The Chainlink Endgame: Integrating the World Into the Tokenized Asset Economy
TL;DR
- This blog outlines the Chainlink endgame: our vision for Chainlink and its position in the blockchain industry.
- Blockchain use cases have become increasingly advanced with the advent of tokenized real-world assets (RWAs). Applications now require institutional-grade workflows that mirror those seen in the global financial system.
- It’s unrealistic for institutions to build entire workflows in-house or manage a growing list of vendors to support all their unique requirements. Instead, they need an all-in-one solution for creating and powering the whole lifecycle of their onchain applications.
- Chainlink is the only all-in-one oracle platform that supports the data, interoperability, compliance, privacy, orchestration, and legacy system integration needs of advanced blockchain applications.
- The world’s largest financial institutions, governments, and DeFi protocols are using Chainlink to bring the global financial system onchain and unlock faster, cheaper, more transparent, and more accessible services than the status quo.
- Offchain and onchain revenue from the adoption of Chainlink oracle services fuels the Chainlink Reserve—a strategic onchain reserve of LINK tokens designed to support the long-term growth and sustainability of the Chainlink Network.
Table of Contents
- Overview
- The Evolution of Blockchain Applications
- The Chainlink Oracle Platform
- Capital Markets and DeFi Adoption of the Chainlink Platform
- UBS Asset Management, SBI Digital Markets, & Swift for Tokenized Funds
- ANZ Bank and Fidelity International for Cross-Chain Settlement of CBDCs, Stablecoins, and Tokenized Assets
- Kinexys by J.P. Morgan and Ondo Finance for Cross-Chain, Atomic Settlement of Tokenized Treasury Fund
- Swift and Chainlink for Transfer Tokenized Assets Cross-Chain
- Fidelity International and Sygnum for Servicing Tokenized Funds With NAV Data
- Aave for Supporting Its Money Markets and Stablecoin
- Lido for Scaling Its Staking Services Across Blockchains
- Accelerating Institutional Workflows and Advanced Blockchain Apps
Overview
Bitcoin: The novel experiment in decentralized money that ignited the blockchain industry. What began in 2008 as a single blockchain with a singular focus has now grown into a complex landscape of hundreds of blockchains, thousands of digital assets, hundreds of millions of users worldwide, and an ever-expanding list of innovative applications and use cases.
With more and more institutions realizing the indisputable value of blockchain technology, there’s now a global system of existing infrastructure and technologies that need to connect with blockchain-based systems. The key challenge, though, is how to securely and efficiently navigate this increasingly complex landscape. Trying to solve every technical challenge in-house is simply not an option anymore, as it requires significant operational overhead, technical debt, and project-management resourcing to oversee various tech stacks. However, employing a growing and fragmented list of point-to-point solutions is not ideal either, adding even more complexity to the situation.
This predicament is similar to the early days of the Internet and online applications; that is, until the TCP/IP standard unified disparate intranets into a single global Internet and the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) abstracted away the complexities of online application development. The blockchain industry now needs its own TCP/IP and JRE standard.
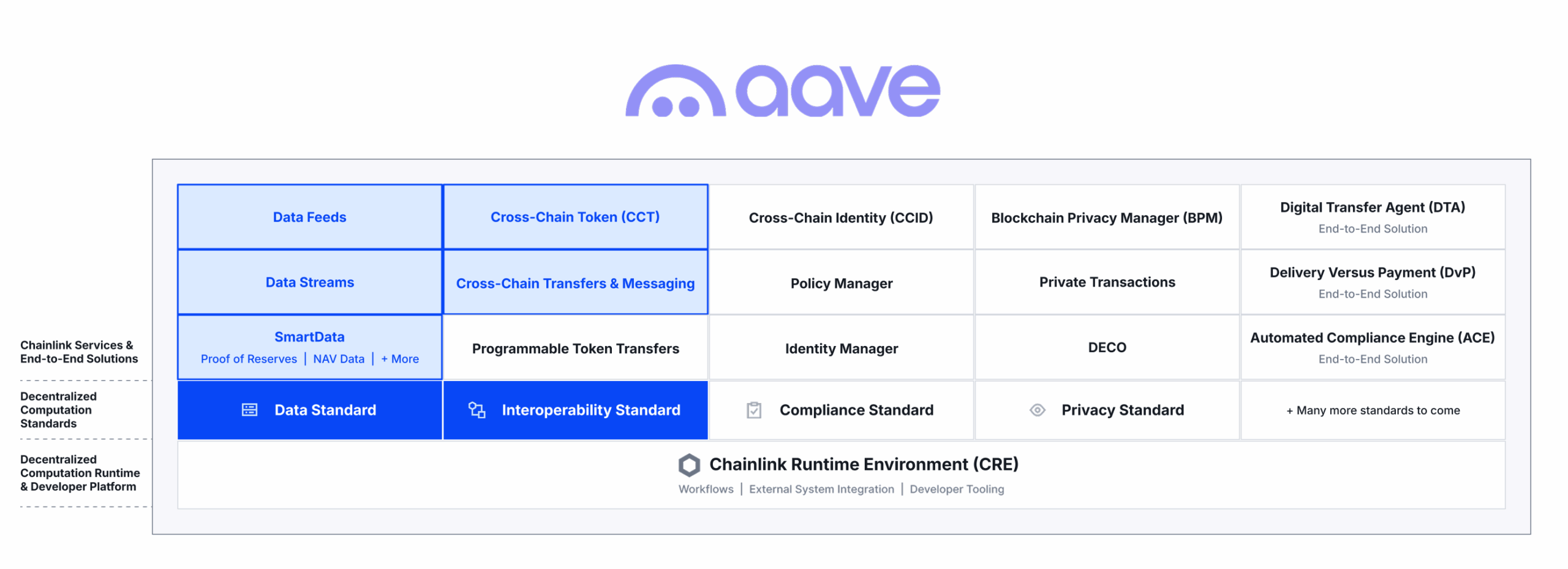
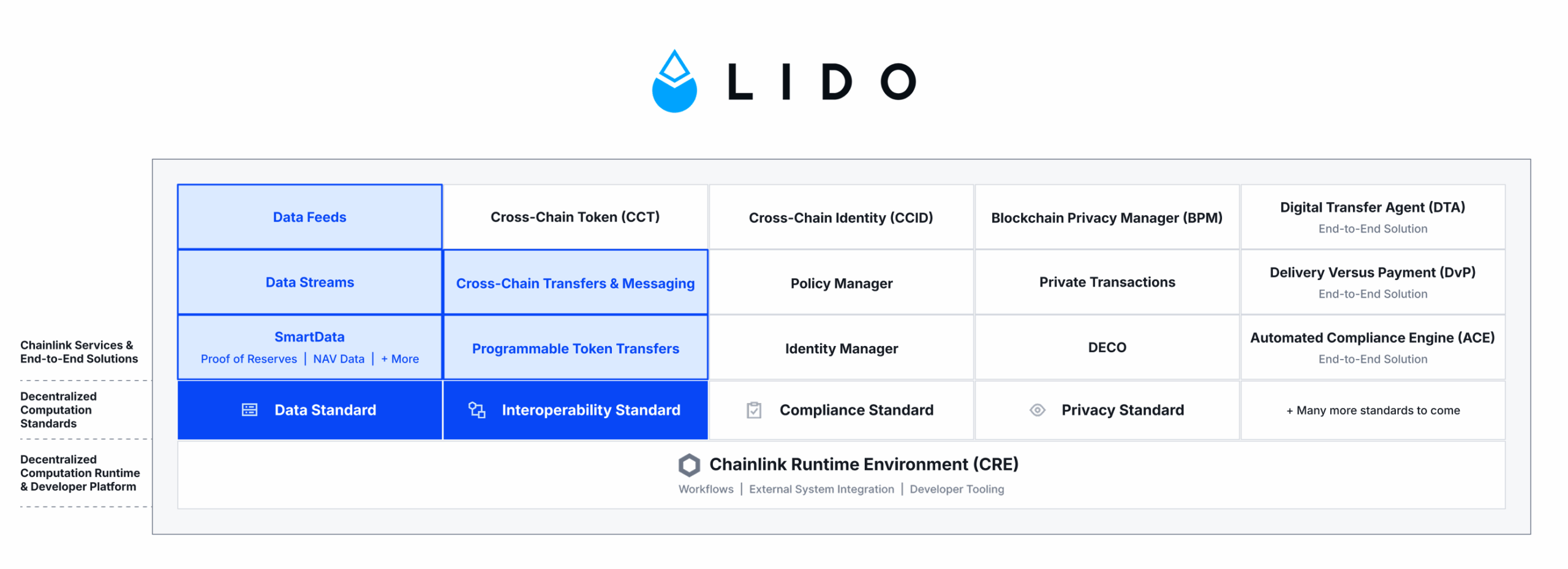
Enter Chainlink: the industry-standard oracle platform that unifies disparate blockchain networks and enables seamless orchestration of applications across onchain and offchain systems. The Chainlink stack supports multiple open standards for designing and operating oracle services, which currently span four key verticals: 1) Data, 2) Interoperability, 3) Compliance, and 4) Privacy. Built upon these standards exists an ever-expanding collection of modular, purpose-built oracle services, which can be easily created and seamlessly combined using the Chainlink Runtime Environment (CRE). CRE is the orchestration layer for building, composing, and managing oracle services to support end-to-end solutions, which run in a highly secure, reliable, and cryptographically verifiable manner.
Chainlink is the only oracle platform where institutions and developers can combine different blockchains, external data sources, and legacy systems, along with embedding critical compliance and privacy capabilities, all into a unified workflow represented through a single piece of code executed in a decentralized manner via the Chainlink Runtime Environment..
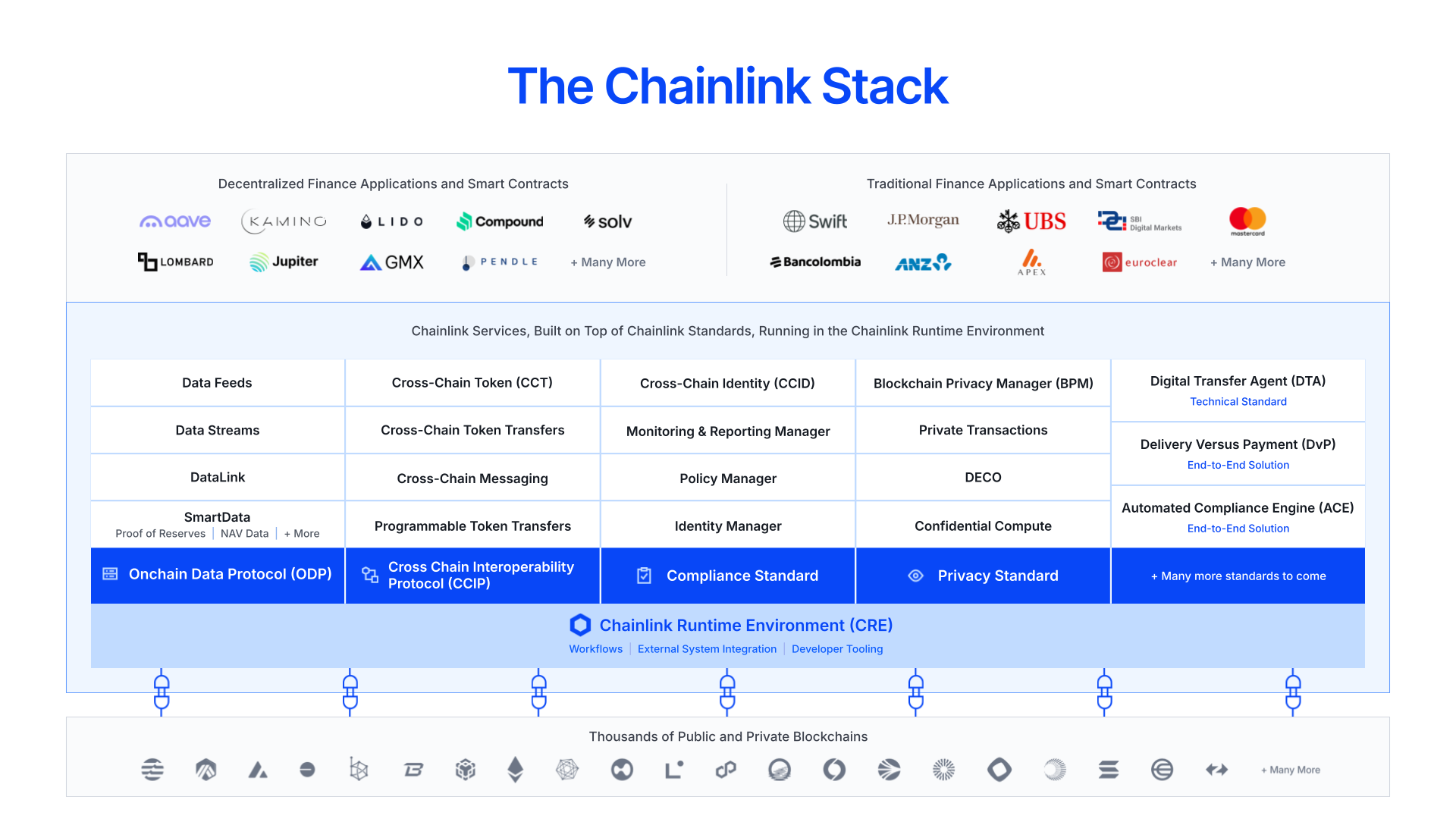
Instead of relying on point solutions that only address a fraction of an application’s needs and require a complex patchwork of service providers with different interfaces, security assumptions, and economic models, developers can leverage Chainlink to access all of the services they need for their blockchain applications to function end-to-end. With Chainlink, multi-chain, multi-asset, multi-jurisdictional, and multi-system applications are not only possible but also easy to build, orchestrate, and future-proof against changes in the industry. Only through Chainlink can institutions create these advanced onchain applications that mirror the sophistication seen in existing financial systems, yet achieve more efficiency and automation thanks to the superior composability, programmability, and reliability of blockchains.
Chainlink has already achieved two major security milestones: ISO 27001 certification and a SOC 2 Type 1 attestation. The ISO 27001 certification affirms that Chainlink has established a robust Information Security Management System (ISMS) encompassing the infrastructure, development, operations, administration, and security of CCIP, Price Feeds, and SmartData Feeds, as provided by Chainlink Labs, one of the primary contributing developers of Chainlink. The examinations were performed in accordance with attestation standards established by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (“AICPA”) by an independent accounting firm. ISO 27001 certification and completion of the SOC 2 Type 1 attestation further validate Chainlink’s position as enterprise-grade infrastructure suitable for real-world, in-production use cases with the largest financial institutions.
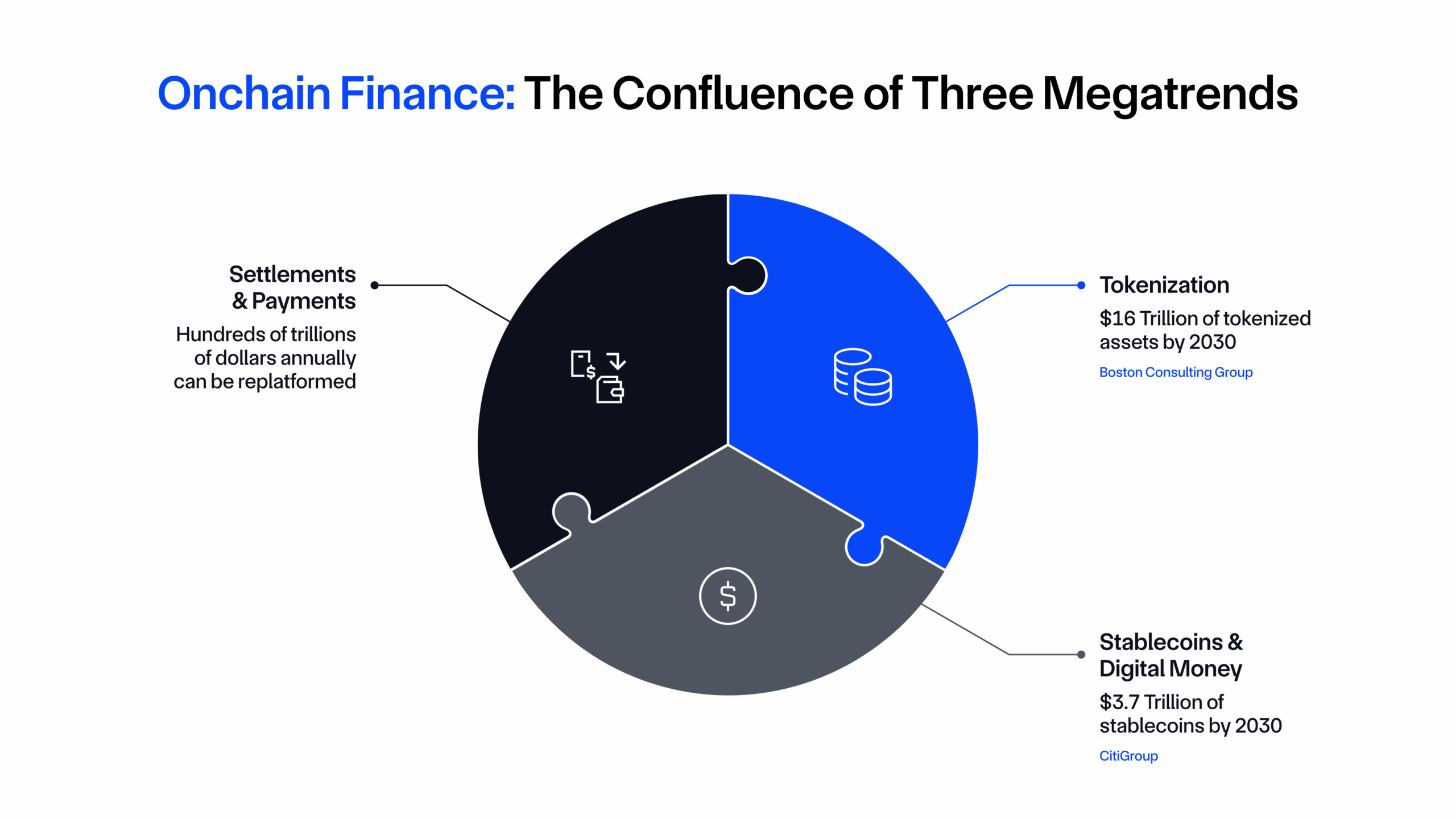
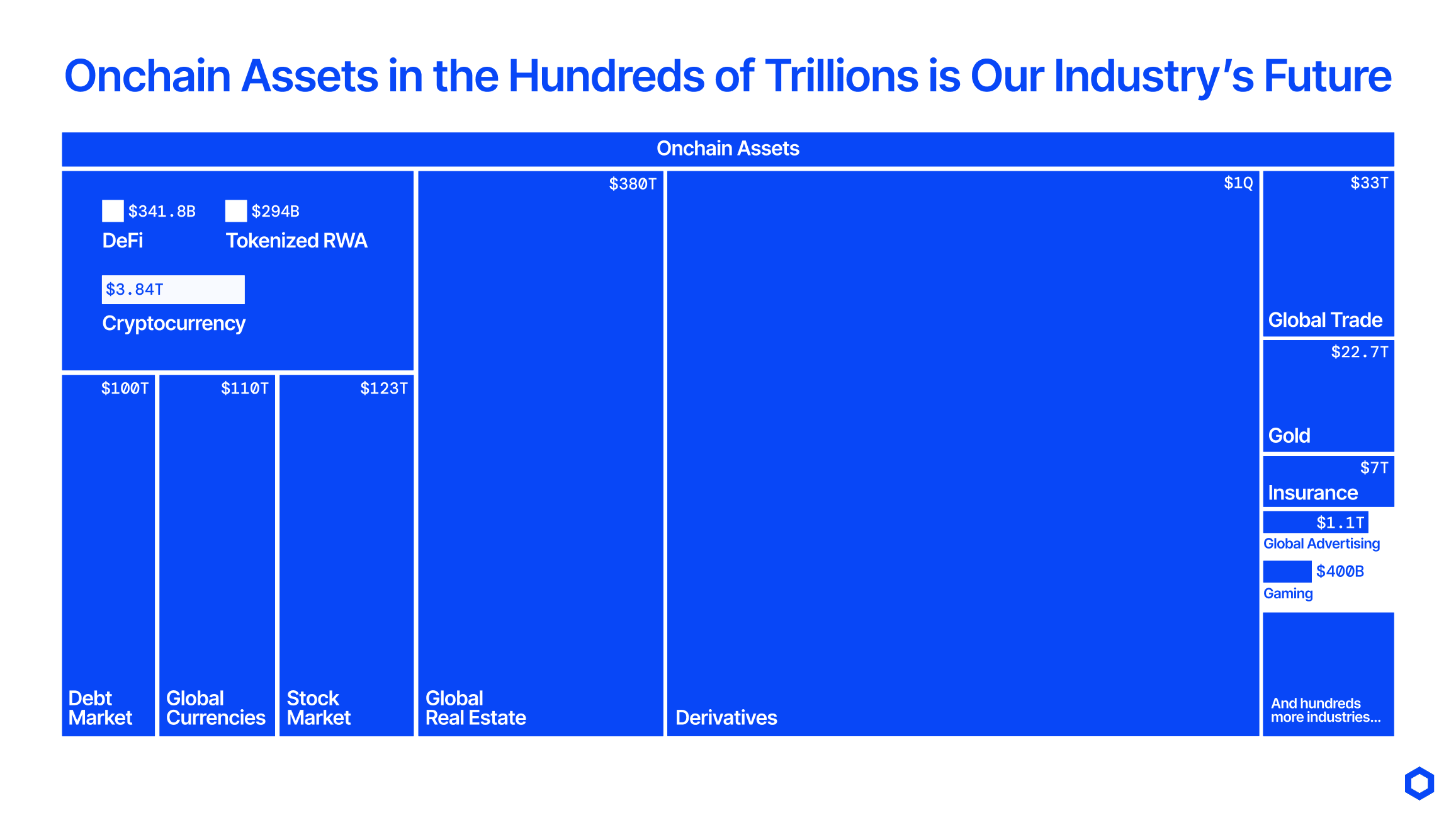
Having a full-lifecycle, institutional-grade, open technology platform is a massive unlock for large institutions and Web3 protocols looking to capitalize on the massive opportunity to modernize finance through tokenized assets and onchain applications. The Boston Consulting Group projects ~$16 trillion in tokenized illiquid assets by 2030—approximately 10% of global GDP—while the World Economic Forum estimates that tokenization could target up to $867 trillion in financial assets, representing nearly all global assets. Settlements and payments involving these assets amount to hundreds of trillions in value, much of which can be re-platformed by onchain rails.
Chainlink unlocks this opportunity by operating as the global standard powering onchain finance, providing the key data, cross-chain, compliance, privacy, and orchestration oracle infrastructure. Chainlink is already working directly with some of the world’s largest financial institutions and infrastructures, including Swift, Euroclear, Mastercard, J.P. Morgan Kinexys, Fidelity International, UBS, Apex Group, ANZ Bank, SBI Digital, and many more, as well as top DeFi protocols like Aave, GMX, Lido, Ether.Fi, Kamino, Pendle, Jupiter, Compound, and more. This includes work around foundational onchain finance use cases, such as leveraging Chainlink oracles to service tokenized assets, automate compliance and policy enforcement, settle tokenized asset transactions via Delivery vs. Payment (DvP) and Payment vs. Payment (PvP), and distribute key data onchain for the world to access. The Chainlink Network has already enabled tens of trillions in transaction value, delivered 18B+ total verified messages, and secures more than 70% of DeFi globally.
The following blog will outline how the Chainlink oracle platform uniquely supports advanced blockchain applications that enable the world’s largest institutions and DeFi protocols to unlock real-world value onchain.
The Evolution of Blockchain Adoption: From Simple to Increasingly Advanced Applications
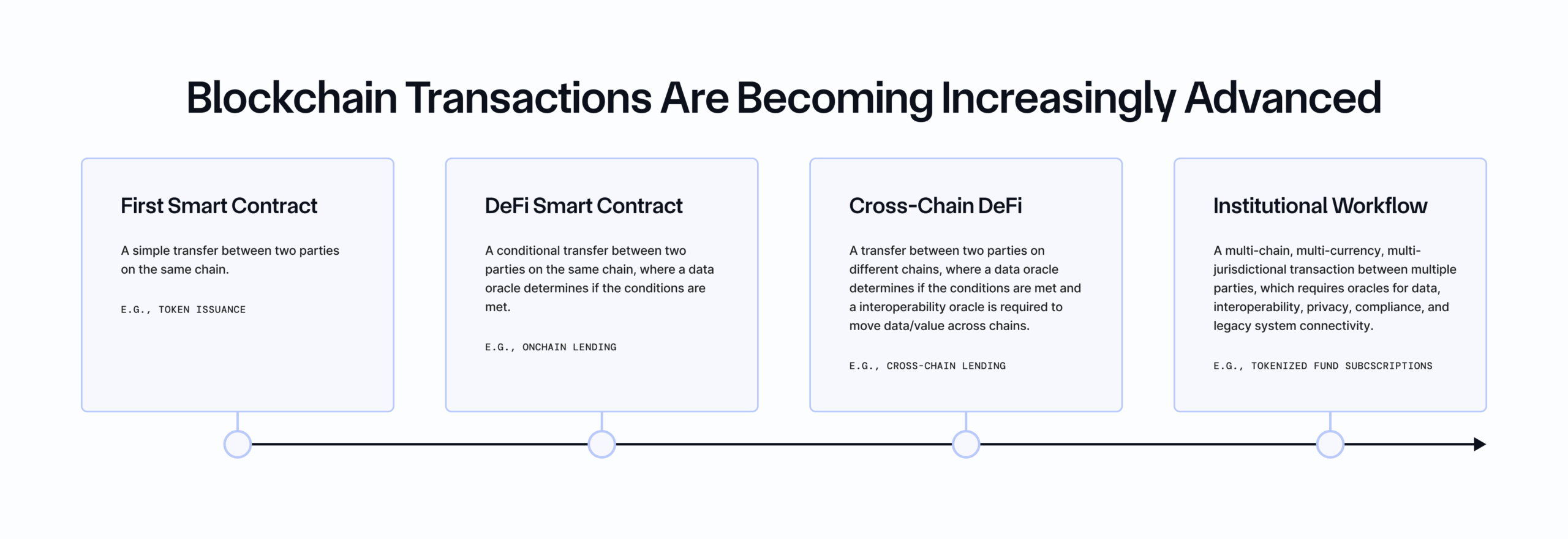
Blockchains started as a simple concept: a decentralized ledger of transactions and assets that could be transferred between users on the same network. As the first blockchain, Bitcoin introduced peer-to-peer payments, the most basic type of blockchain transaction that enabled anyone around the world to easily send and receive Bitcoin.
Ethereum then introduced smart contracts, which unlocked more complex blockchain transactions. Smart contracts enabled programmable conditions to be attached to onchain transactions (i.e., if x happens, then execute y action), allowing basic blockchain applications to emerge, such as decentralized exchanges that allow users to trade different assets on the same chain without an intermediary.
Chainlink unlocked the industry’s next major advancement with the introduction of decentralized oracle networks, enabling smart contracts to securely and reliably access external data to determine if their programmable conditions were satisfied. Smart contracts could now react to and interact with the outside world, leading to the rapid growth of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)—an industry that grew from under \$500M during Chainlink’s launch to more than $341B+ today. By bringing real-time market prices to DeFi, Chainlink directly enabled more advanced applications and use cases, such as opening and liquidating collateralized loans, settling derivative and insurance contracts, rebalancing liquidity pools, and much more.
The proliferation of DeFi ultimately led to a surge in blockchains launched. This introduced an additional level of complexity, as transactions suddenly involved assets and applications across multiple blockchains rather than existing on just a single chain. From that point onward, interoperability oracles became a critical component of more advanced applications, in addition to data oracles.
There is now a clear pattern emerging where increases in innovation and adoption of the blockchain industry are directly correlated to the industry’s ability to support more advanced transactions. With the rapid increase in tokenized real-world assets (RWAs) and support from the world’s largest financial institutions and governments, it’s clear that the new era of onchain finance requires transactions that can interact with multiple assets, multiple blockchains, multiple datasets, and multiple jurisdictions while also requiring integration with legacy systems, embedded compliance, and privacy-preserving capabilities.
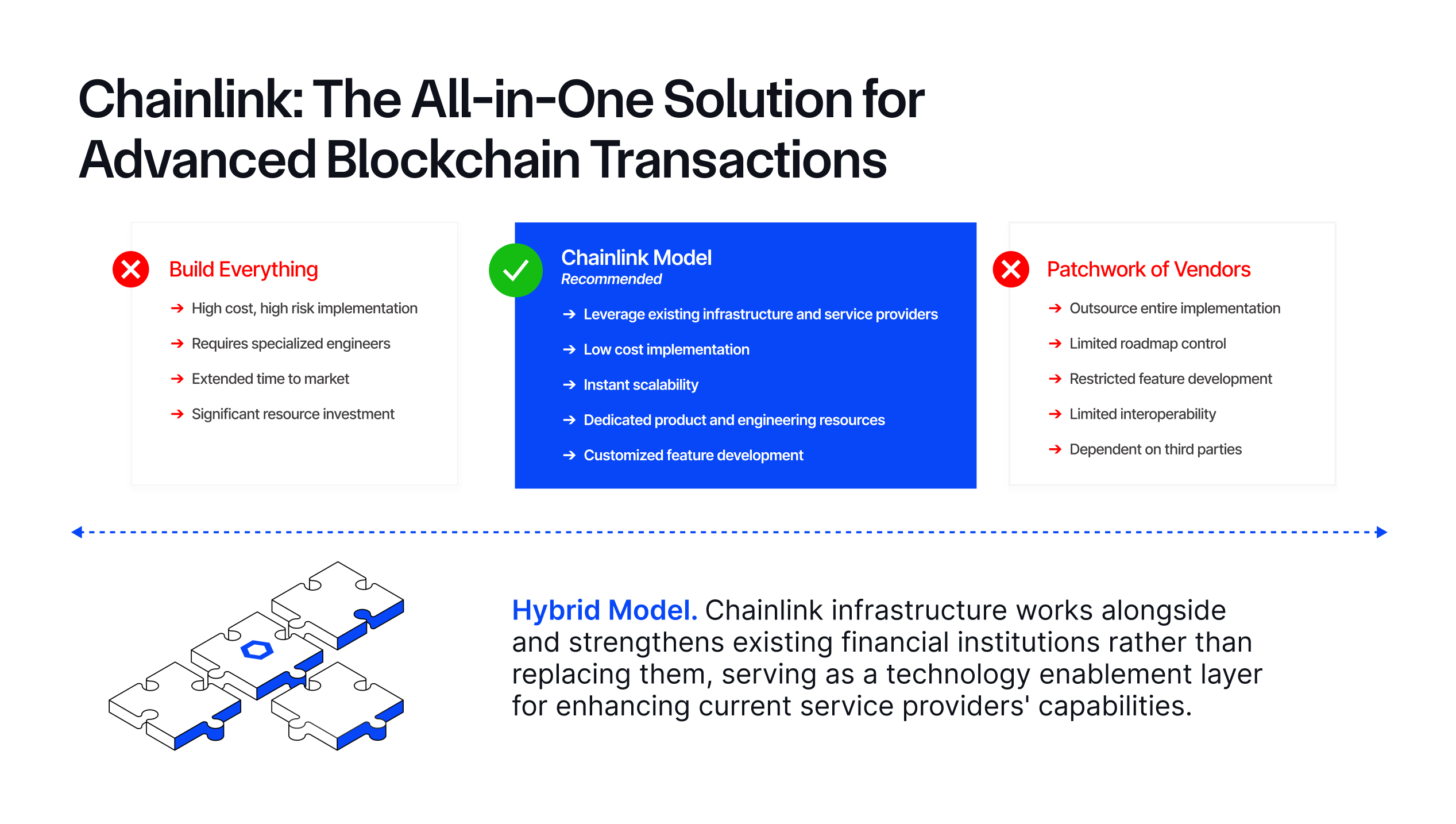
However, many blockchain applications are struggling to meet the increased complexity of integrating more blockchains and supporting more advanced functionalities and use cases. Their struggles often come down to relying on inefficient scaling methods, such as:
- Build Everything: Some teams attempt to build all of the infrastructure needed to support advanced onchain transactions in-house. This is extremely time-consuming, resource-intensive, and challenging given all the different components involved, which are constantly changing. These teams need to become experts across a wide range of disciplines—from blockchain core development and infrastructure management to handling compliance and privacy requirements—all of which take resources away from building the application’s core business logic.
- Patchwork of Vendors: Some teams adopt an ever-growing list of vendors, each assigned to a specific problem, like data or interoperability. Not only does this increase complexity—as you have to do point-to-point integrations with each vendor, use different incompatible interfaces and standards, adopt varying economic and billing models, figure out how to orchestrate activity across each service, and stay up to date with each of the vendors’ processes—but it also increases risk since you are introducing different security and trust assumptions with each vendor, which can be difficult to reason about practically. An exploit or gap in security in any one vendor places the entire application at risk.
Fortunately, there is a more secure and efficient way to adopt blockchain technology and build advanced onchain applications: Chainlink.
Chainlink: The Industry-Standard Oracle Platform Powering Advanced Blockchain Transactions
With tens of trillions of value set to be tokenized in the coming years, and hundreds of trillions set to be transacted onchain annually, it’s more critical than ever to enable advanced transactions that mirror the sophistication seen in global markets today.
Historically, each new computing paradigm was catalyzed by a key platform technology: PCs had Windows, Mobile had iOS, Cloud had AWS, and now onchain finance has Chainlink—the catalyst for not only bringing traditional finance (TradFi) volume to DeFi but also for transitioning the entire global financial system onchain.
The Chainlink stack consists of four open standards for designing and operating oracle services, covering data oracles, interoperability oracles, compliance oracles, and privacy oracles. Developers and institutions leverage these oracle services to address specific use case requirements of advanced blockchain applications or to support end-to-end solutions. The Chainlink platform, powered by the Chainlink Runtime Environment, makes it easy to develop new or integrate and customize existing services on top of the Chainlink standards. Developers can also use CRE to compose their own workflows across multiple standards, services, and offchain systems to support more sophisticated use cases. Once these services and workflows have been created, they can be deployed across various chains to maximize an application’s reach, embodying a ‘build once, connect anything’ framework.
Chainlink is positioned to be at the heart of the modern global financial system, both as the standards, services, solutions, and platform used to build onchain financial applications, and as the decentralized computing infrastructure powering the full lifecycle of transactions across onchain and offchain environments. Chainlink is the only oracle platform enabling developers and institutions to access all the critical requirements for advanced blockchain applications, along with the orchestration capabilities to build, manage, and execute sophisticated transactions by distilling them down to a single piece of code that runs securely and reliably via CRE.
This all-in-one approach creates a network effect: the more people that build on and integrate with Chainlink, the more valuable the Chainlink oracle platform becomes for everyone. The Chainlink platform also drives an economic flywheel, where the more Chainlink oracle services are used, the more user fees that are generated for the network. These user fees support Chainlink’s long-term economic growth and sustainability while also creating proper incentives for Chainlink’s ecosystem of service providers. Chainlink currently supports multiple payment and billing mechanisms, including enterprise plans (integrations, usage, and maintenance), usage-based payments (per-call and subscription), revenue-sharing agreements (percentages of app revenue), and bespoke programs designed for the Web3 ecosystem, such as Build and Scale.
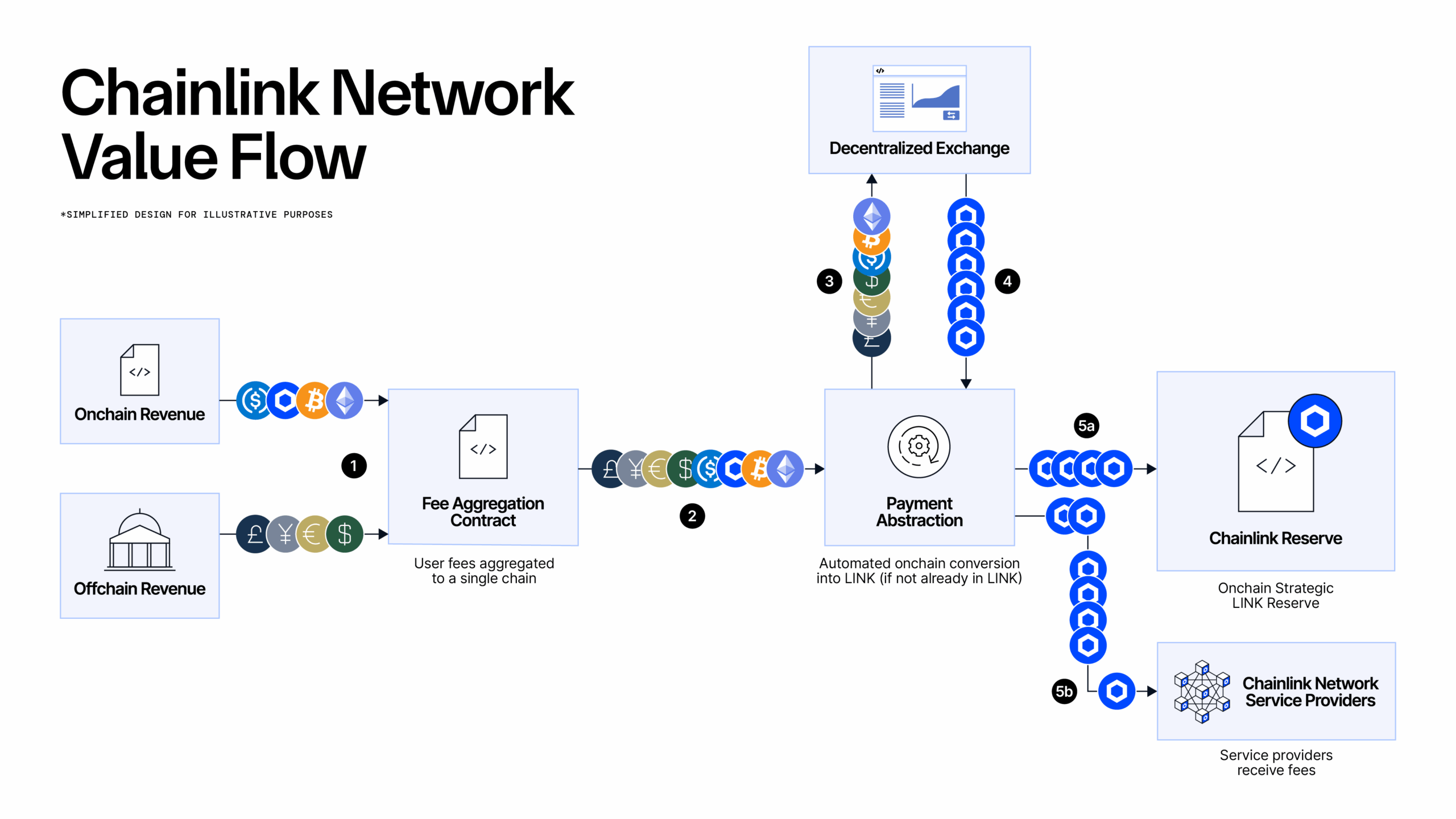
LINK is the native token of the Chainlink Network and is used across the ecosystem. Users pay network fees in LINK to interact with Chainlink services, network service providers (e.g., nodes) receive rewards in LINK, and community participants stake LINK to support the network’s cryptoeconomic security. To reduce payment friction, Chainlink services leverage Payment Abstraction—onchain infrastructure that enables users to pay fees for Chainlink services in their preferred form of payment. Payments are then programmatically converted to LINK via a decentralized exchange. Payment Abstraction supports both onchain and offchain forms of payment, including crypto-native assets (e.g., ETH & USDC) and traditional fiat currencies (e.g., USD).
Payment Abstraction is also being used to build up the Chainlink Reserve, a strategic onchain reserve of LINK tokens designed to support the long-term growth and sustainability of the Chainlink Network. The Chainlink Reserve uses Payment Abstraction to convert offchain revenue from enterprises and onchain revenue from apps into LINK, which is stored within the strategic reserve. Demand for Chainlink has already created hundreds of millions of dollars in revenue, and with increasing demand from a number of the world’s largest enterprises, the Reserve is expected to grow directly alongside the industry in the future.
To better understand the entire Chainlink stack, we’ll examine the infrastructure underpinning Chainlink, how each Chainlink standard underpins critical oracle services needed by advanced blockchain transactions, and how the Chainlink developer platform supercharges innovation and supports end-to-end solutions and custom workflows across services.
Network Infrastructure: Decentralized Computation Powering Everything on Chainlink
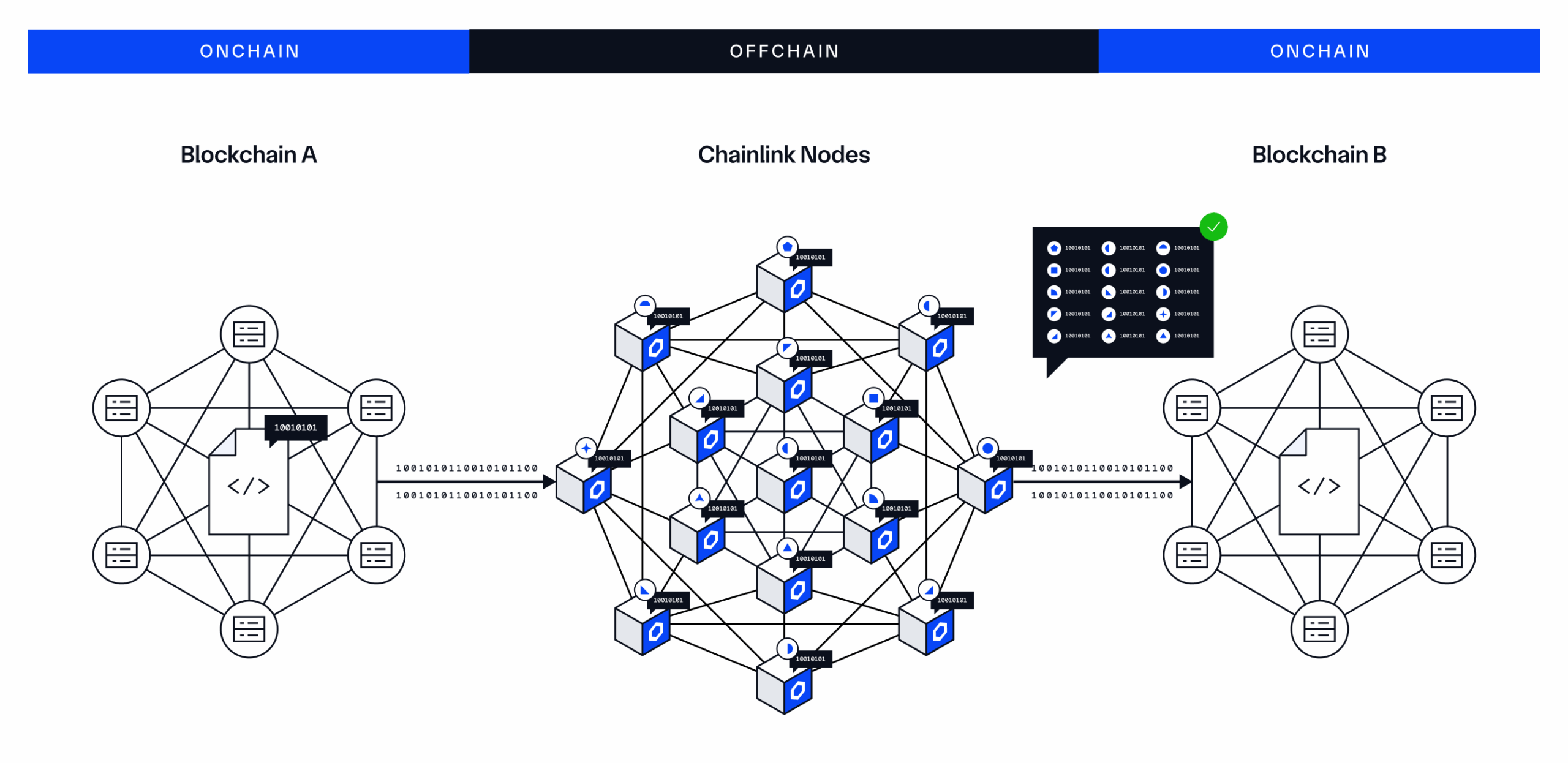
The infrastructure underpinning Chainlink consists of computer networks that execute the computations required by users. The networks are referred to as decentralized oracle networks (DONs), and are composed of multiple independent operators (i.e., oracle nodes) that come to consensus on a particular computation (i.e., consensus computing). DONs execute these computations using the Offchain Reporting (OCR) protocol, which works via the following steps:
- Each oracle node makes an independent observation about a specific event from one or multiple sources.
- The DON reaches consensus based on an aggregation of all the nodes’ observations.
- The aggregated outcome is reported to a predefined destination, located either onchain or offchain.
DONs are the backbone of CRE, executing all the code needed by all services, solutions, and custom workflows deployed on Chainlink. Chainlink is not a single DON but rather a collection of different, independent DONs running in parallel, each performing specific tasks (akin to microservices). The Chainlink Network, consisting of all DONs, already secures $90B+ in total value, has delivered 18B+ total verified messages, and has enabled tens of trillions in onchain transaction value.
Chainlink Data Standard: Access to Secure and Reliable Data Onchain
Problem: Most blockchain transactions require some form of external data to determine if specific conditions were met prior to triggering the execution of smart contract code. High-quality data is paramount to maintaining blockchain application security and ensuring accurate outcomes, as manipulated data can result in unexpected outcomes and the loss of user funds. Due to their inherent security model, blockchains do not have direct access to external data in the real world and thereby require oracle infrastructure to deliver the data, often referred to as the blockchain oracle problem.
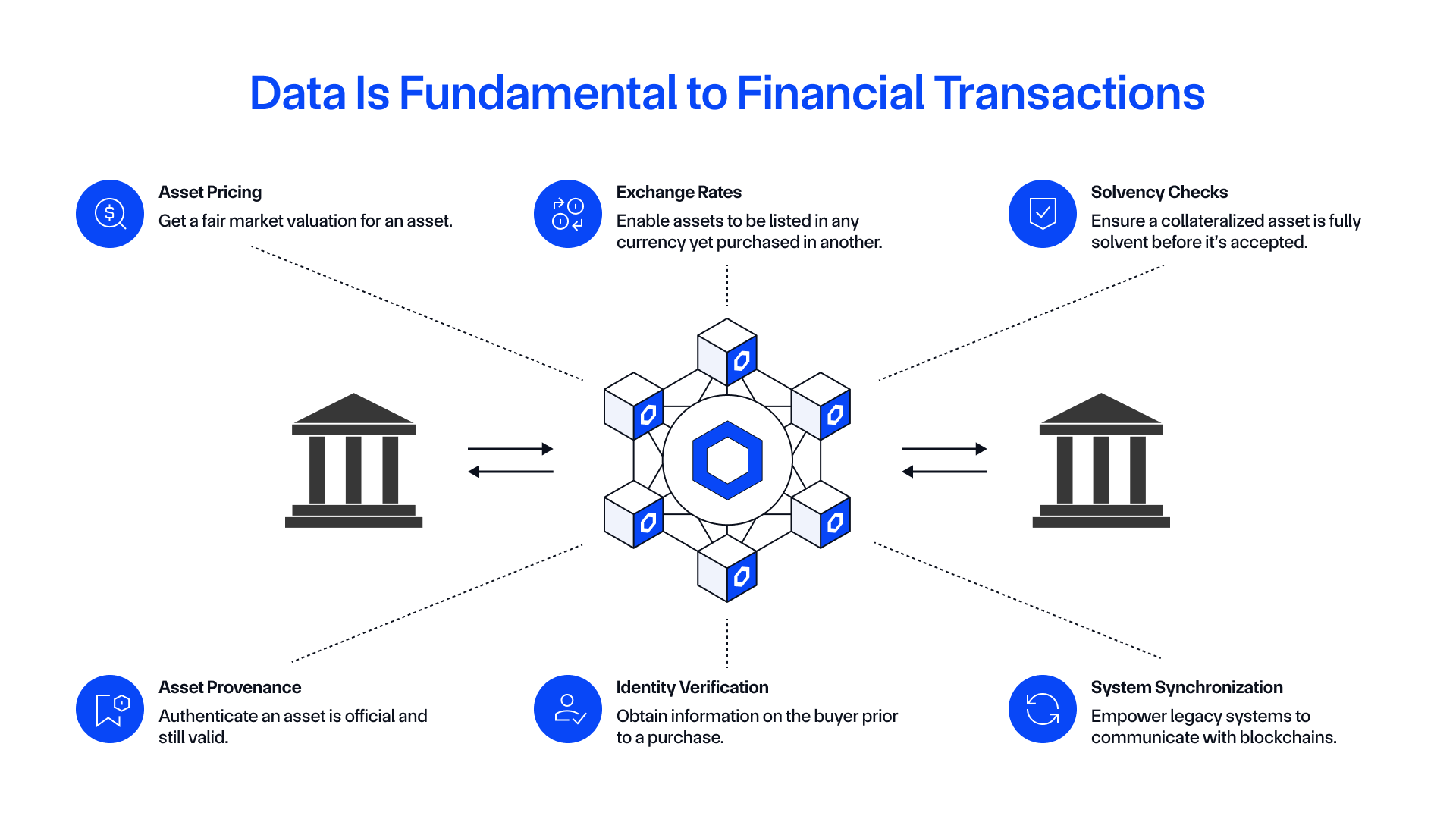
Solution: The Chainlink data standard, powered by the Onchain Data Protocol (ODP). ODP is an open, protocol-level specification for how a DON aggregates and verifies external data and publishes it onchain. It also encapsulates how applications securely access the data via a consistent set of interfaces across any blockchain—regardless of source, format, aggregation, delivery models, chains used, or use case. All of Chainlink’s data oracle solutions are unified under the ODP standard, giving institutions the foundation they need to seamlessly and securely bring core financial data onchain and power the next generation of global markets.
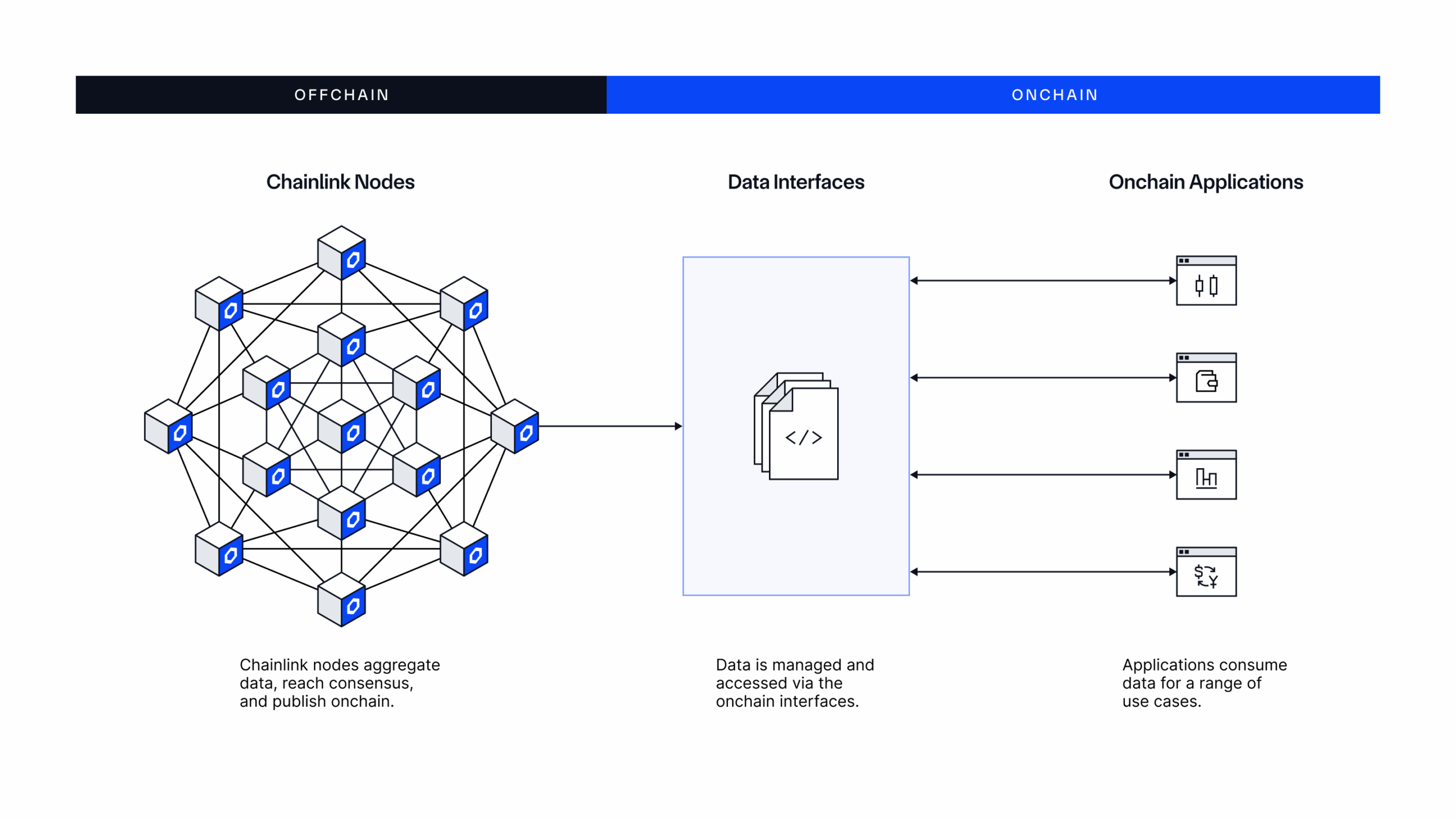
Chainlink ODP supports data oracle services that enable developers to bring any external data onchain and use it as part of their blockchain transactions. Some examples include:
- Price Feeds for accurately pricing digital assets in real time, such as cryptocurrency, stablecoins, equities, commodities, ETFs, fixed income, and more.
- SmartData for servicing tokenized assets. For example, Proof of Reserve can verify the current collateralization of onchain assets backed by offchain or cross-chain reserves, while Net Asset Value (NAV) can price tokenized funds to support onchain subscriptions and redemptions.
- Any other data type needed to facilitate an onchain transaction, such as lending rates, assets under management (AUM), sports scores, weather information, and more.
Chainlink has long been the standard for secure, decentralized data oracles. The Chainlink Data Standard has been adopted at scale by developers across every major blockchain, cloned hundreds of times across the onchain ecosystem, and integrated by leading institutions across DeFi and traditional finance. Chainlink’s data oracle services—including Data Feeds, Data Streams, SmartData, and more—have been used by over 12,000 smart contracts over the past 6 years, setting the blueprint for how real-world data is used across Web3. Multiple Chainlink data oracle services, specifically Chainlink Price Feeds and SmartData Feeds for Proof of Reserve and NAV,have completed a SOC 2 Type 1 attestation and the ISMS of these services has been certified under ISO 27001.
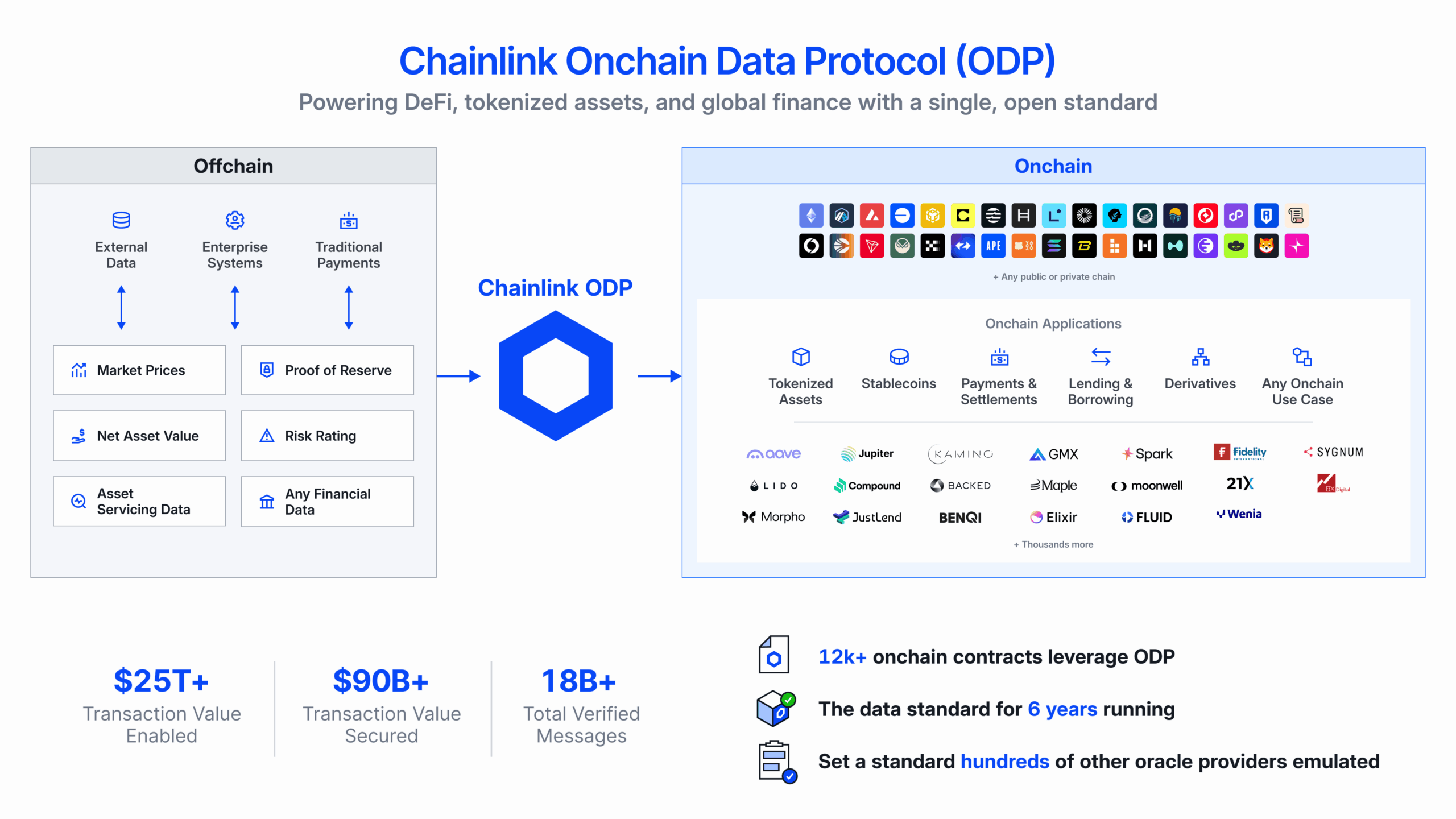
Chainlink, via DataLink, is also the standardized oracle infrastructure that established data providers use to publish and commercialize their data onchain—securely and seamlessly across leading blockchains, without the need to build or maintain blockchain infrastructure. Chainlink enables fully configurable access controls to ensure data providers maintain complete ownership and governance over how their data is accessed, even across public blockchains. With demand for tokenized real-world assets rapidly increasing, forward-looking data providers are using Chainlink to establish leadership in the digital asset space and unlock new revenue streams, while the growing volume of high-quality data accessible onchain is empowering developers to build new products, launch assets, and support robust markets.
Chainlink Interoperability Standard: Seamless Liquidity and Communication Across Blockchains
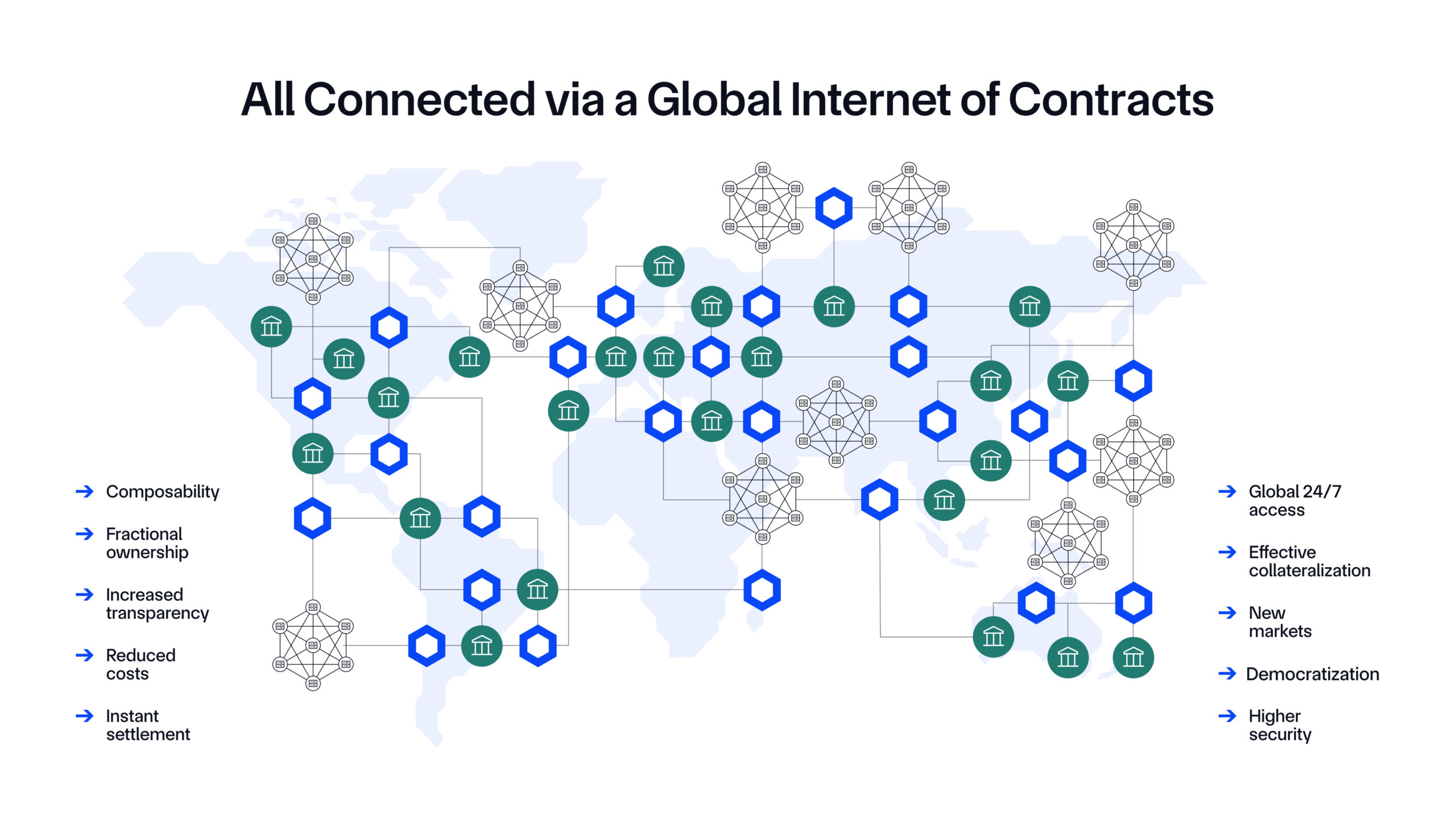
Problem: There are currently hundreds of public and private blockchains and potentially thousands more to come in the future, each with its own distinct assets, applications, and users. To maximize liquidity and support cross-chain applications, a unified interoperability standard for sending data and value across blockchains must be established, akin to how TCP/IP unifies the Internet we know today.
Solution: The Chainlink interoperability standard, powered by the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP). CCIP is an open, protocol-level specification for how a DON reads data on a source blockchain, verifies it, and writes it on a destination blockchain. The ISMS of CCIP has been certified under ISO 27001 and CCIP has completed a SOC 2 Type 1 attestation covering the Trust Services Criteria for security, availability, and confidentiality—demonstrating its commitment to secure and resilient infrastructure and operations.
Utilizing interoperability oracles, CCIP enables data and tokens to be seamlessly and securely transferred across blockchains. CCIP also supports Programmable Token Transfers, where data (messages) and value (tokens) can move together across chains, particularly to instruct the receiving smart contract what to do with the tokens once they arrive, such as deploying them in a lending market or using them to purchase an asset. The result is CCIP connecting all public and private blockchains into a single Internet of Contracts, driving unified liquidity and efficient cross-chain applications.
CCIP supports the Cross-Chain Token (CCT) standard for making any new or existing token cross-chain-enabled via CCIP. CCT allows self-serve deployments, full control and ownership for developers, enhanced programmability, and zero-slippage transfers—all backed by CCIP’s industry-standard defense-in-depth security. Notably, CCTs are token logic agnostic, meaning token developers can deploy pre-audited token pool contracts to turn any ERC20-compatible token into a CCT or deploy their own custom token pool contracts for bespoke token use cases. CCTs do not require token developers to inherit any CCIP-specific code within their token’s smart contract. Furthermore, token developers can participate in the security of their tokens through the Token Developer Attestation feature by attesting to token burn or lock events on source chains before CCIP can mint or unlock tokens on destination chains.
Chainlink Compliance Standard: Built-In Compliance For Onchain Assets and Applications
Problem: The global financial system requires adherence to various forms of compliance within different geographic regions in order to conduct transactions, such as KYC/AML or transaction rate limits. These compliance requirements are implemented to protect against fraud or illicit activity and ensure specific jurisdictional or internal business requirements are satisfied. As a result, token issuers, financial institutions, and DeFi protocols need a way to embed compliance into their tokenized assets and blockchain applications in a manner that’s efficient, reliable, and specific to their unique needs.
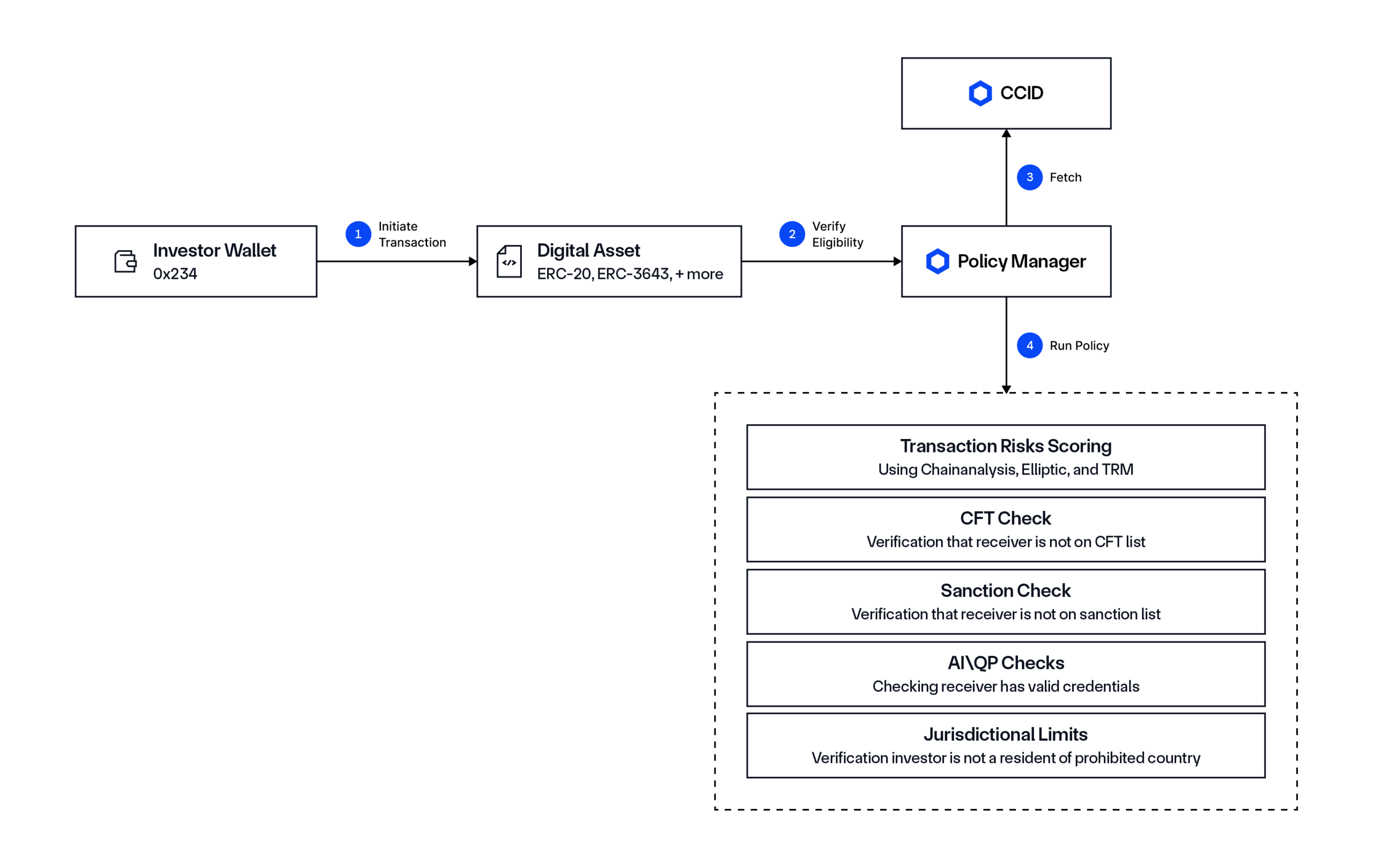
Solution: The Chainlink compliance standard, powered by the Onchain Compliance Protocol (OCP). OCP is an open, protocol-level specification defining how to utilize DONs to define and store compliance data onchain and utilize identity data and policies in smart contracts. OCP allows existing identity systems (e.g., GLEIF’s vLEI, ERC-3643) to be integrated with onchain infrastructure via the Cross-Chain Identity (CCID) framework, with policies enforced onchain and offchain using the Policy Manager. Compliance policies can be embedded directly within smart contracts and any token type, credentials can be verified without exposing personal data, and identity attestations can be coordinated across blockchains and jurisdictions. This is enabled by CCT and its compliance extension, which functions as a connector between smart contracts and CCID and the Policy Manager.
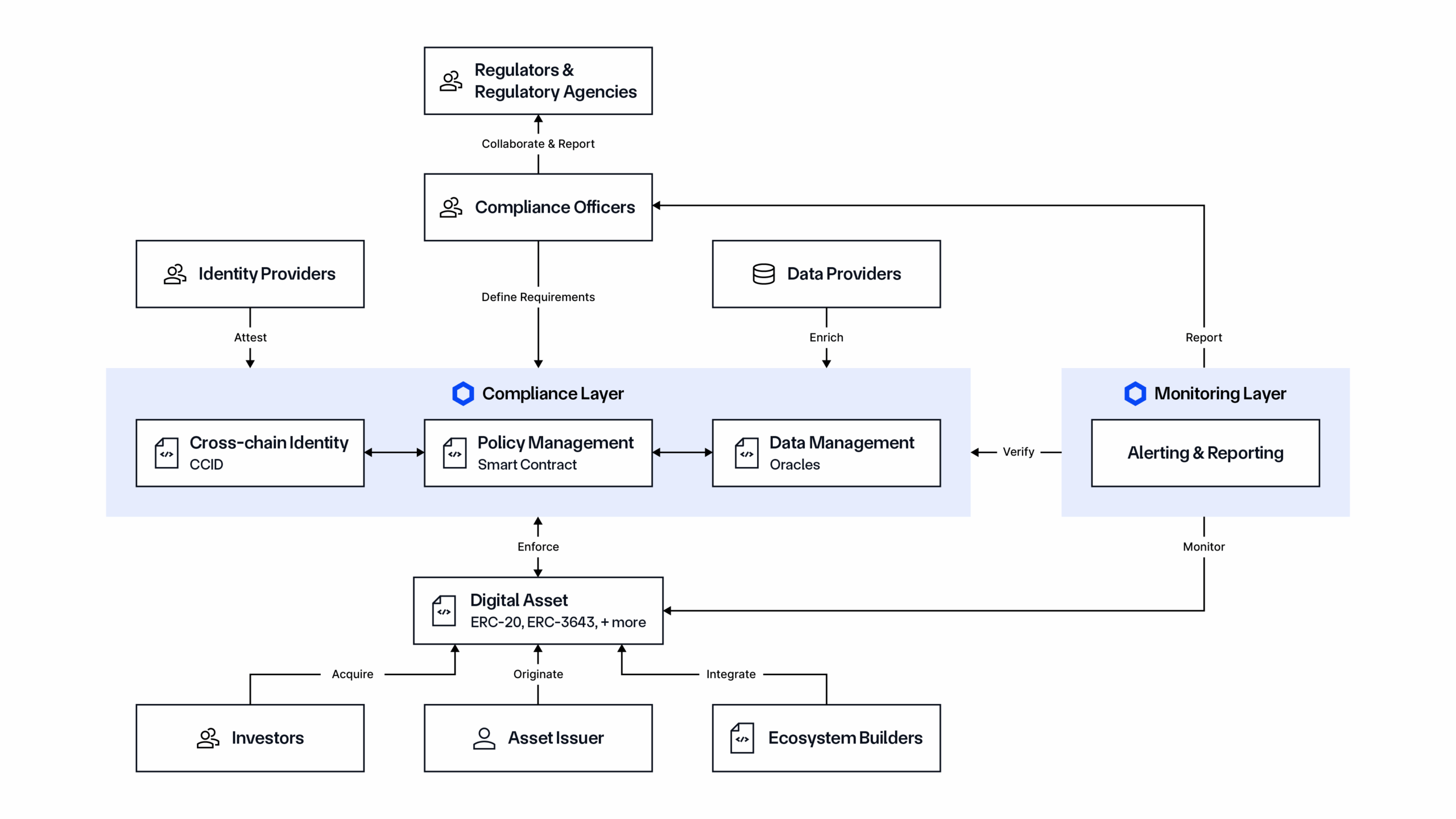
Chainlink Automated Compliance Engine (ACE) is an end-to-end solution that leverages OCP to provide key compliance oracle services for managing onchain interactions and both configuring and monitoring policies and their execution. Chainlink ACE features:
- Policy Manager: A customizable rules engine that enables users to define, manage, and enforce compliance policies directly within smart contracts, with onchain or offchain execution.
- Identity Manager: A middleware that links real-world identity sources to various onchain formats, including CCID and other existing standards like ONCHAINID. It enables the registration, distribution synchronization, and lifecycle management of identity credentials across networks without storing NPI/PII onchain.
- Monitoring & Reporting Manager: A service for observing and detecting non-compliance issues, risk concentration, and other anomalies, facilitating real-time alerts, proactive risk mitigation, and strengthened operational resilience. It also enables institutions to obtain reports to support internal and regulatory compliance.
Through OCP and ACE, regulated financial institutions can deploy their assets on public and permissionless networks while supporting their own policies and compliance obligations. Compliance and policy enforcement logic can be easily reused, upgraded, and enforced across any combination of token standards, execution environments, or legal jurisdictions. As a result, critical compliance-focused use cases for onchain finance are now possible, such as reusable digital identities, regulated asset usage in DeFi protocols, compliant-enabled cross-chain digital asset settlements, and more.
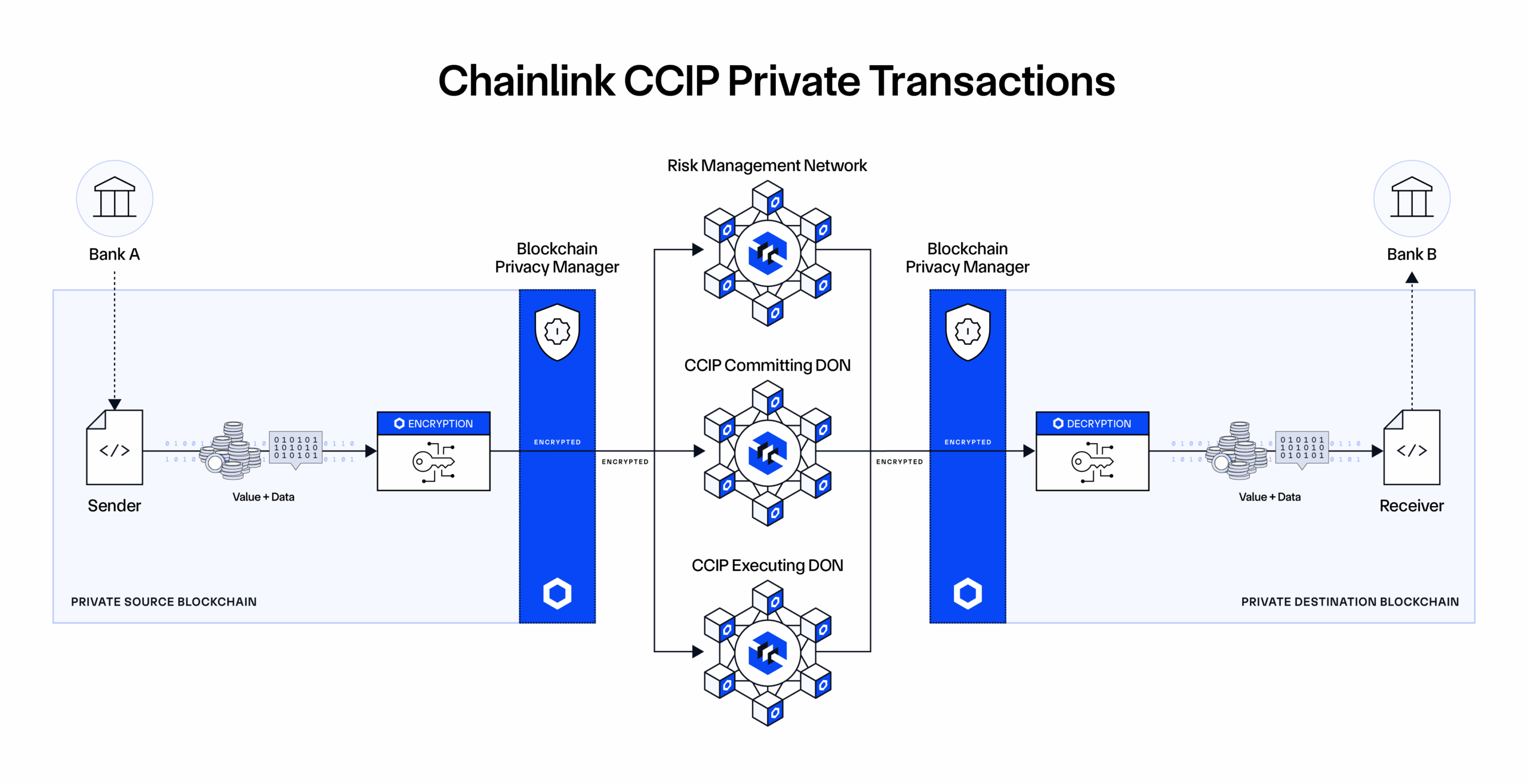
Chainlink Privacy Standard: Encrypted Trusted Computing
Problem: Blockchain transactions, particularly those involving regulated institutions and assets or requiring the use of sensitive data, need a way to maintain privacy over different aspects of the transaction. Without privacy, many forms of blockchain transactions simply cannot take place, whether due to regulatory or consumer constraints.
Solution: The Chainlink privacy standard utilizes privacy oracles to unlock private smart contracts that conceal sensitive client data, trading strategies, and business logic. It includes multiple Chainlink services, including Confidential Compute, DECO, Blockchain Privacy Manager, and CCIP Private Transactions. Through the Chainlink privacy standard, institutions can interoperate across public chains, private chains, and legacy systems while incorporating privacy into key parts of the transaction, such as:
- Privacy of transaction computations: Confidential Compute combines the performance of trusted execution environments with advanced, trust-minimizing cryptographic techniques to deliver decentralized confidential computing to any blockchain.
- Privacy of data entering and leaving blockchains: The Blockchain Privacy Manager enables institutions to integrate the public Chainlink Platform and their existing systems with private blockchain networks while limiting onchain data exposure.
- Privacy of cross-chain transactions: CCIP Private Transactions leverages the Blockchain Privacy Manager and a novel onchain encryption/decryption protocol to enable institutions to transact across multiple private blockchains using the public CCIP network while keeping the transaction details confidential.
- Privacy of offchain data shared onchain: DECO enables statements about offchain data to be shared onchain without revealing the underlying data.
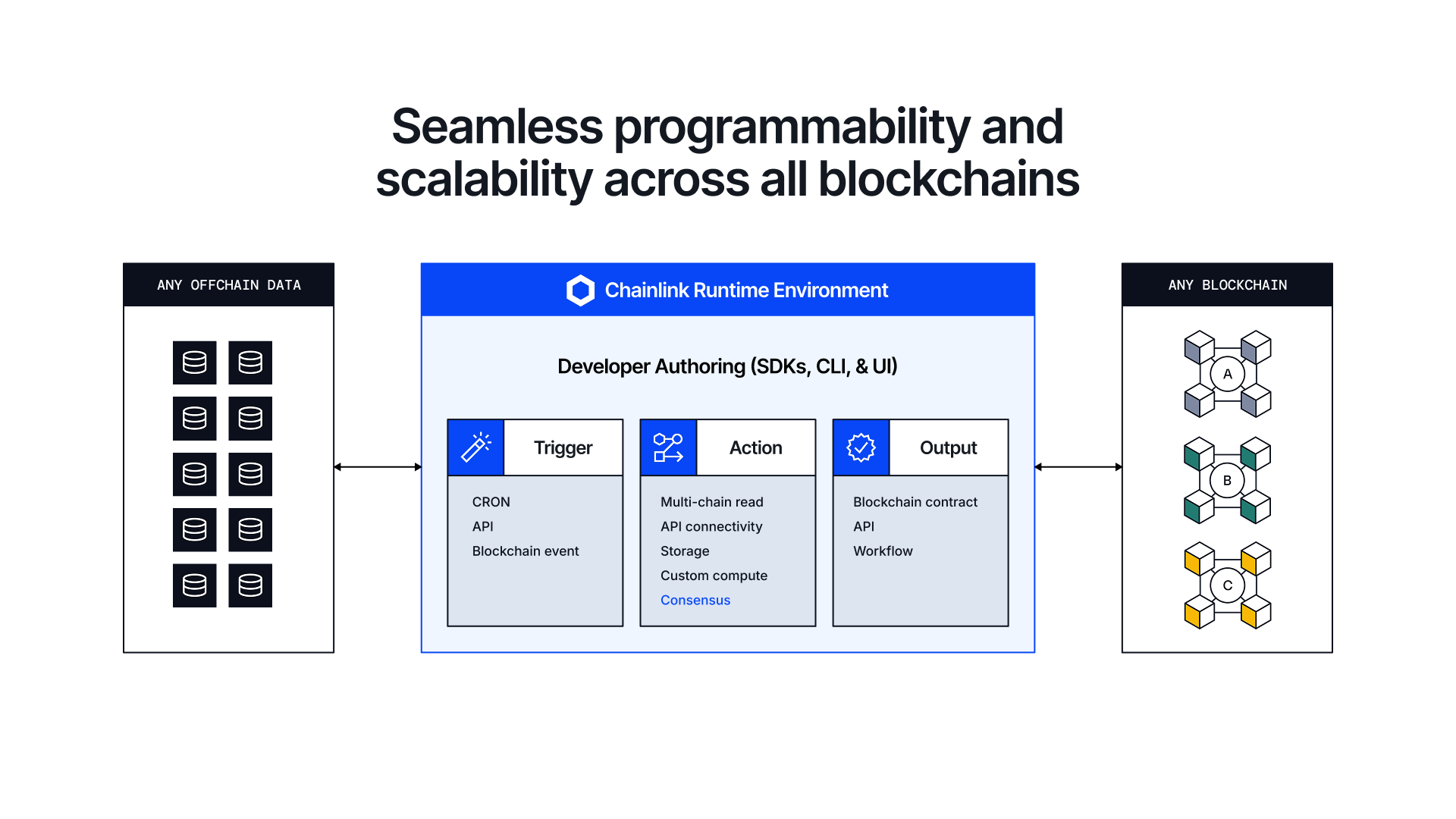
Chainlink Platform: Self-Serve Development and Orchestration Across Chainlink Services
Since Chainlink underpins the four standards above, it’s the ideal platform for coordinating, managing, and automating the execution of complex workflows across multiple oracle services and various onchain and offchain systems. The Chainlink platform, powered by the Chainlink Runtime Environment, enables developers and institutions to seamlessly combine blockchains, legacy systems, real-world data, cross-chain interoperability, compliance policies, and privacy capabilities into a single piece of workflow orchestration code, which is reusable, easily modifiable, and executable in a decentralized manner.
CRE provides critical functions—fixed messages, specific data sources, reads/writes to chains, external adapters for legacy system integration, and foundational contract standards—as capabilities so developers can compose them into a workflow with a trigger-action-output form. The trigger kicks off the workflow, such as the occurrence of an onchain or offchain event, which then leads to various types of actions by Chainlink DONs, with the final output(s) delivered to a predefined destination(s).
For example, take a cross-chain liquidity balancer requiring multiple functions. Instead of integrating numerous different vendors and three different chains, you can compose them in one workflow via CRE, abstracting away all integration complexity. This orchestration capability is what Terraform did for cloud DevOps, what JRE did for early Internet-era financial apps, and what CRE is now doing for hybrid offchain/onchain applications. Orchestration is critical to mass adoption because once you reach the level of sophistication required to support existing capital markets onchain, efficient coordination and management of complexity is the main problem to solve.
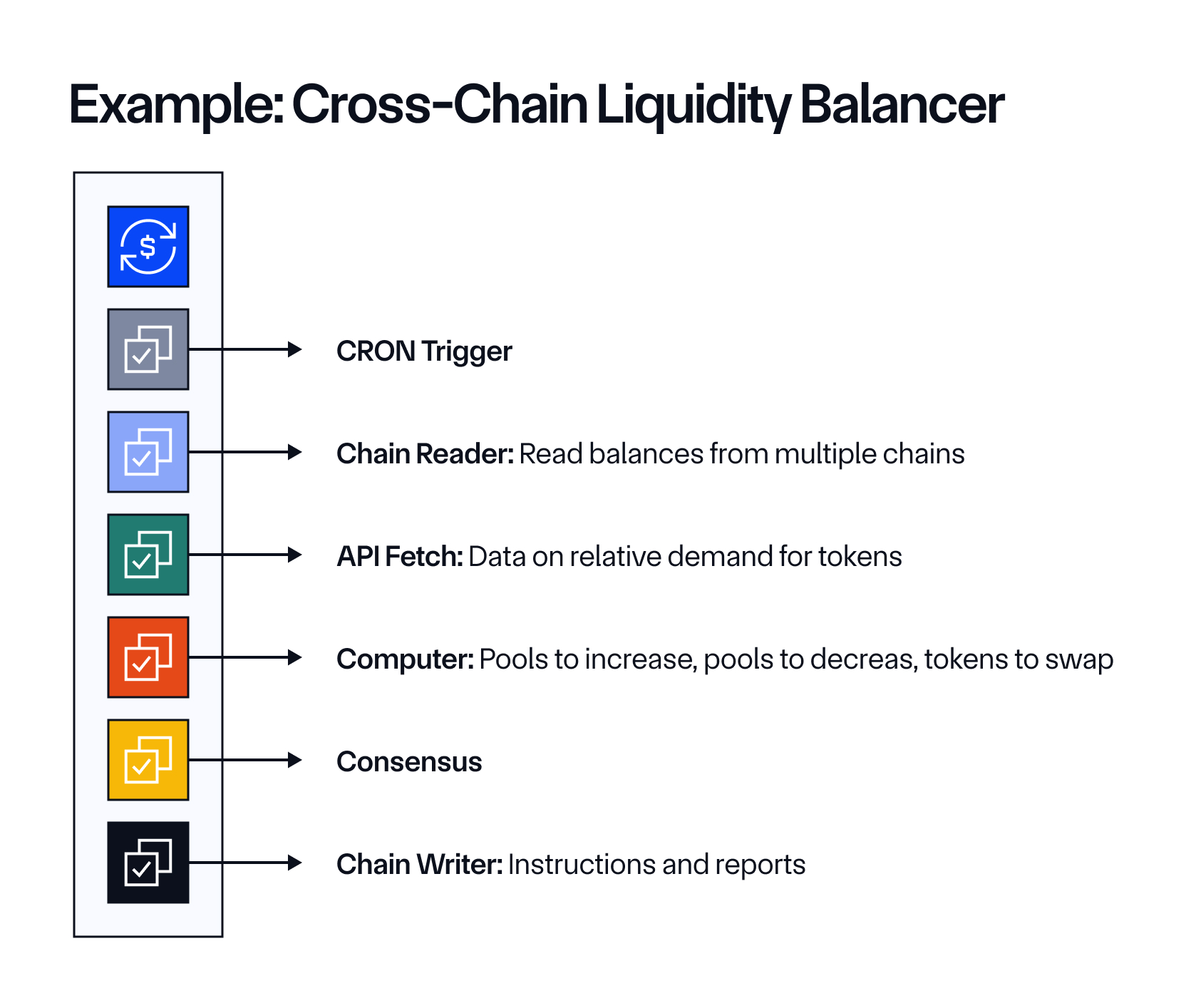
CRE can support the entire life cycle of advanced transactions, of which are required to enable use cases that mirror existing financial markets. Below is an example of a sophisticated use case for stablecoins that is made simple and scalable via CRE.
Example: Institution A wants to buy shares in a tokenized fund from Institution B. Institution A wants to buy the tokenized fund shares using a Euro stablecoin on a Public Blockchain, while Institution B only wants payment in a USD stablecoin on a Private Chain. This type of Payment vs. Payment (PvP) plus Delivery vs. Payment (DvP) transaction requires several key services from Chainlink:
- Data: Price Feeds for exchange rates between the stablecoins, Proof of Reserves to verify the reserves of the stablecoins, and NAV data to price the tokenized fund.
- Interoperability: Cross-chain messaging and token transfers between the public and private chains.
- Compliance: KYC/AML verification of Institution A and Institution B prior to the transaction.
- Privacy: Confidential interactions with the Private Blockchain, wherein onchain data isn’t exposed to third parties.
- Platform: Integration of the institutions’ existing systems with the blockchains so they can relay data to the transaction and receive status updates. The platform also enables the efficient creation of the workflow and orchestrates each step until the transaction is complete.
- DTA and DvP: The Digital Transfer Agency (DTA) smart contract facilitates the transfer of the tokenized fund, while the Delivery vs Payment (DvP) workflow enables the atomic swap of the stablecoin for the tokenized fund. Both DTA and DvP are end-to-end solutions that combine various services to support the use case’s lifecycle. They will soon be supported by the Chainlink platform.
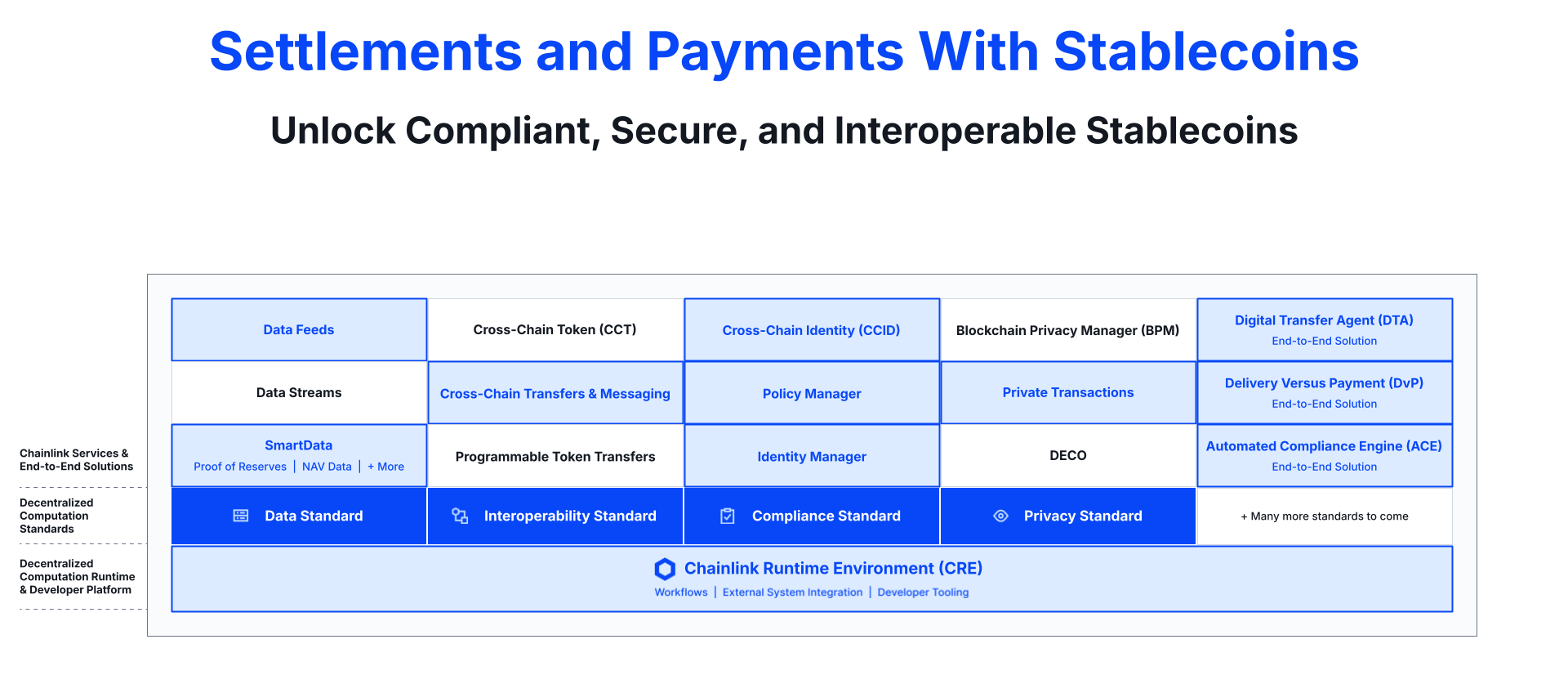
Chainlink: Bringing Global Capital Markets Onchain and Powering the Majority of DeFi
The world’s largest institutions and top DeFi protocols are using Chainlink to build and execute advanced blockchain transactions that involve multiple different oracle capabilities across data, interoperability, compliance, privacy, and orchestration.
UBS Asset Management, SBI Digital Markets, Swift, and Chainlink Enabling Next-Generation Tokenized Funds
As part of the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) Project Guardian, UBS Asset Management, SBI Digital Markets, and Chainlink demonstrated how Chainlink enables the creation of tokenized funds with automated fund management operations and transfer agency processes. Furthermore, the use case showcased how tokenized funds can leverage traditional Swift’s existing payment rails for issuance and settlement. As a result, digital asset transactions have access to the existing Swift fiat payment system, which is already used by 11,500+ financial institutions across 200+ countries and territories.
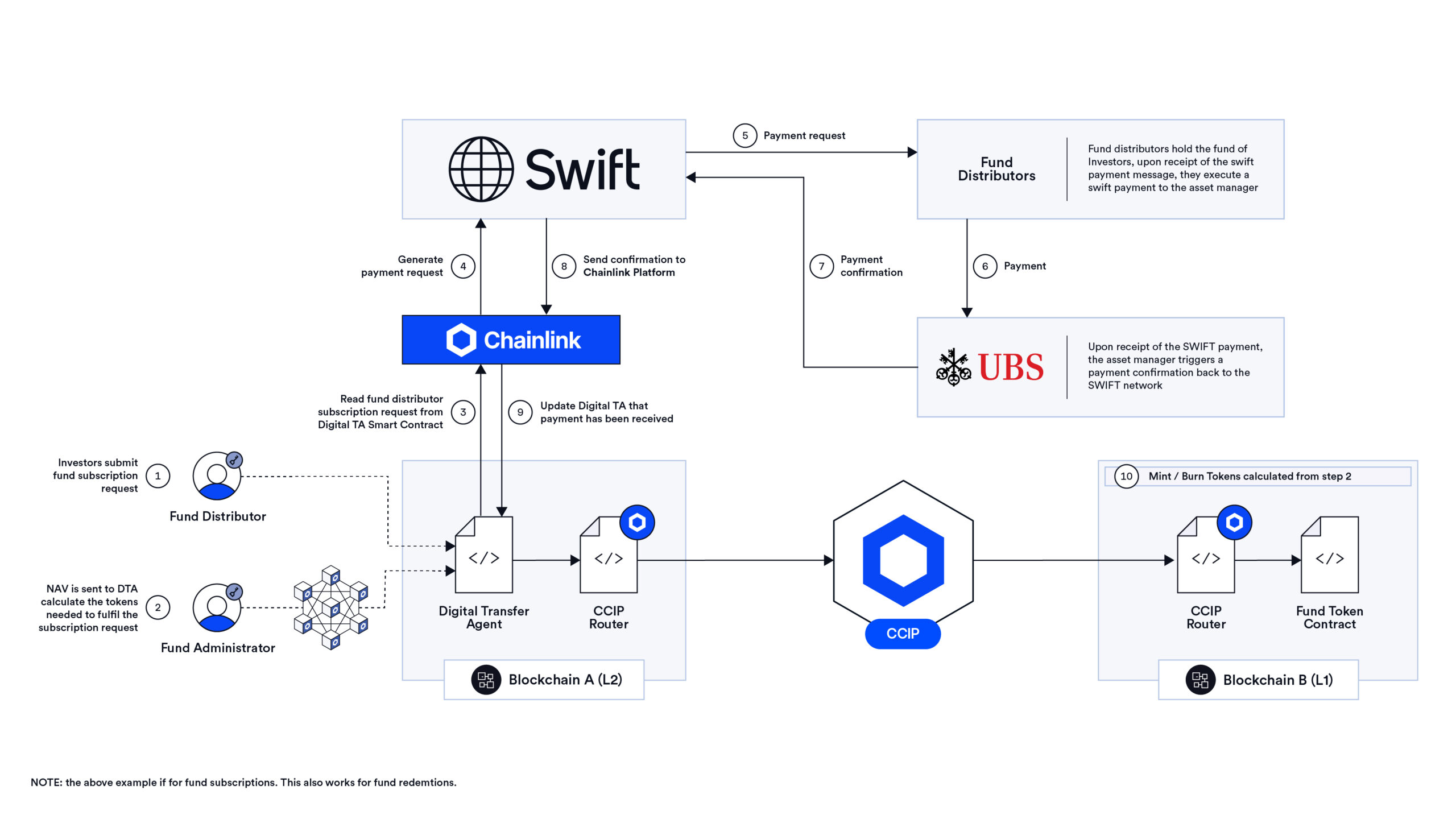
The solution enables tokenized funds to maintain their share register on one blockchain while using the Chainlink interoperability standard for the processing of intensive fund lifecycle activities like subscriptions and redemptions on another blockchain and cross-chain operations between the DTA contract and the tokenized fund. The Chainlink data standard is also used to bring NAV data onchain, while the Chainlink CRE platform integrates existing systems onchain so asset managers can receive transaction status updates and Swift can facilitate offchain payments for tokenized funds. The offering comes together as end-to-end solutions via Chainlink’s Digital Transfer Agent (DTA) and Delivery vs Payment (DvP) offerings.
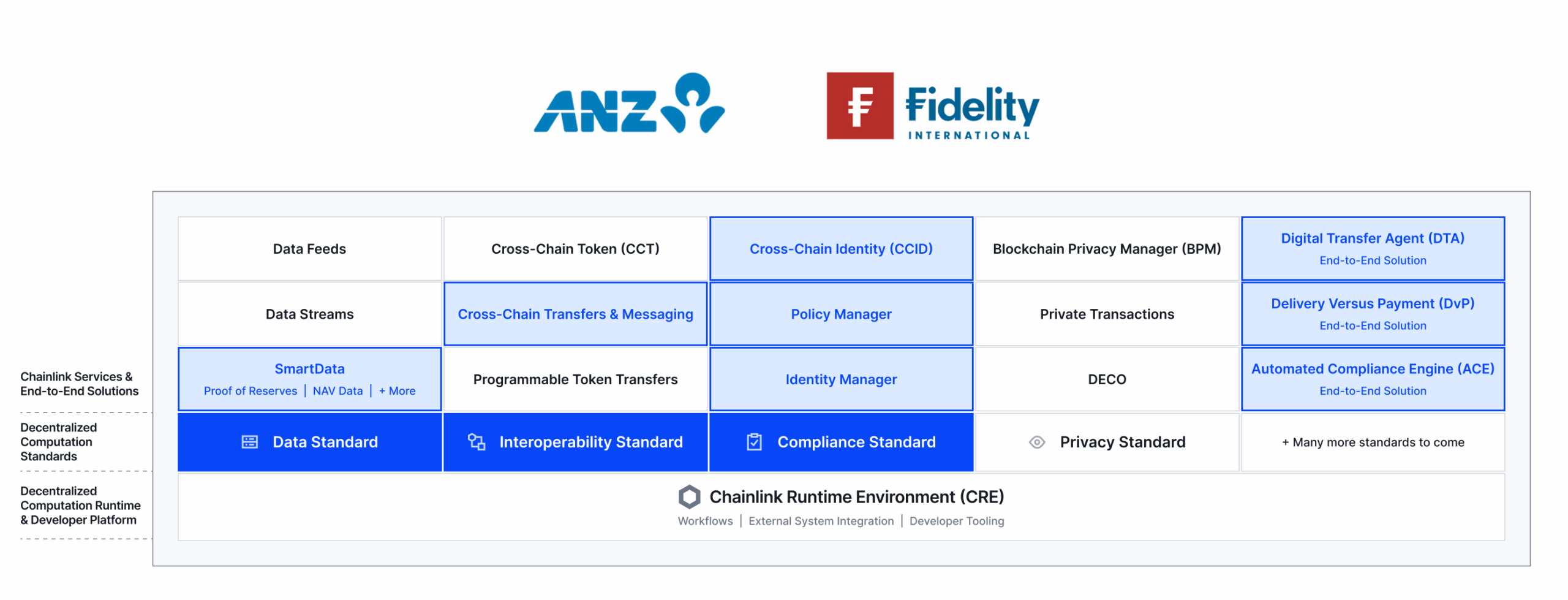
ANZ Bank and Fidelity International Use Chainlink for Cross-Chain Settlement of CBDCs, Stablecoins, and Tokenized Assets
Recently, Visa highlighted Chainlink’s work with ANZ Bank and Fidelity International under phase 2 of the Hong Kong Monetary Authority’s e-HKD program. The participants built a PvP settlement workflow involving an Australian Stablecoin (A$DC) on ANZ’s DAS Chain and a wrapped Hong Kong CBDC (e-HKD) on Ethereum Sepolia—using Chainlink oracles for cross-chain interoperability, compliance verification, and legacy system integration.
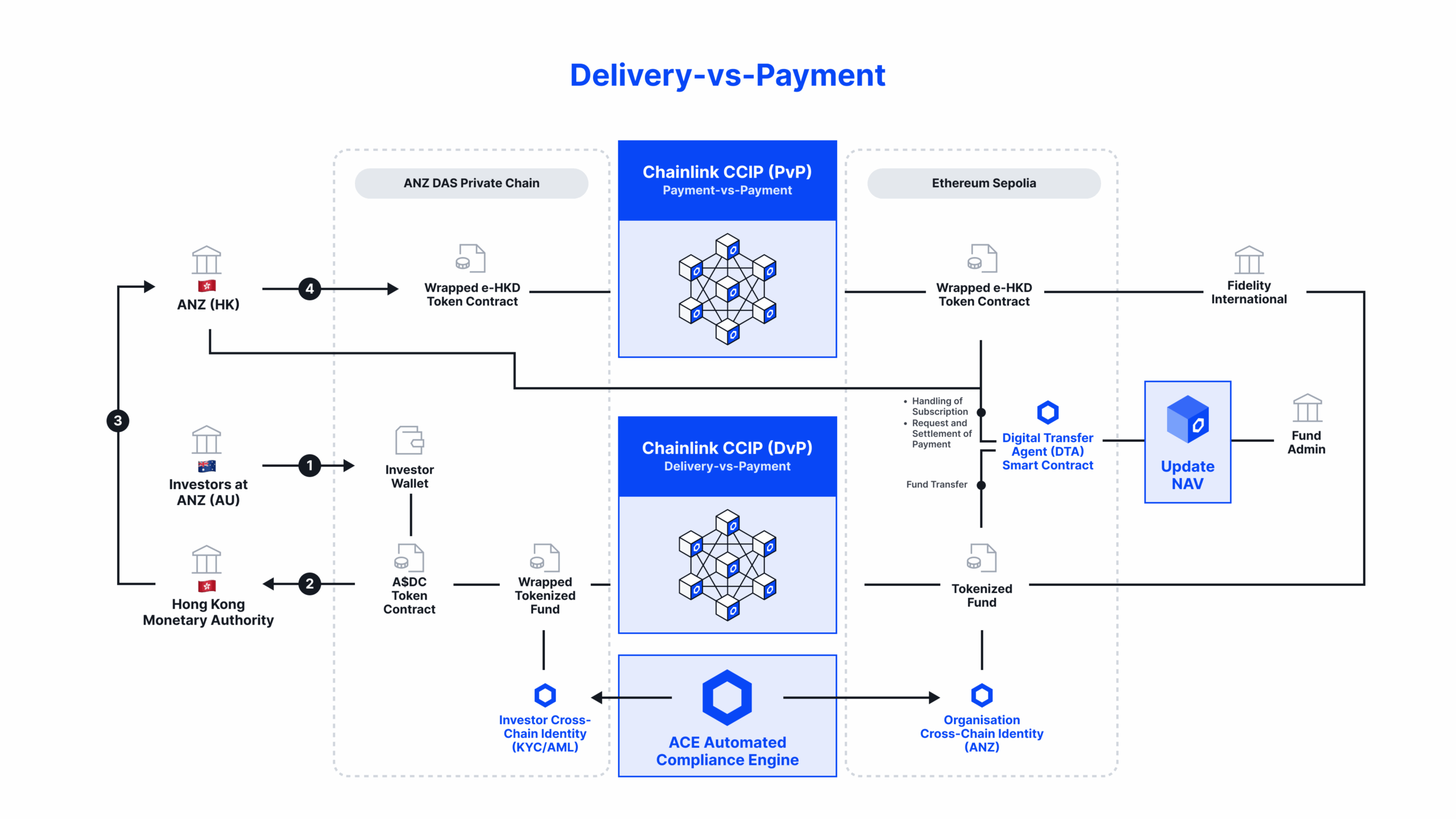
The next phase involves a DvP workflow with an Australian investor purchasing a tokenized asset in Hong Kong, leveraging Chainlink for cross-chain interoperability, compliance verification, and NAV pricing, along with a new Chainlink Digital Transfer Agent solution. The use case highlights how Chainlink oracles can be leveraged to overcome three key challenges in creating next-gen smart contracts for institutional transactions:
- Providing access to data onchain enables tokenized assets to be properly priced and supports automated onchain transfer agent operations. Chainlink is providing NAV data to enable the Digital Transfer Agent smart contract to automate updates, ensuring accurate pricing for subscriptions and redemptions of a tokenized money market fund.
- Powering cross-chain interoperability enables digital assets and data to be securely transferred across multiple public and private blockchain networks. Chainlink CCIP is powering a cross-chain PvP settlement workflow that supports atomic settlement for the cash (e-HKD CBDC and ANZ’s stablecoin) leg of the transaction.
- Bringing verifiable identity data onchain while protecting user privacy enables new use cases that meet the high regulatory requirements and internal policy controls of institutions. Chainlink is enabling compliance by allowing ANZ’s offchain identity registry to be verified onchain and support reusable credentials, ensuring transactions adhere to required regulatory standards across Hong Kong and Australia.
Combining these capabilities, the Chainlink oracle platform is empowering Fidelity International and ANZ to validate how secure, privacy-preserving, and compliance-ready workflows streamline tokenized fund operations across chains at scale.
Kinexys by J.P. Morgan, Chainlink, and Ondo Finance Complete Cross-Chain, Atomic Settlement of Tokenized Treasury Fund
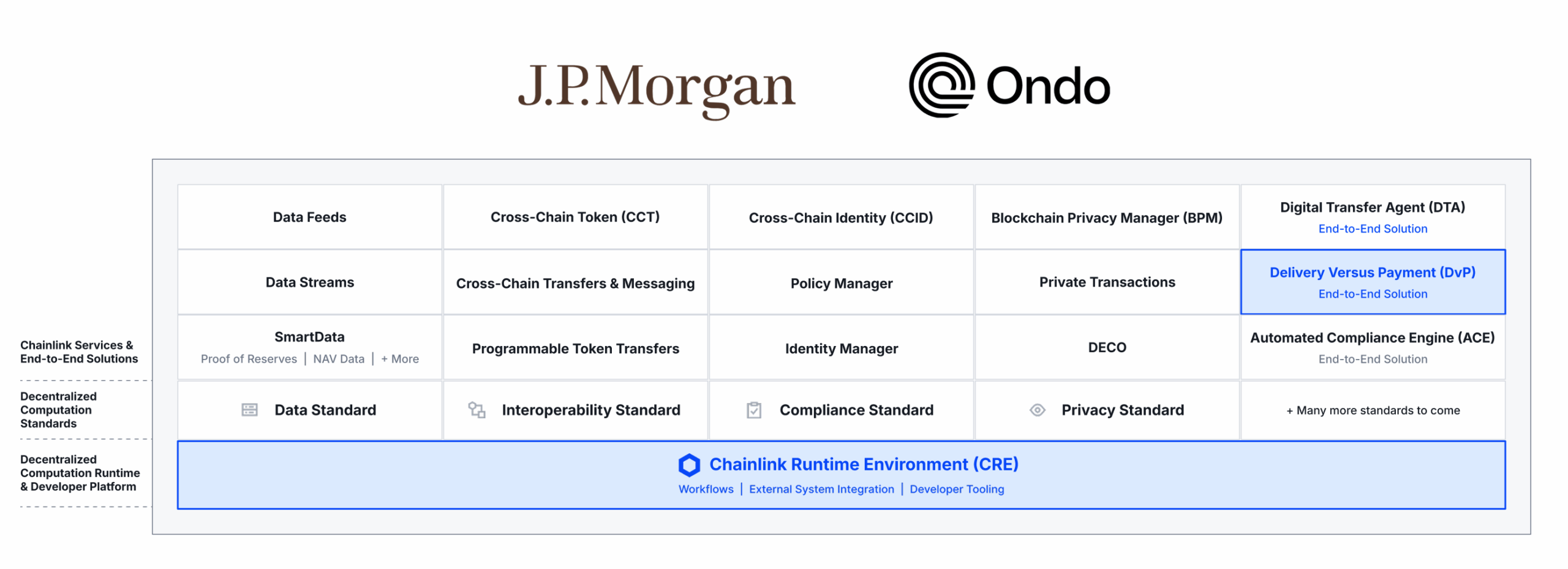
Kinexys by J.P. Morgan, the world-leading financial services firm’s blockchain business unit, and Ondo Finance, a pioneer in the tokenization of real-world assets, leveraged Chainlink’s cross-chain and orchestration capabilities to successfully complete a cross-chain DvP transaction that combined a permissioned interbank payment network (Kinexys), a public blockchain (Ondo Chain), and a tokenized U.S. Treasuries Fund (OUSG).
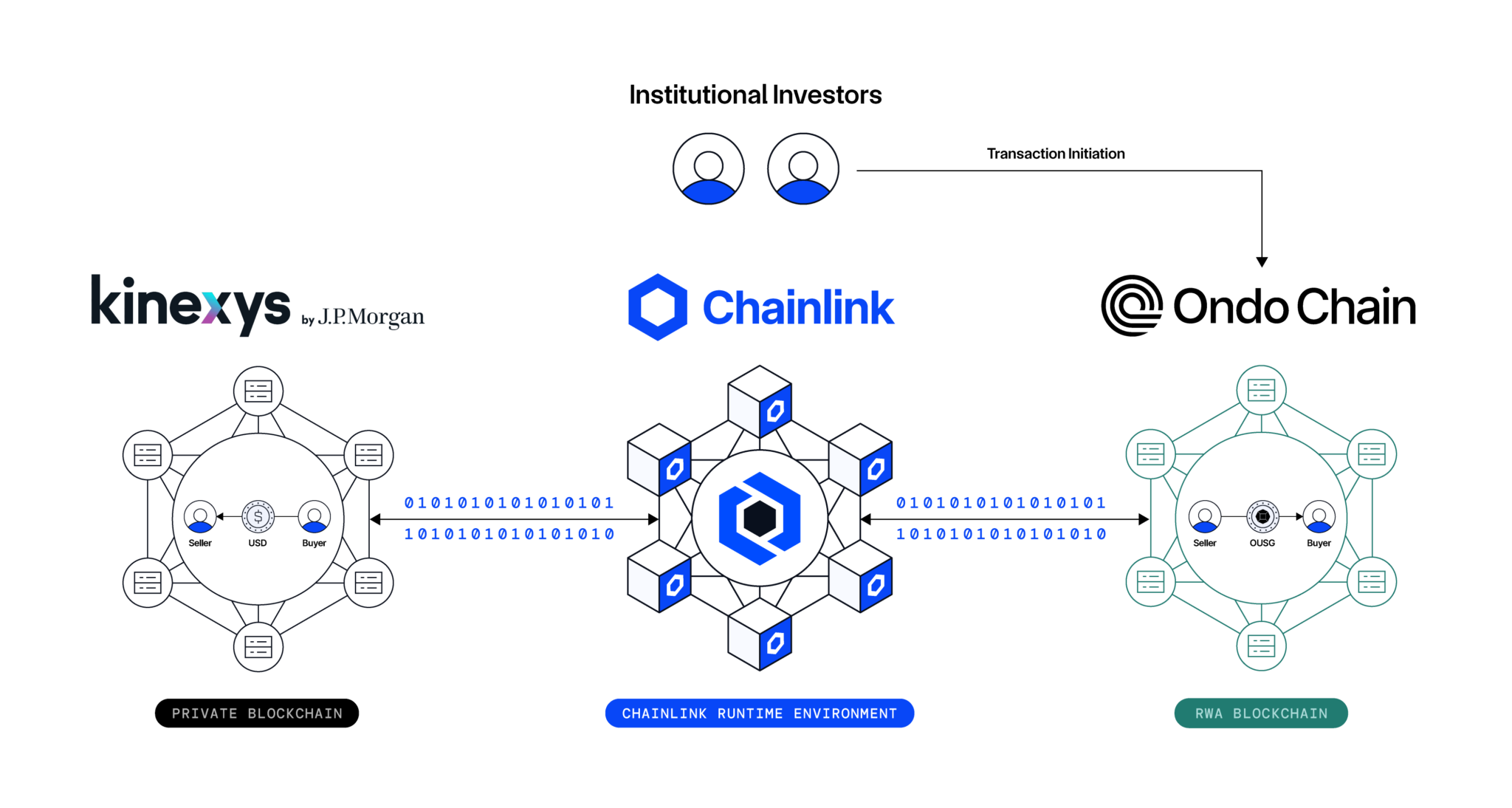
This key milestone marks the first cross-chain, atomic settlement of a tokenized asset between Kinexys’s permissioned blockchain and a public blockchain network. The transaction involved the exchange of Ondo Chain’s Short-Term U.S. Government Treasuries Fund (OUSG) as the asset leg with J.P. Morgan’s Kinexys network serving as the payment leg. The DvP solution was powered end-to-end by CRE, which facilitated seamless settlement between Kinexys and Ondo Chain’s testnet environment while preserving institutional-grade security and compliance standards.
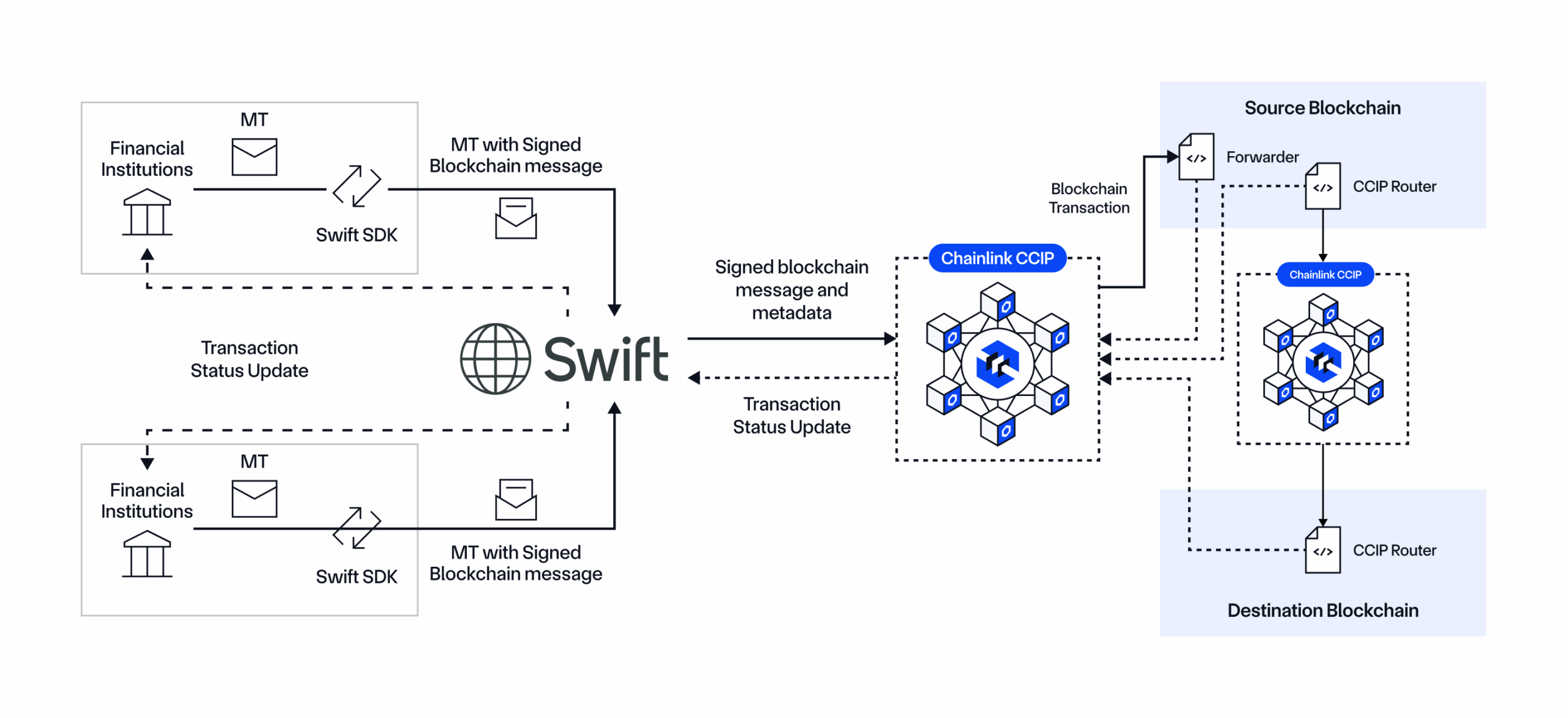
Swift and Chainlink Demonstrated a Secure and Scalable Way To Transfer Tokenized Assets Cross-Chain Using CCIP
Swift—the international bank messaging standard for 11,500+ banks—is working with Chainlink to enable financial institutions to connect to any existing public/private chain using Chainlink and their existing Swift infrastructure and messaging standards. Chainlink CCIP was used to enable the cross-chain settlement of tokenized assets across public and private blockchains. The successful collaboration featured 12+ world-leading financial institutions, including Euroclear, Clearstream, ANZ, Citi, BNY Mellon, BNP Paribas, Lloyds Banking Group, and SDX.
The Chainlink platform supports this by enabling the creation of adapters that connect any type of legacy system to the Chainlink Network. Once created, the adapter makes it so institutions can interact across public and private blockchains from a single integration with CCIP, removing the need for point-to-point integrations with each chain. It also makes it easier for legacy systems to interact with other legacy systems also integrated with the Chainlink platform, creating a network effect where the more institutions that adopt the Chainlink platform, the easier and faster it is to do transactions across counterparties.
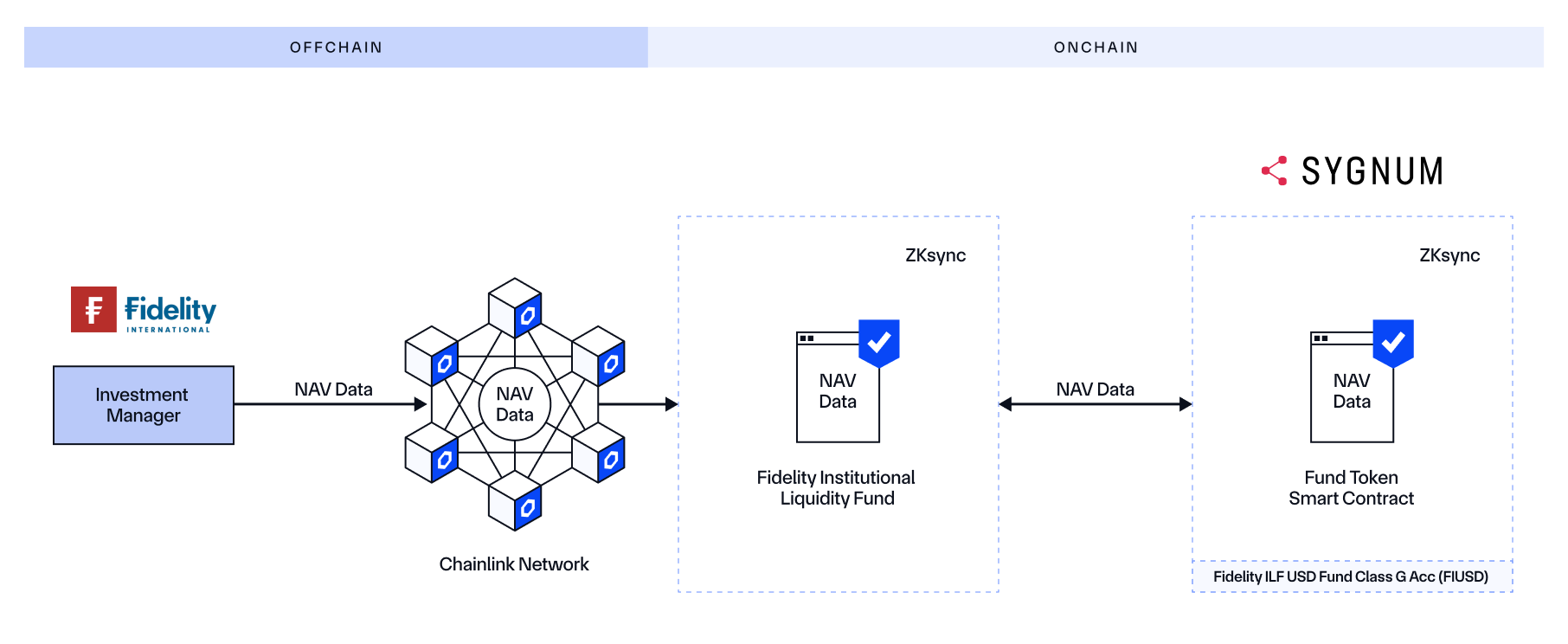
Fidelity International and Sygnum Leverage Chainlink To Service Tokenized Funds With NAV Data
Fidelity International, Sygnum, and Chainlink collaborated to bring Net Asset Value (NAV) data onchain to enable the tokenization of Fidelity International’s $6.9 billion Institutional Liquidity Fund on the zkSync public blockchain. With Chainlink, NAV data is accurately reported and synchronized onchain in an automated and secure manner, providing real-time transparency and built-in access to historical data for Sygnum, its clients, and broader market participants.
Aave Adopts Multiple Chainlink Services To Support Its Money Markets and Stablecoin
Aave, one of the largest DeFi protocols with 64B+ in total value locked (TVL), has adopted multiple Chainlink services across data and cross-chain to support its onchain money markets and decentralized stablecoin GHO. Aave has exclusively used Chainlink for over six years, enabling it to scale to more chains and markets while continually providing its users with the highest level of oracle security and reliability.
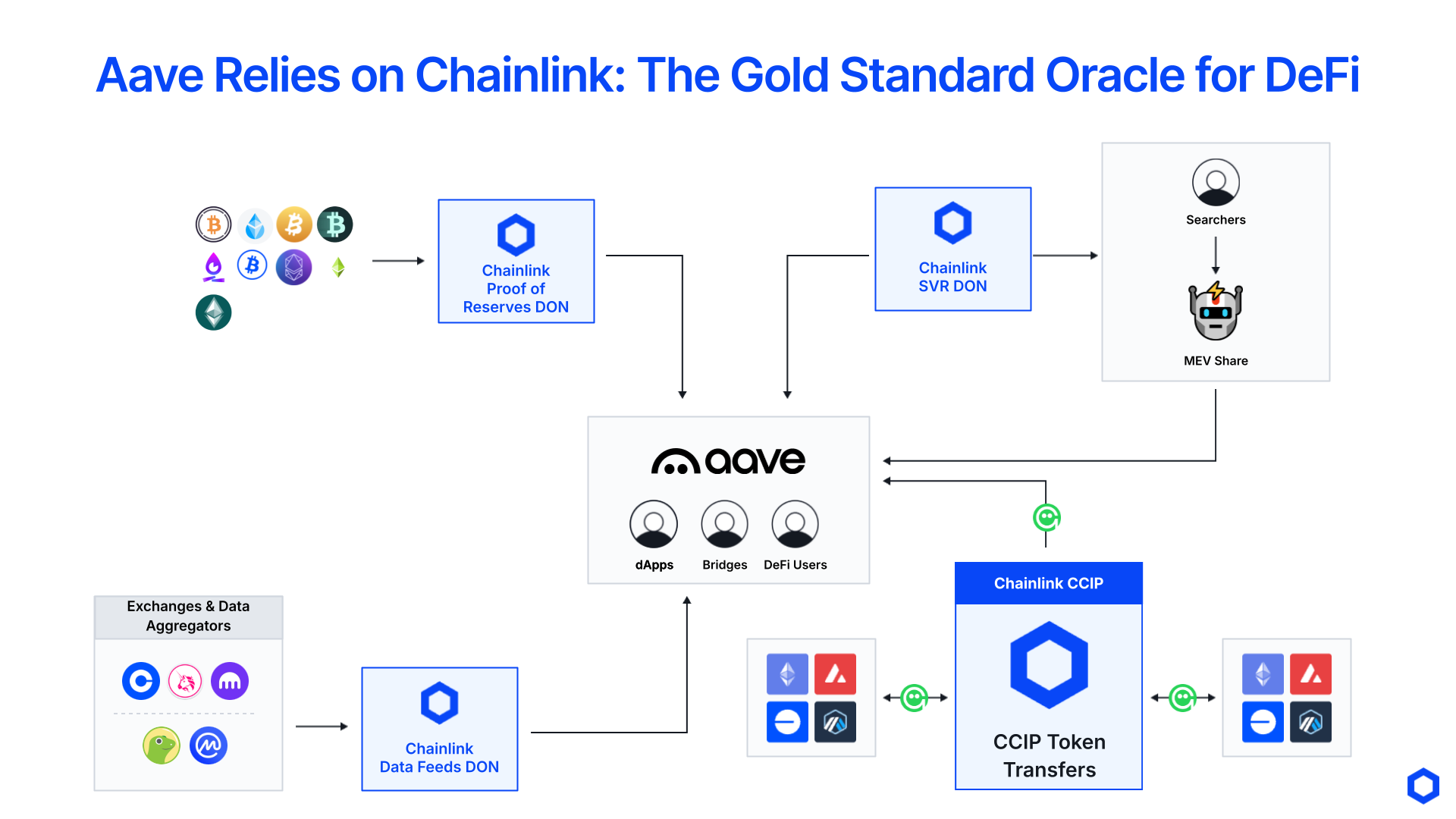
Aave leverages Chainlink Data Feeds and Data Streams to access secure and reliable market data for pricing collateral, both when issuing loans and executing liquidations. Aave supplements its use of Data Feeds on Ethereum by leveraging the Chainlink Smart Value Recapture (SVR) service to recapture MEV, providing them with an additional source of revenue. Aave also leverages Chainlink SmartData for Proof of Reserve data to ensure any tokenized or wrapped assets it supports are fully backed by offchain or cross-chain reserves.
Beyond Data, Aave leverages Chainlink’s interoperability standard to make their GHO stablecoin a CCT, which enables it to be transferred cross-chain via CCIP. They also use CCIP for cross-chain messaging to support cross-chain governance across the different chains they are deployed on. Aave’s usage of Chainlink doesn’t stop here, as Chainlink can enable them to scale to more asset types and chains, such as helping them with their Horizon initiative aimed at supporting tokenized real-world assets as collateral.
Lido Scale Staking Services Across L2 Blockchains Using Chainlink Platform
Lido, one of the largest DeFi protocols with 38B+ in TVL, utilizes Chainlink to support a liquidity staking solution that expands across multiple layer-2 blockchains. Lido also relies on Chainlink to price and secure its liquid staking tokens across DeFi.
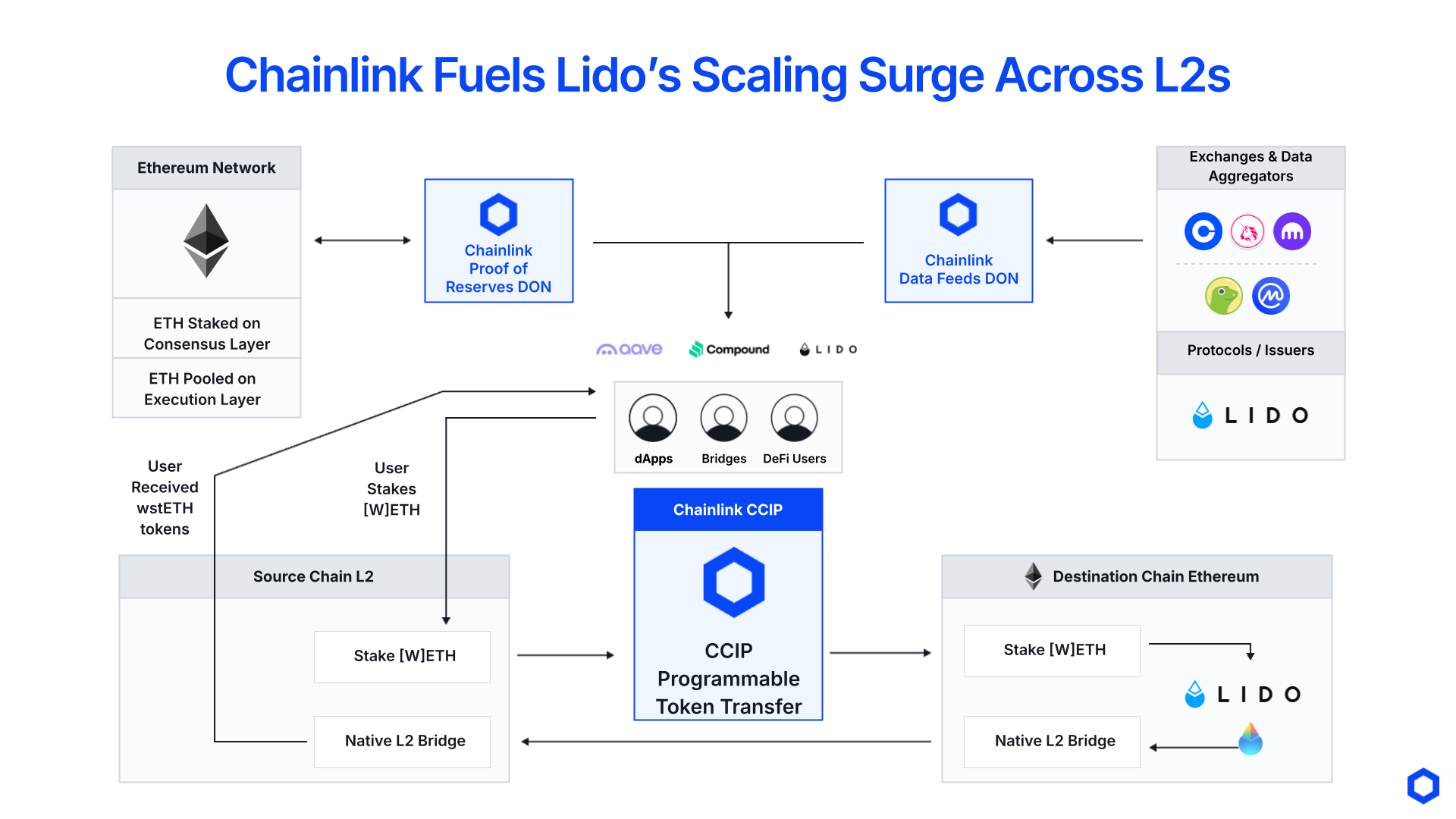
Lido makes use of the Chainlink data standard by sponsoring Data Feeds and Data Streams for pricing its liquid staking tokens. It also supports Proof of Reserve feeds, which prove that its liquid staking tokens are fully backed by reserves held on the Ethereum layer-1 blockchain. These data services enhance the utility of Lido tokens by enabling other DeFi protocols to support secure and reliable markets around them. Lido also leverages the Chainlink interoperability standard for cross-chain messaging and programmable token transfers to power its Direct Staking rails, which enable users to stake their ETH directly from other blockchain networks and receive Lido’s liquid staking token wstETH—all without having to leave the other blockchain.
Exponentially Accelerating Institutional Workflows and Advanced Blockchain Apps with Chainlink
The blockchain industry is only getting more sophisticated, as more chains launch, more applications emerge, and more legacy institutions across more jurisdictions integrate with blockchains.
Having access to all the critical data, computations, and legacy systems, along with coordinating transactions across multiple onchain and offchain systems, is essential to unlocking valuable use cases in the blockchain industry. This is especially true for institutional workflows and advanced DeFi apps, which interact across private and public blockchains, involve regulated digital assets across multiple jurisdictions, and require integration directly with legacy systems. Chainlink is the only all-in-one oracle platform providing connection to all the essential resources and solutions, along with a developer platform for orchestrating them into a unified application that is executed securely, reliably, and compliantly end-to-end. It’s why the Chainlink stack is increasingly being adopted by the largest financial institutions and top DeFi protocols as the standard powering one, many, or all parts of their onchain transactions’ lifecycles.
To learn more about Chainlink, visit chain.link, subscribe to the Chainlink newsletter, follow Chainlink on Twitter and YouTube, and follow Chainlink Labs on LinkedIn.
