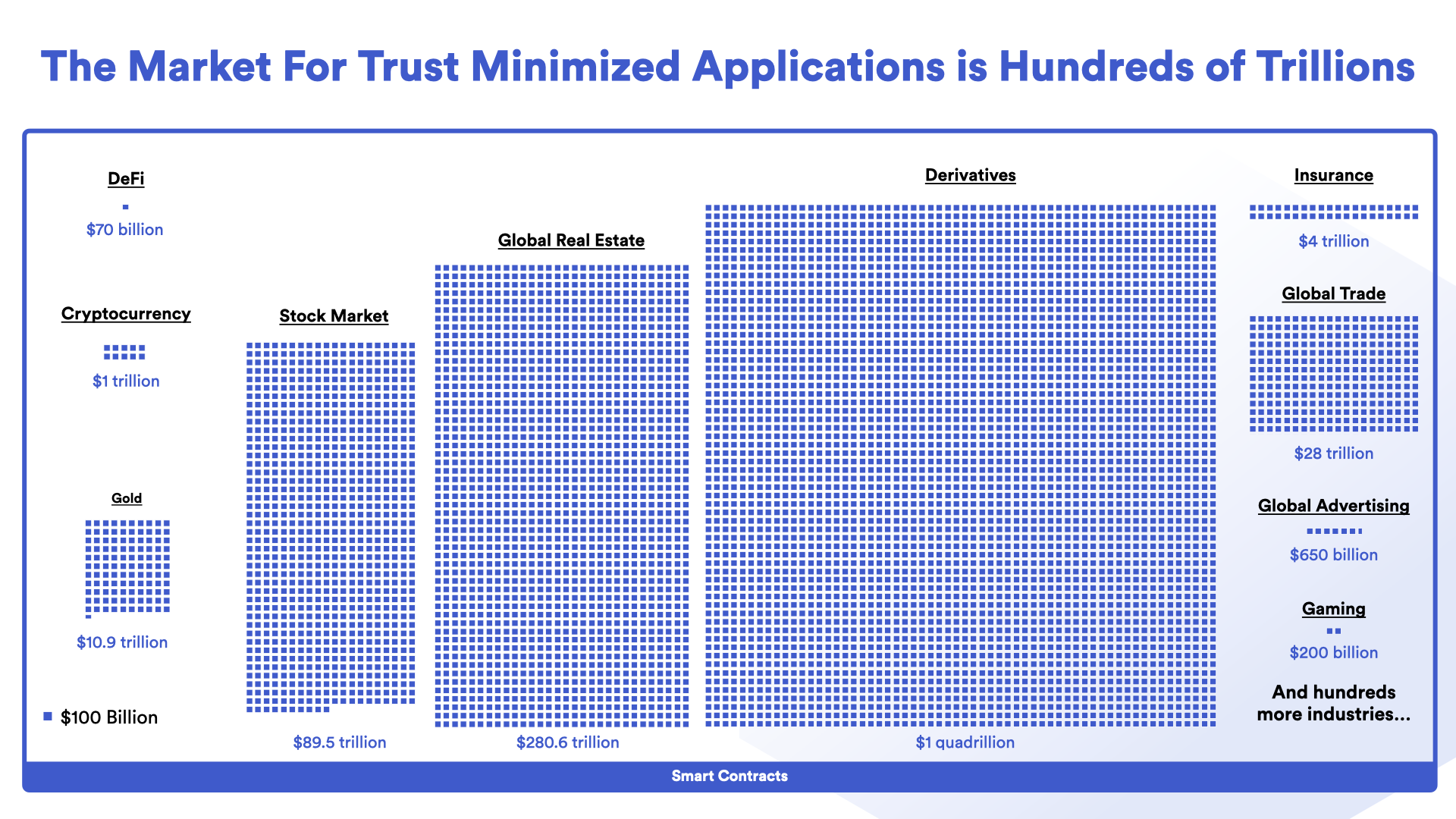
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is one example of a vertical that has utilized Chainlink and the hybrid smart contract design pattern to rapidly grow from a niche use case to being a viable parallel financial economy—managing approximately $250B in Total Value Locked (TVL) at its peak in 2022. However, DeFi itself only represents a smaller portion of the trillion-dollar cryptocurrency market and a minute fraction of the over $867T in value locked up in traditional financial markets that can be disrupted by broader blockchain and oracle-related technologies.
Currently, DeFi and the greater hybrid smart contract economy are still in their infancy, with real-world use-cases across global trade, insurance, real estate, derivatives, and more largely underexplored. Furthermore, hybrid smart contracts may represent a small segment of a much larger trust-minimization industry, where technologies like blockchains and oracles bring objectivity, decentralization, and transparency to backend processes that execute off-chain.
Chainlink is focused on unlocking all this value by serving as a generalized decentralized off-chain computation protocol that allows Web3 smart contracts and Web2’s existing systems to obtain decentralized services that meet the hyper reliability, provable security and decentralized accuracy guarantees needed to make them a trust-minimized application. For instance, Chainlink can:
- Turn any Web2 system into a trust-minimized version of itself without a full rebuild
- Perform secure off-chain computation to generate privacy, scalability, or verifiability for on-chain smart contracts
- Supply decentralized data feeds used to trigger the settlement of high-value contracts
- Provide attestations used to increase the transparency of off-chain collateral
- Deliver key message outputs from smart contracts to trigger off-chain system processes
- Move data and assets between heterogeneous blockchains based on user-defined logic after launch of the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP)
Given the generalized nature of oracles, Chainlink aims to create an oracle services layer that’s capable of supporting not only the total addressable market for smart contracts across all blockchains, but also the coming demand for decentralized services that can be seamlessly plugged into existing backends. The logical question then is how do these oracle services develop and how do they become economically sustainable?
Common Approaches to Creating an Industry Standard
When looking at how industry standards are established across both traditional industries and the Web3 economy, the commitment of financial resources to support key growth initiatives is commonplace. By funding the development of new services and expanding the capabilities of existing services, projects become well-positioned to capture both current and future projections of market demand. Supporting growth initiatives is often paired with subsidizing costs for early users and service providers in order to cultivate a powerful network effect that consolidates a project’s current market share and expands the number of revenue sources through more competitive and diverse service offerings.
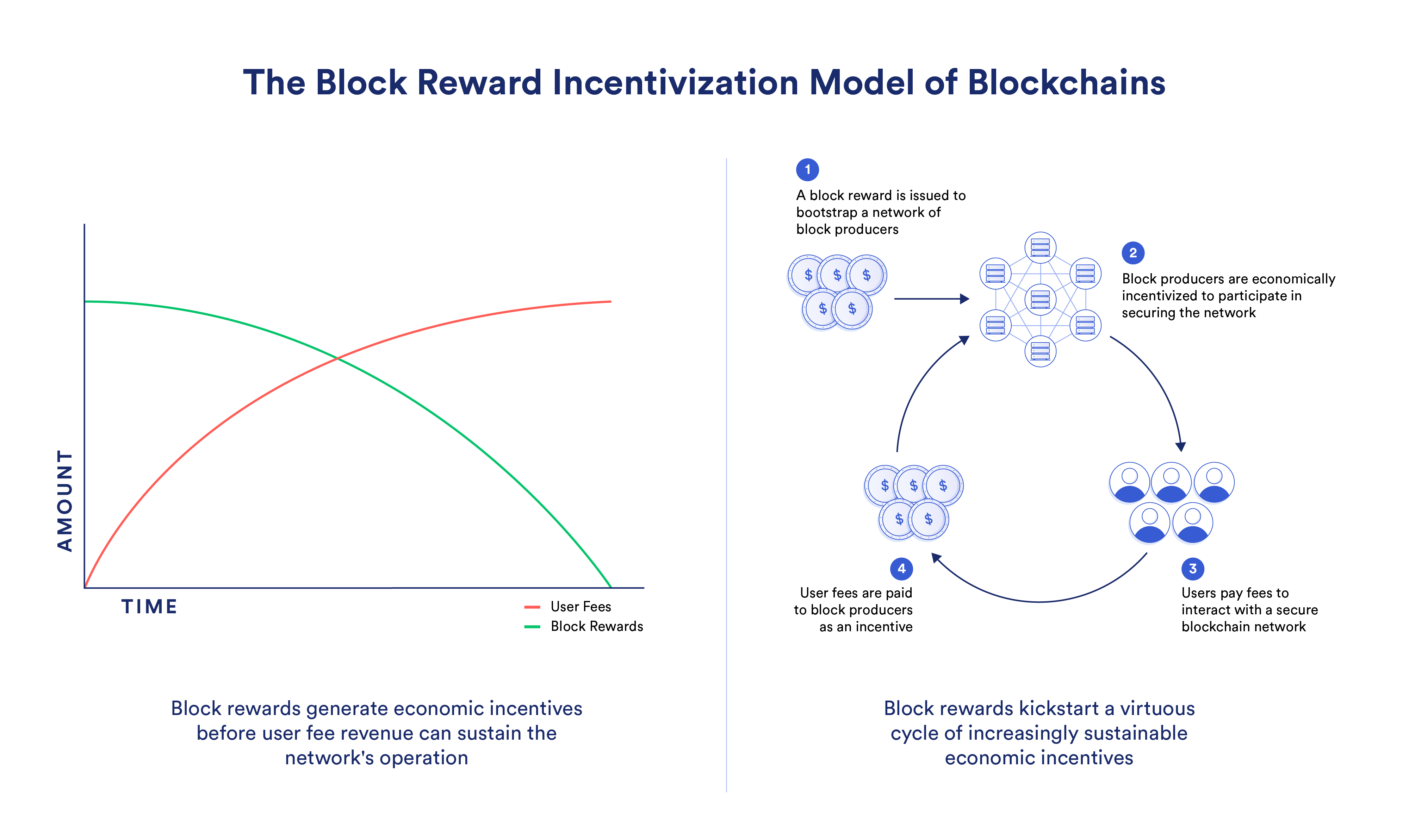
When it comes to the Web3 economy, blockchains kickstart their growth through the use of a block reward incentivization model, where miners/validators (block producers) are rewarded newly minted cryptocurrency for their contribution to the network. This enables blockchains to create a secure network of block producers to protect against network attacks. Without a block reward, blockchain networks suffer from a critical chicken or egg problem:
Users will not pay fees to use a blockchain without a secure network of nodes, and a secure network of nodes cannot exist if there’s no paying users or economic incentives.
However, when a block reward mechanism exists and is utilized properly, economic incentives are generated to support a secure network of nodes and create time for the network to eventually transition to an economic model where transaction fee revenue from adoption can fully sustain the network’s operation.
How Oracle Rewards Accelerate the Adoption of Chainlink
Similar to the block reward incentivization model of blockchains, Chainlink oracle networks generate early-stage economic incentives through the use of oracle rewards—incentives paid to node operators in addition to user fees. For instance, Chainlink Data Feeds are decentralized oracle networks that provide DeFi applications access to high-quality financial market data. Chainlink Data Feeds are launched based on demand from users for a specific piece of data on a specific blockchain (e.g. the BTC/USD exchange rate on Ethereum). After launch, Data Feeds are initially supported through oracle rewards, in addition to user fees paid by the feed’s active sponsors.
Since Chainlink Data Feeds function as shared public goods, any number of users can consume and fund the same feed. With each new paying sponsor of a Data Feed, and as existing sponsors generate more fees, a greater portion of the Data Feed’s costs can be covered by user fees. Eventually, once user fees surpass the network’s operation costs, the Data Feed’s operation no longer requires oracle reward support and the feed becomes economically sustainable. In fact, multiple Chainlink Data Feeds have already reached a state of sustainability on higher-throughput blockchains such as BNB Chain and Polygon.
To accelerate the rate at which Chainlink Data Feeds and other Chainlink services reach economic sustainability, numerous cost reduction solutions have been deployed to allow oracle rewards to be used more efficiently. For example, the launch of Off-Chain Reporting reduced the operating costs of Data Feeds up to 90%, enabling 10x more data to be delivered on-chain, which resulted in a rapid increase in the number of Data Feeds deployed. In combination with the increasing scalability of blockchains, additional cost reduction solutions are underway to fuel the growth of the Chainlink ecosystem, including:
- OCR 2.0: An upgrade to the Off-Chain Reporting protocol powering Chainlink Data Feeds that will facilitate increased cost-efficiency for data delivery, allowing for a greater number of oracle networks to be deployed and user fees to be generated.
- Fast-Lanes: A technical solution where a blockchain allocates a portion of its bandwidth to or establishes priority transaction ordering for public goods such as oracle networks. This can significantly reduce or eliminate the on-chain costs associated with oracle updates, increasing response times and reliability during blockchain network congestion.
- Blockchain Gas Grants: An initiative where blockchain projects commit to offsetting the on-chain gas costs of oracle networks. This approach is backwards-compatible and doesn’t require technical changes to the underlying blockchain network. Grants from a number of leading blockchain ecosystems are expected to be announced in the near future.
As more Chainlink oracle networks reach economic sustainability, oracle rewards can be reallocated to support new Data Feeds and other Chainlink services, opening up additional potential fee opportunities for node operators and rewards for community stakers over time. This approach to oracle network economics has already helped ensure individual users are not required to pay the full costs of a Data Feed’s operation, cultivating a strong network effect around Chainlink.
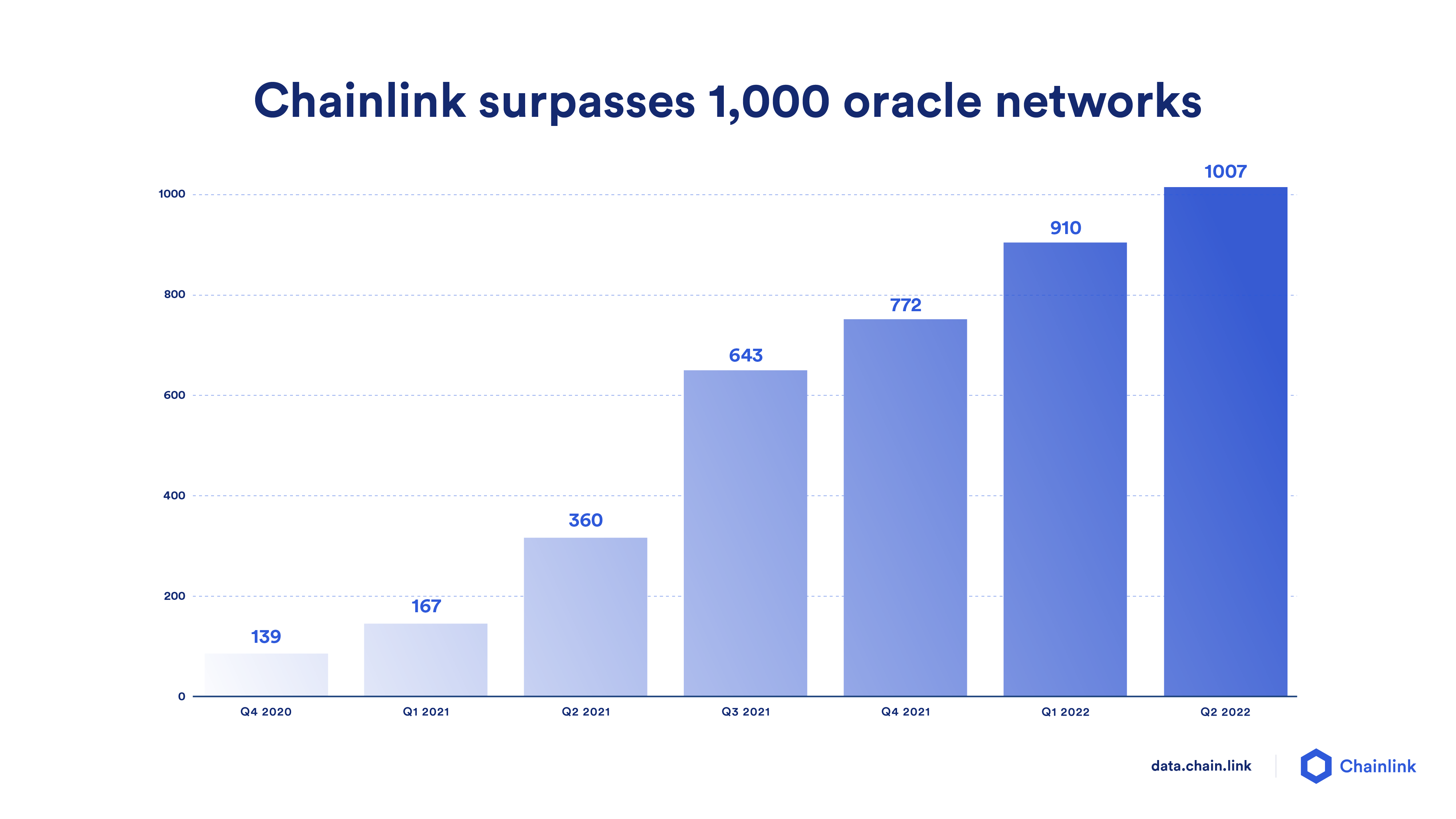
Through this proven economic model, over 1,000 Chainlink oracle networks have been successfully deployed across over a dozen blockchain networks to meet user demand. As reported in a recent research report by Bank of America, Chainlink was crucial in helping fuel DeFi’s growth to over $203B in Total Value Locked and will help accelerate the adoption of next-generation blockchain use cases across finance, insurance, supply chain, and more.
Chainlink Economics 2.0 via Growth Initiatives and Staking
With the achievement of key milestones such as multiple Chainlink services for off-chain compute being widely adopted, economic sustainability for multiple oracle networks achieved on various chains, and crossing over 1,000 live oracle networks deployed across a growing number of chains, we are entering the next stage of the Chainlink Network’s growth: Chainlink Economics 2.0.
To help facilitate this important transition, the Chainlink Foundation has been created to lead an increasingly complex set of growth initiatives, many of which are based on deploying additional LINK tokens. The Foundation’s core goal is to support the sustainable long-term growth of the network by:
- Setting a LINK token release schedule to support key growth initiatives, including oracle rewards for node operators and staking rewards for stakers.
- Furthering technical standards, specifications, and best practices for the community of open-source developers and node operators helping build and support Chainlink.
- Hosting, reviewing, and contributing to the maintenance of Chainlink’s open-source software for developers through platforms such as GitHub and npm.
- Running and supporting Chainlink hackathon events to encourage developers to build with Chainlink and Web3 technologies.
- Operating the Chainlink Grant Program to fund the improvement of oracles and the Chainlink Network and dependencies.
To create clarity for the Chainlink community, and as a critical part of Chainlink Economics 2.0, the Foundation expects that no more than 5% of total supply (50 million LINK tokens) will be moved into the circulating supply, over the next 9 months, through the first quarter of 2023. These releases to circulating supply will support the growth of the network, including the upcoming launch of staking later this year. It is expected that the upcoming launch of staking should have an indirect offsetting effect to these token releases, partly depending on whether the amount committed by stakers reaches the planned initial cap of 75 million tokens. The Foundation expects that these token releases into circulating supply will be small in the near term and will be focused on the already occurring oracle rewards, until additional deployments are required for additional key initiatives in the third quarter of 2022 and into the first quarter of 2023.
Non-circulating tokens from genesis wallets will be migrated this week to upgrade their on-chain security. The tokens will be divided into smaller wallet sizes with larger multisignature signing committees, using the most up-to-date security best practices. Migrations from the genesis wallets will not affect circulating supply and do not represent a release of tokens.
Below is a list of the initial addresses where non-circulating tokens will be held after the migration. These tokens are subdivided among multiple LINK wallets, however only 50 million LINK are available to enter circulating supply over the next nine months (primarily coming from the 7 wallets of 7 million LINK each) to be used for various purposes, including oracle network rewards, the initial staking rewards and the initiatives described below, among others. The new wallet addresses and their planned holdings after the migration is completed this week are listed below:
In order to create additional clarity for the Chainlink community and avoid confusion, the ongoing circulating supply of LINK can be viewed at chain.link/circulating-supply, which will reflect the current circulating supply both before and after these migrations. As noted above, the initial migrations from genesis wallets into the new secure wallets listed above will not result in any additional circulating supply.
The first releases following the wallet migration specified above will be related to paying for the already occurring oracle rewards, enabling the continued operation of existing oracle networks. Releases over time will then gradually extend to the below categories in order to facilitate the continued expansion of the Chainlink Network into more decentralized services, across more chains, and with greater cryptoeconomic security from the upcoming launch of staking:
- Oracle Rewards to lower initial user costs and generate strong network effects across all key verticals. Combined with user fees, this supports the node operators that secure Chainlink services.
- Staking Rewards for node operators and community members participating in Chainlink staking. This will help generate greater levels of cryptoeconomic security and user assurances for Chainlink services over time.
- Expand existing Chainlink services by launching additional networks to further increase the diversity of datasets available on-chain for developers. This helps cultivate the creation of new smart contract applications in a secure and cost-efficient manner.
- Support additional blockchains, making Chainlink the go-to oracle solution across the multi-chain ecosystem, including layer-1 and layer-2 networks. This also includes expanding support for both EVM and non-EVM blockchain networks.
- Develop new Chainlink oracle services to extend the functionality of the smart contract economy. This includes work on the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), Fair Sequencing Services (FSS), DECO, and an enterprise abstraction layer.
- Other ecosystem growth initiatives to support the adoption, security, service offerings, and ease of use of Chainlink. Some growth initiatives include Chainlink Grants, hackathon sponsorships, research and development, code audits, and bug bounty programs.
Through supporting the growth of these programs, the Chainlink Network can become a more self-sustaining, expansive, and secure ecosystem of decentralized services, which enables the next generation of smart contracts and trust-minimized Web2 applications to exist.
Conclusion
Chainlink has grown to be one of the most value-securing, widely used, and widely integrated systems in the entire blockchain industry. Chainlink’s growth can be attributed to its security and the variety of key decentralized services that Web3 and Web2 developers can now rely upon. With the Chainlink Network crossing the critical milestones of having self-sustainable economics on multiple oracle networks and with over 1,000 individual oracle networks launched, it’s clear that the next stage of growth is ready to begin with the rollout of Economics 2.0.
We’re immensely excited about what the network can provide to all Web3 developers as well as various Web2 systems that want to become trust-minimized. All of this growth will require a committed community and ecosystem, and we are as always, immensely grateful for your commitment and support as we continue to build a world powered by cryptographic truth.
To learn more, visit chain.link, subscribe to the Chainlink newsletter, and follow Chainlink on Twitter, YouTube, and Reddit.
If you want more technical context, we suggest you read the original Chainlink whitepaper, Chainlink 2.0 whitepaper, and developer documentation.
—
Disclaimer: This post is for informational purposes only and contains statements about the future, including anticipated product features, development, and timelines for rollout of these features. These statements are only predictions and reflect current beliefs and expectations with respect to future events; they are based on assumptions and are subject to risk, uncertainties and change at any time. There can be no assurance that actual results will not differ materially from those expressed in these statements, although we believe them to be based on reasonable assumptions. All statements are valid only as of the date first posted. These statements may not reflect future developments due to user feedback or later events and we may not update this post in response.
