How Chainlink Accelerates the Global Transition to Cryptographic Truth
In his monumental keynote at the Smart Contract Summit #1, Chainlink Co-founder Sergey Nazarov outlined a grand vision for a global transition to a world governed by cryptographic truth—a point in time where hybrid smart contracts provide the source of truth for how the world operates. This post outlines the key takeaways from his talk, including recent Chainlink innovations and an overarching vision for how blockchains and decentralized oracle networks are combining to reinvent global systems and usher in a new age of economic fairness.
If you’d like to read more about the most significant themes that defined SmartCon #1, check out our other article on the 7 Key Takeaways From Smart Contract Summit #1.
The Significance of Cryptographic Truth
Most of how the world operates today is based on “just trust us” paper promises and brand-based agreements on which banks, financial institutions, and entities in numerous other industries base their operations. This mode of agreement involves a significant amount of trust, as there is no firm commitment to uphold agreements other than an institution’s or individual’s choice or desire to do so.
With the emergence of Bitcoin in 2009 and Ethereum with programmable smart contracts not long after, we now have a powerful alternative—cryptographic truth that can guarantee outcomes enforced by cryptography, encryption, maths, and physics.
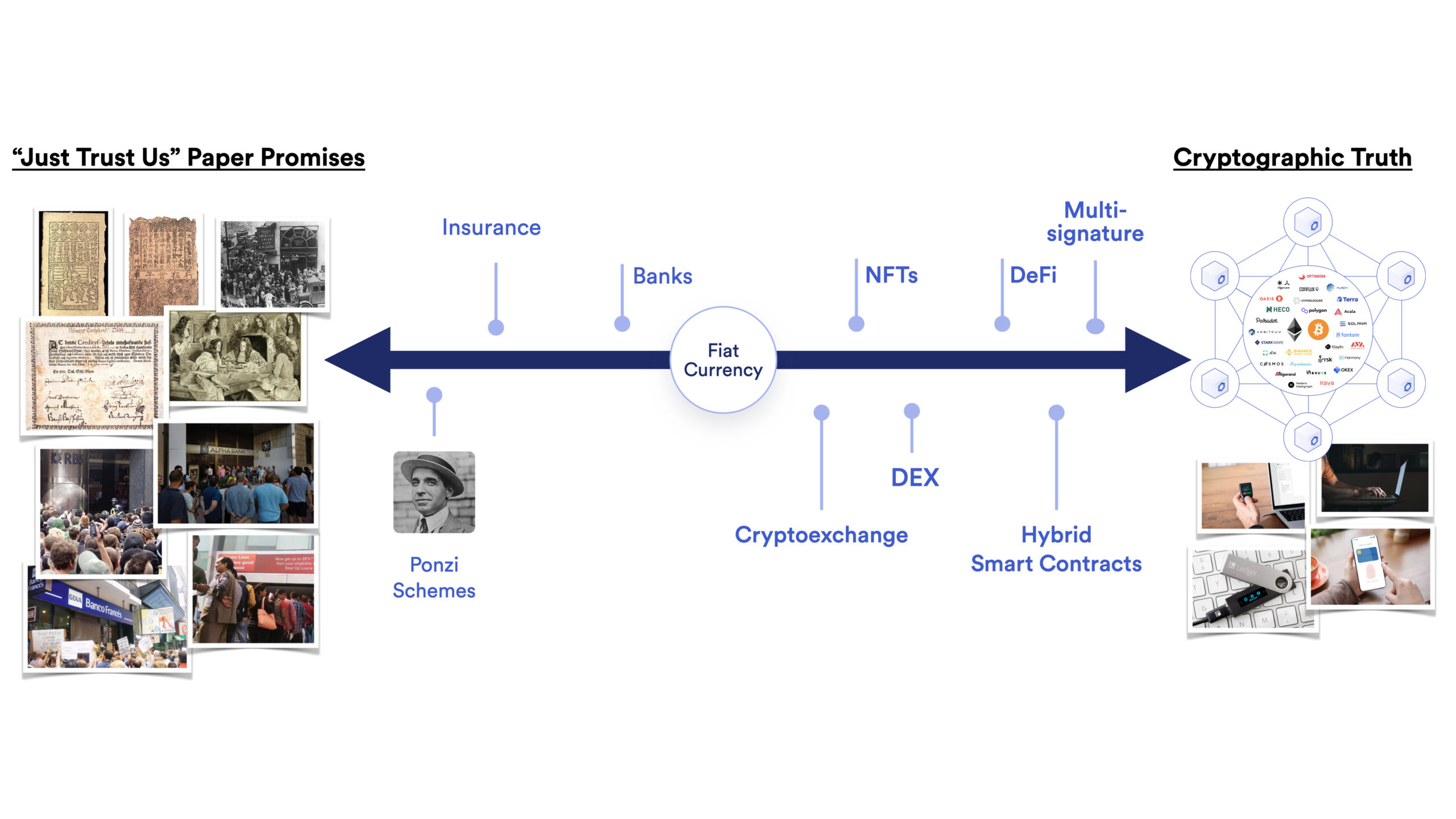
Rooted in the fundamental belief that truth is better than trust, Chainlink’s vision is to build a world powered by truth. Whereas paper promises require a significant amount of trust and have no firm commitments attached, in the world of blockchains, smart contracts, and oracles, code is guaranteed to execute in a certain way, ensuring expected behavior with guaranteed outcomes enforced by physics.

Chainlink’s goals are to build decentralized systems that link everything to truth, creating a fair, unbiased world. By eliminating fundamental disputes about what the truth is, society can move past the pitfalls of paper promises that have been failing and causing economic booms, busts, and crises for hundreds of years. In our current world of paper promises, anybody can change the rules how they want. In the emerging world of cryptographic truth, the only way to change the rules is to transparently codify them and achieve distributed consensus.
The shift from paper promises to cryptographic truth will give the developed world an even playing field where a small group of actors can’t take advantage of the elasticity of the rules and also provide people in emerging market economies access to agreements, contracts, and capabilities that they never had access to before.
“It’s not just about finance, gaming, insurance; it’s about the way the world works—and the way the world works influences everybody. It influences developed markets, emerging markets, the average consumer, institutions. The way we’re going to make the world work is cryptographic truth.”
How Hybrid Smart Contracts Enable Cryptographic Truth
Blockchains are a highly secure environment for enabling social coordination, as the underlying infrastructure can’t be undermined by any individual participant. Predefined software logic and cryptography ensure that agreements based on cryptographic truth are settled exactly in the way they were intended.
However, there is an inherent trade-off to be made for this security when it comes to capabilities. The necessity to expand the types of collaboration enabled by blockchains led to the birth of blockchain oracles that allowed blockchains to securely interact with external data and systems. The vision behind Chainlink is to extend, augment, and improve what smart contracts can do to enable a new, more advanced class of smart contracts called hybrid smart contracts that extend what blockchains and smart contracts are used for.
The seamless connectivity between on-chain code and external data and systems is made possible by the following layers:
- The blockchain that cryptographically secures the state of agreements through immutable on-chain code.
- The off-chain world of trust-minimized off-chain computation in the form of Decentralized Oracle Networks (DONs), which can be broken down into three further categories: 1) Off-chain data, 2) Off-chain compute, 3) Cross-chain compute
- Existing systems, services, backends, and infrastructure.
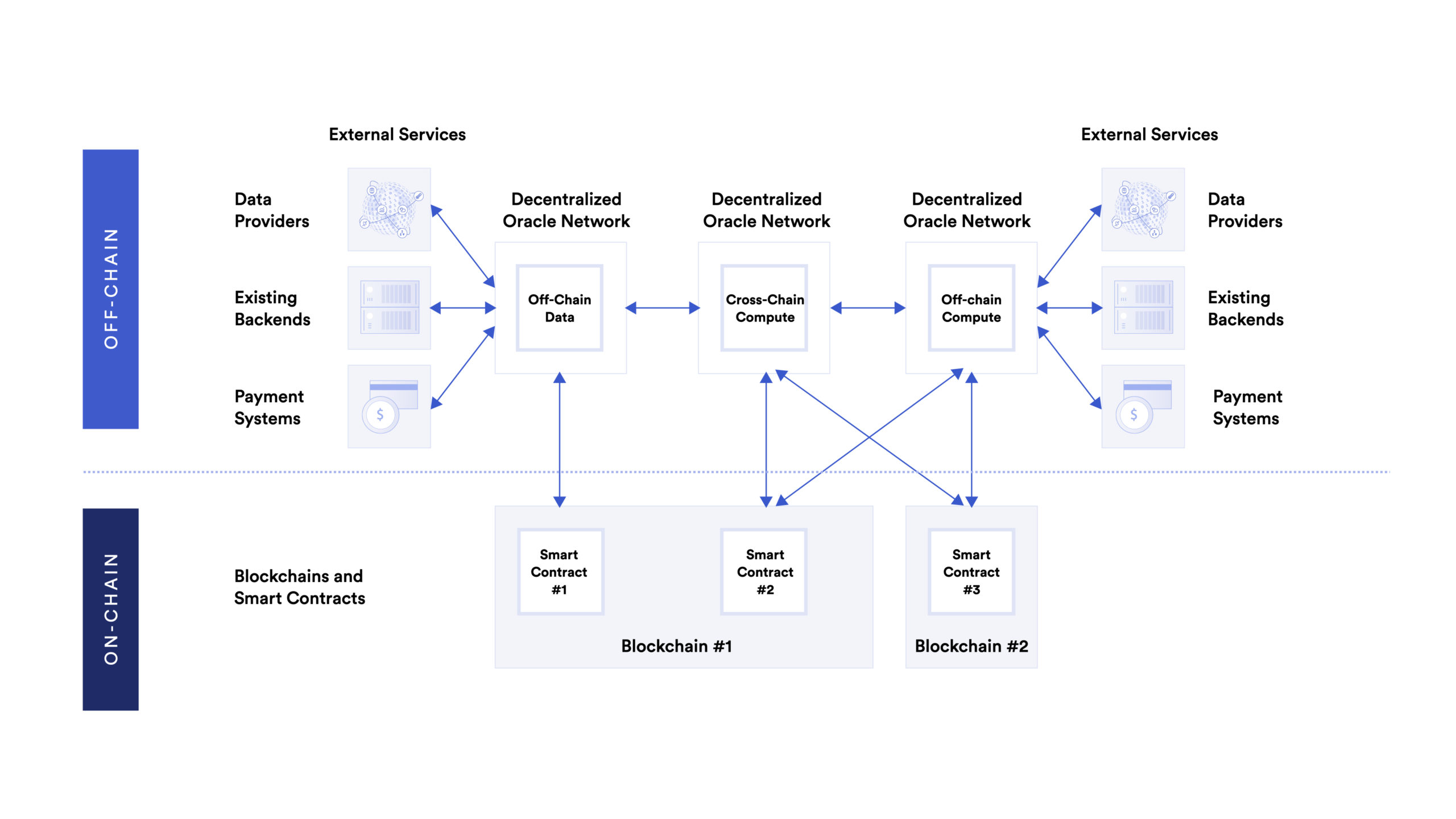
The future of smart contract-based applications is multiple off-chain services being used by on-chain contracts that interoperate with each other to create advanced applications which then go on to power the finance, gaming, insurance, global trade, and other industries and begin to refine them to spread the benefits of cryptographic truth to segments of the global market that wouldn’t otherwise be reached.
While the growth of the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) market has been undoubtedly impressive, it is likely only the beginning of a more immense transformation. All of the world’s financial contracts, products, incentives, ownership rights, carbon credits, insurance processes, payment rails, capital markets, and more will eventually be in smart contracts. When all of these instruments are codified as smart contracts on blockchain networks, global markets will be composable with one another in the same fashion that DeFi products today are permissionlessly composable. Hybrid smart contract applications and systems enable the transparent and verifiable exchange of information that stands in stark contrast to the paper promises of today, which continually result in unpredictable outcomes and contractual breaches.
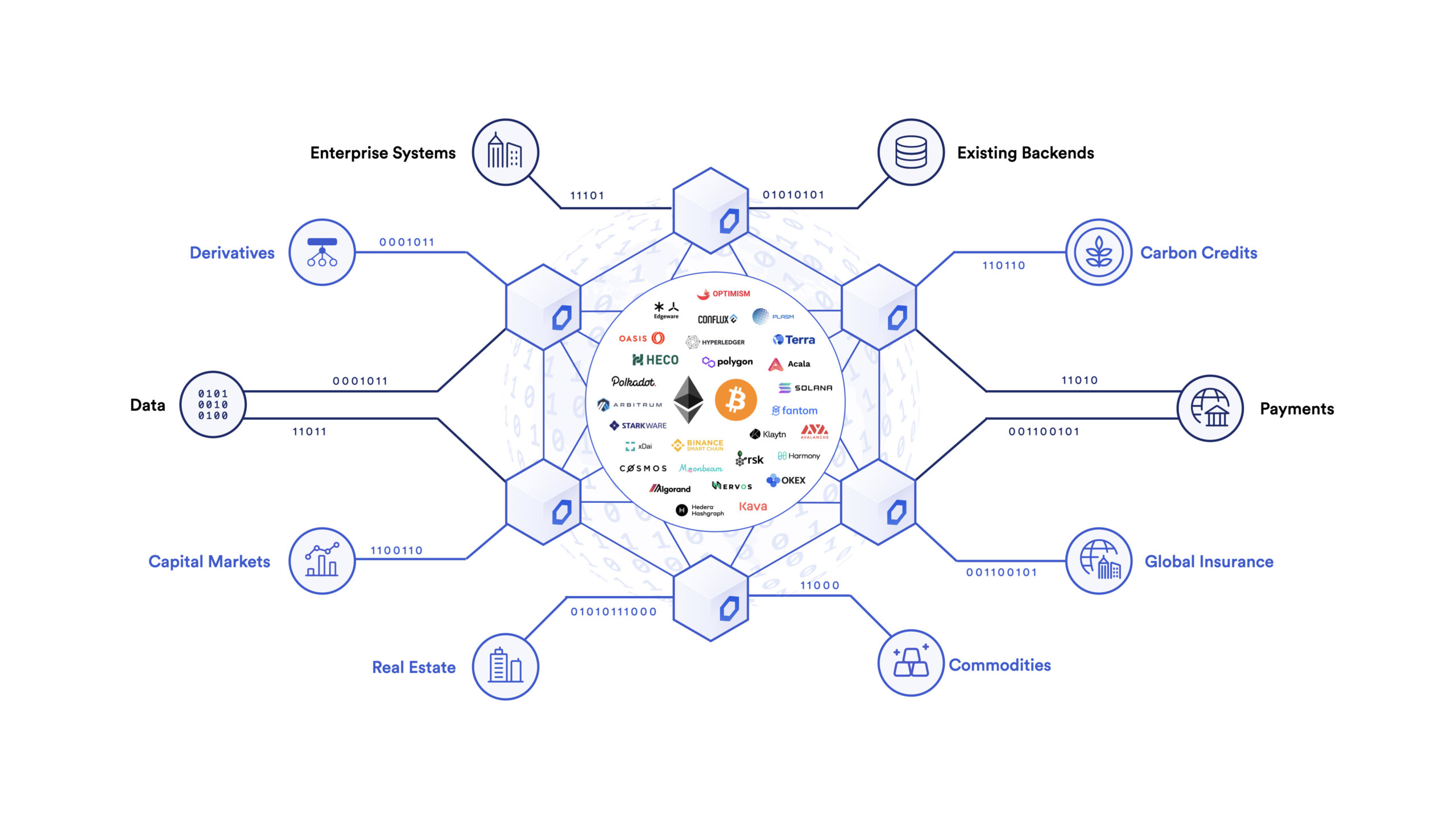
With advanced hybrid smart contracts, the benefits of cryptographic truth can be far-reaching, allowing off-chain systems to seamlessly interoperate with on-chain code and create superior applications that enable new forms of economic and social coordination.
“Our fundamental goal is to transition the world from a paper promises model to the cryptographic truth model, which requires smart contracts to be able to meet the operational demands of all industries where it will change how they operate.”
Understanding Chainlink’s Suite of Decentralized Services
The goal of Chainlink is to create a global standard for cryptographic truth by enabling the cryptographic guarantees of smart contracts to extend into the wider world. In simple terms, the more advanced smart contracts become, the more industries the blockchain industry can reach and reinvent.
In the following section, we describe the main pillars of Chainlink’s expanding suite of decentralized services, including the recently launched Chainlink Automation and the novel Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP).
Chainlink Price Feeds
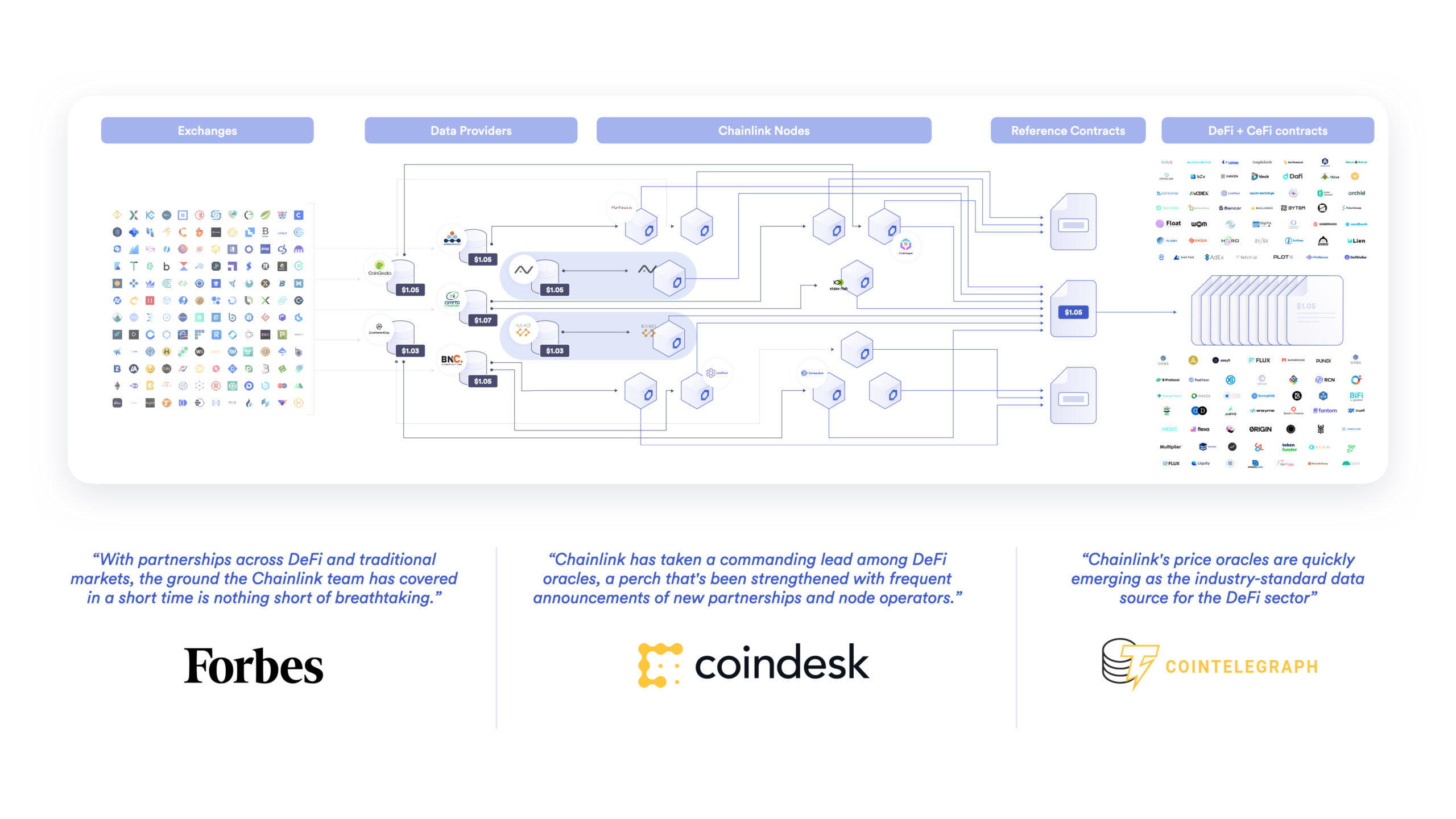
Chainlink Price Feeds enable smart contracts to retrieve the latest price of an asset in a single function call and are the quickest way to connect smart contracts to the real-world financial market data regarding a wide range of assets, including cryptocurrencies, stablecoins, commodities, forex, indices, and more.
Architected with a secure system design set of principles, including a multi-layer data aggregation system, that have been time-tested for years against flash loan attacks, blockchain network congestion, and various other outlier events, Chainlink Price Feeds have allowed DeFi to grow into what it is today. This is demonstrated by the fact that a large portion of leading DeFi applications, including Aave, Compound, Synthetix, and more use Chainlink in production to ensure they have a reliable system of external pricing data.
Chainlink Proof of Reserve
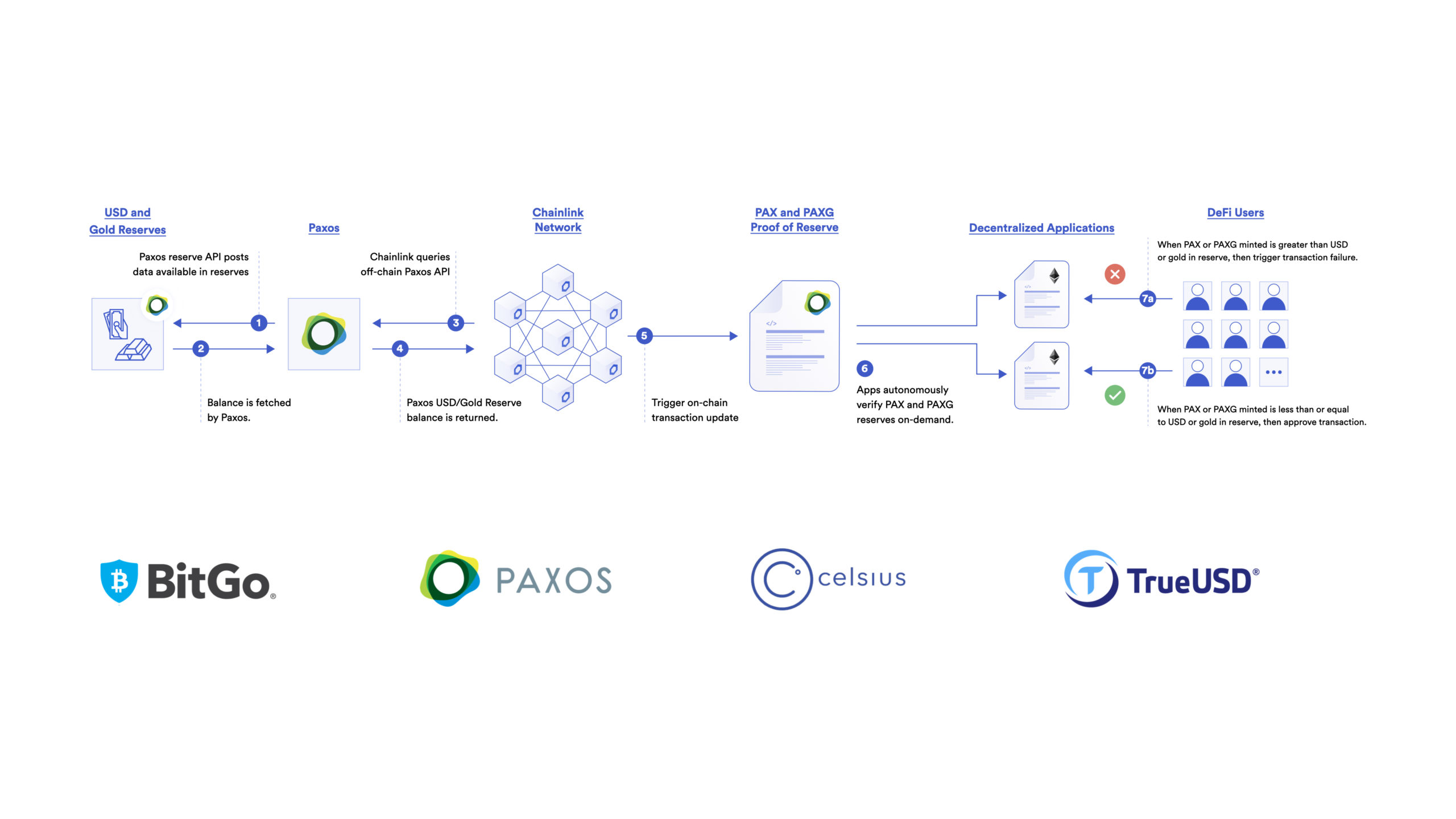
Chainlink Proof of Reserve is a collection of on-chain reference feeds that provide smart contracts with the data needed to calculate the true collateralization of any on-chain asset backed by off-chain reserves. Chainlink Proof of Reserve replaces a one-year auditing process with a high-frequency automatic rolling audit using definitive data sources that anyone can verify on a block-by-block basis.
Chainlink Proof of Reserve can also enable the creation of automated on-chain insurance agreements that allow anyone with a phone and an Internet connection to insure their on-chain crypto holdings and be automatically paid what they are owed based on definitive, cryptographic truth.
Chainlink VRF (Verifiable Random Function)
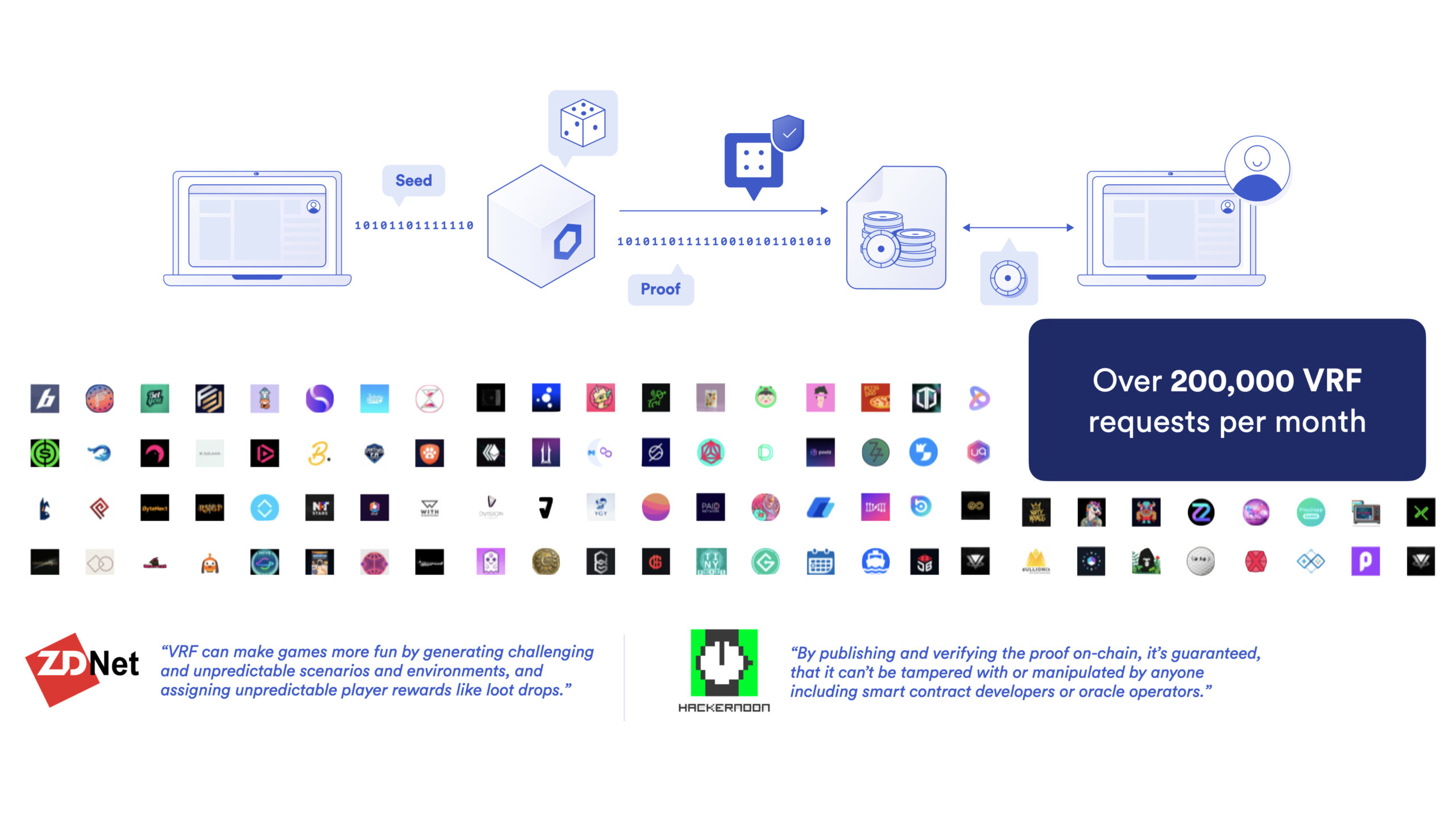
Chainlink VRF is a provably fair and verifiable source of on-chain randomness purpose-built for smart contract applications. Developers can use Chainlink VRF as a tamper-proof random number generator to create dynamic NFTs, fair prize pools, governance mechanisms, or any other applications which rely on unpredictable outcomes.
Chainlink VRF works by combining block data that is still unknown when the request is made with the oracle node’s pre-committed private key to generate both a random number and a cryptographic proof. The cryptographic proof generated cannot be tampered with by either the oracle nodes, development teams, or external parties. As of writing, Chainlink VRF is generating over 200,000 requests per month.
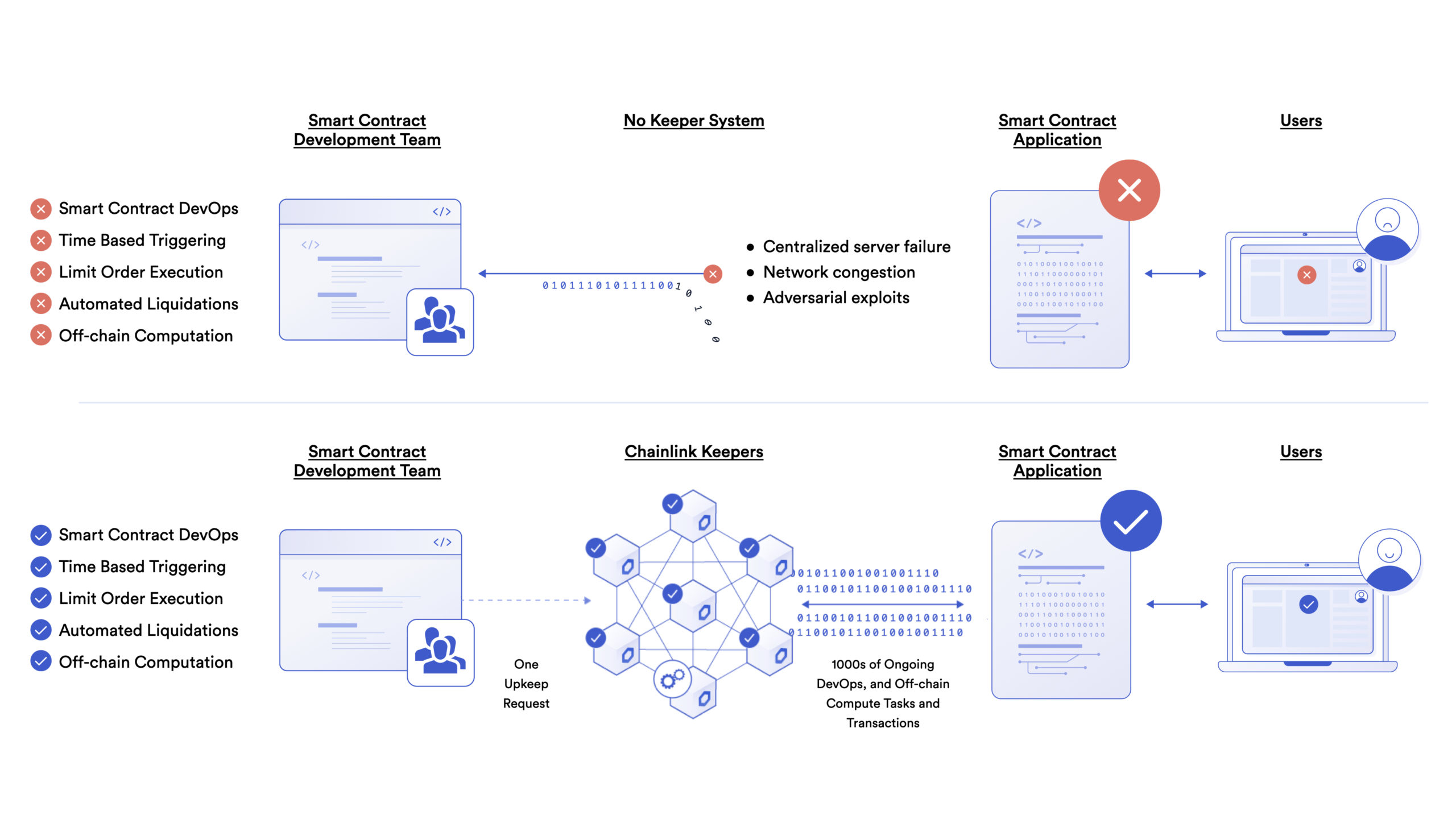
Chainlink Automation
Not only are external data and secure access to that data critical for hybrid smart contracts, but trust-minimized off-chain computation is also key for making smart contracts fully-functional, in terms of scalability, privacy, and ultimately, utility. Off-chain computation needs the same set of end-to-end guarantees as off-chain data to ensure that systems keep running in all market and network conditions.
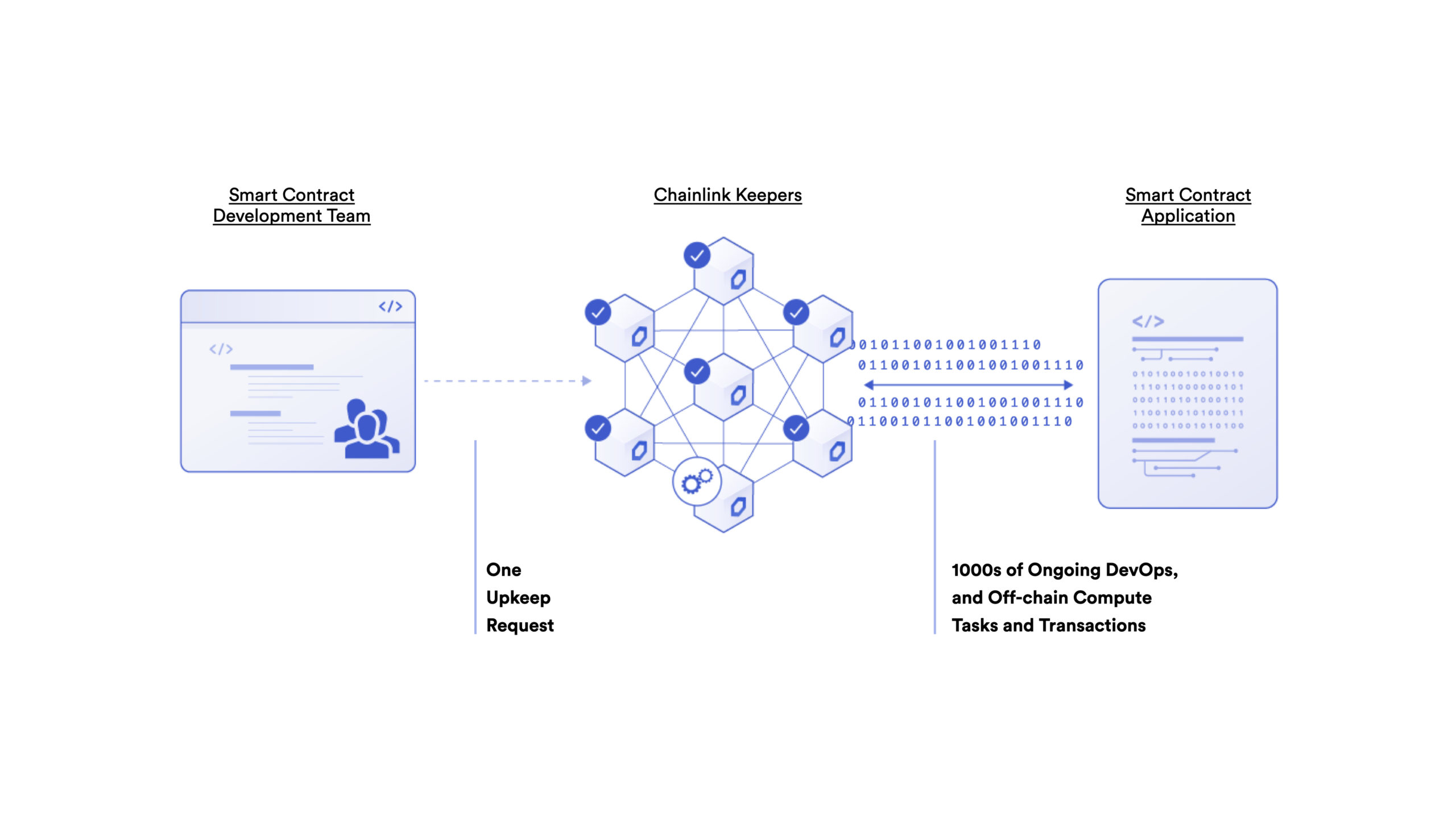
Chainlink Automation is a decentralized transaction execution solution that provides a reliable method for performing key computations and DevOps operations that a contract cannot do itself, such as liquidations, limit orders, and more, but have to be done in a decentralized, trust-minimized, hyper-reliable manner. It uses low-cost, verifiable off-chain computation and a highly reliable network of incentivized nodes to provide a decentralized transaction automation service.
Chainlink Automation enables smart contracts to give a computation that isn’t possible to be performed on-chain directly for either capability, cost, or privacy reasons to a decentralized system. Developers don’t need to build the infrastructure themselves but can off-load the responsibility of off-chain computation, while those computations maintain decentralization and trust-minimized guarantees that are expected from blockchains. The long-term vision for advanced hybrid smart contracts is executing a portion of the code in a Chainlink Automation Network that only exists for that specific contract and is committed to running that code.
Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP)
A broader vision for advanced smart contracts is the ability to string together multiple contracts from multiple blockchains into one decentralized application, leading to cross-chain smart contracts where all the different features of all the various blockchains and their capabilities are accessible. Cross-chain interactions allow for multiple dApps and smart contracts interoperating with each other on multiple blockchains to create combinations that weren’t previously possible.
The recently announced Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) seeks to provide connectivity and make disparate blockchain networks work under one messaging and communication standard. CCIP is an open-source, global standard that will allow blockchains to interoperate with each other, smart contracts on different blockchains to send each other commands, and enable token movement between chains. The new capabilities enabled by CCIP will grow the usefulness of the blockchain industry by broadening the collective understanding of cryptographic truth guarantees.
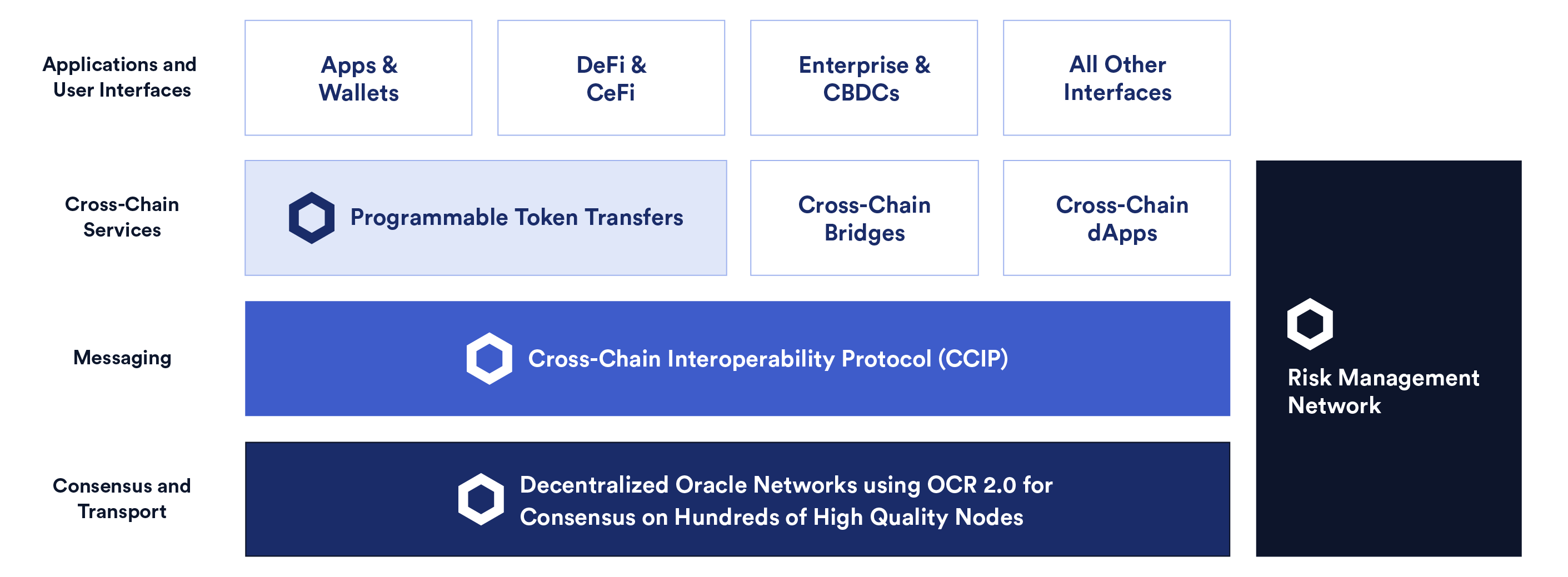
The Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) is part of a larger stack made up of the following levels:
- Consensus and Transport – The physical computing environment where Chainlink Decentralized Oracle Networks (DONs) using the enhanced Off-Chain Reporting protocol (OCR 2.0) reach consensus and guarantee the continual, secure operation of the messaging protocol.
- Messaging – CCIP is a global, open-source standard for blockchain interoperability that enables smart contracts to send cross-chain messages and commands between different blockchains with a universal messaging interface.
- Cross-chain Services – A layer for creating CCIP-powered bridges to generate token movements and cross-chain app interactions. The Programmable Token Bridge is a reference implementation built on CCIP that allows developers to securely transfer tokens across blockchain networks and initiate programmable actions on the destination chain. In other words, these bridges allow for not just token movement but instructions to be sent along with the tokens.
- Risk Management Network – A separate oracle network with nodes independent of those powering CCIP that monitors, manages, and mitigates various key aspects of risk in a transparent, cryptographically enforced, decentralized manner. The Risk Management Network monitors activity at all levels of the messaging, bridging systems, and anything else that CCIP and Chainlink DONs are using for cross-chain communication and token movement, automatically pausing services when malicious activity is detected.
- Applications and User Interfaces: Applications and interfaces that interact with and get the benefit of various chains. Interfaces will be permissionless to deploy and can consist of existing wallets, applications, platforms, and more.
Using these cross-chain services, DeFi apps can attract more value, blockchains can seamlessly interoperate, and CeFi apps can get more access to blockchains, thereby spreading the benefits of cryptographic truth to more segments of the broader economy. CCIP allows user-focused applications to interoperate with all useful smart contracts in all environments with the highest security guarantees and minimal technical investment required.
“What we’ve seen is that as each decentralized service goes live and gains steam, those markets just speed up—there are more developers building applications, and more users needing services.”
Chainlink’s Decentralized Services Are Accelerating the Adoption of Cryptographic Truth
The remaining market for smart contracts is in the trillions of dollars. By introducing cryptographic truth to the broader world and all the industries that it can impact, a new age of productivity, emerging market growth, reliability, and social coordination will be introduced.
 Ultimately, there is a significant opportunity for all of the world’s value to flow through hybrid smart contracts, utilizing various contracts on multiple blockchains that leverage Chainlink’s decentralized services. As value from the web, fintech, and enterprise stack flows into blockchains, existing systems can leverage Chainlink oracle infrastructure to utilize the vast array of trust-minimized services and applications running on-chain.
Ultimately, there is a significant opportunity for all of the world’s value to flow through hybrid smart contracts, utilizing various contracts on multiple blockchains that leverage Chainlink’s decentralized services. As value from the web, fintech, and enterprise stack flows into blockchains, existing systems can leverage Chainlink oracle infrastructure to utilize the vast array of trust-minimized services and applications running on-chain.
The vision of Chainlink is to fundamentally augment what blockchains can do by providing smart contracts secure, seamless access to all the world’s data, proof of reserves, random number generation, automation and off-chain computation, expanded forms of computations through cutting-edge innovations like Fair Sequencing Services (FSS), bridging and messaging capabilities, and other decentralized services. We believe this goal is achieved by enabling distinct industries that could not exist without those decentralized services and serving them in a low-cost, secure, reliable, and high-speed manner. The more Chainlink’s suite of decentralized services enables smart contracts to do, the more widely smart contracts will be adopted, ultimately ushering in a new age of economic fairness and cryptographic truth.
To understand the full vision of the Chainlink Network, read the Chainlink 2.0 whitepaper. To stay up-to-date with the latest Chainlink developments, follow Chainlink on Twitter, sign up for the Chainlink newsletter, and subscribe to the Chainlink YouTube Channel.
