How the Chainlink Network Goes Beyond Data Delivery
Oracles are commonly thought of as blockchain middleware that enable smart contracts to access external data—yet oracle networks, as they exist within Chainlink’s model, are much more than data delivery mechanisms. Through a wide-range of off-chain computational abilities, Chainlink’s decentralized oracle networks are providing blockchains with decentralized services that go far beyond securely fetching external data.
From Chainlink’s widely adopted Data Feeds, an extensive collection of on-chain price oracles for DeFi smart contracts, to Chainlink VRF, which generates a verifiable source of randomness for dynamic NFTs, to Chainlink’s highly customizable external adapters, the Chainlink Network is supporting a rapidly-expanding array of key oracle functions that are enhancing the capabilities of smart contracts across numerous blockchains and layer-2 networks.
In his recent presentation at the 2021 ETHDenver Hackathon, Chainlink Co-founder Sergey Nazarov emphasized the expansive functionality of decentralized oracle networks and how Chainlink-powered off-chain computations service a wide variety of smart contract use cases, from DeFi to parametric insurance to blockchain-based gaming. The following is an excerpt of Sergey’s talk highlighting a key takeaway that the Chainlink Network goes far beyond data delivery to power new features and applications for the fast-growing blockchain economy.
Chainlink is not just about data—it is about an oracle network—and oracle networks are responsible for everything that blockchains are not responsible for. An oracle network is not just about delivering data. It is about providing all the tools and services needed by a contract. Smart contracts run in blockchain platforms are hyper-secure and hyper-reliable, but they are low on feature-richness for security reasons. Oracles extend the capabilities of blockchains by offering decentralized services like off-chain computation.
Centralized systems have completely lost people’s trust in many cases and will continue to lose people’s trust in almost all cases. Centralized services from social media to communications to the financial system are being viewed even by the average person as unreliable. People no longer want to create long-term relationships with these institutions.
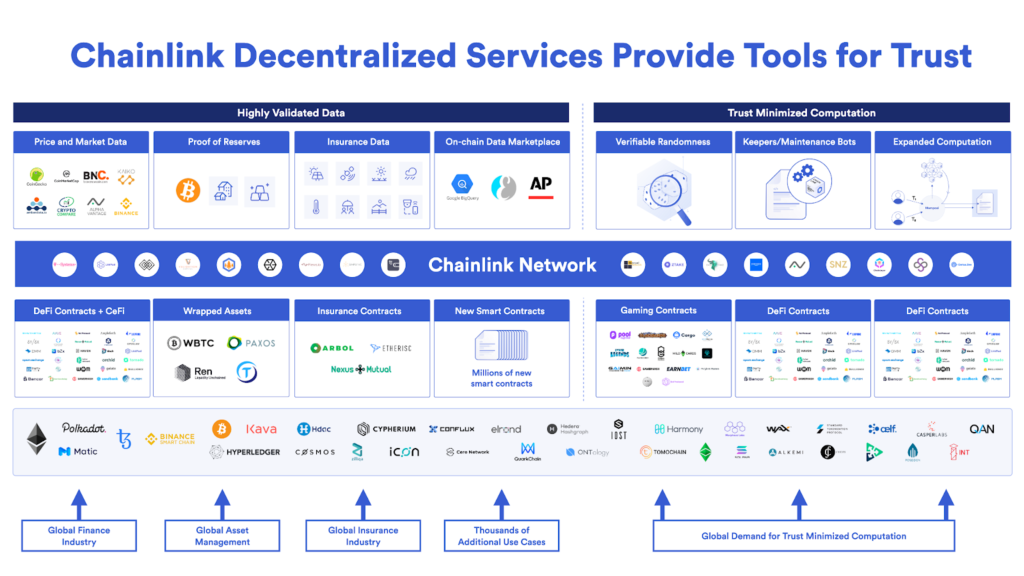
I think the middle ground between highly centralized, feature-rich systems and highly trust-minimized but low-feature blockchain systems is an oracle network. An oracle network sits between every use case and all of the blockchains that those use cases run on, providing blockchains with all the other services they need. All of the other services a blockchain needs are a huge universe of inputs that may start at providing different types of data but quickly moves on to trust-minimized computations that, generally speaking, blockchains usually don’t do and probably won’t do at scale. Oracle networks will expand to do trust-minimized computation, in addition to providing data, and the combination of these will enable a much wider realm of products to be built.
The middle ground between highly centralized, feature-rich systems and highly trust-minimized but low-feature blockchain systems is an oracle network.
The first thing that is becoming very popular in the blockchain gaming community is Chainlink’s Verifiable Random Function (VRF). VRF is working for many different blockchain games that already use it in production, and it’s going live on multiple blockchains. Anyone can easily use it on Ethereum to provide random inputs to games. Beyond that, we are finalizing some of our plans around Chainlink Automation and the ability to maintain a smart contract’s proper operation through a Chainlink Network. This is important, once again, because even DevOps and maintenance of contracts are responsibilities of oracle networks, as these operations need to be trust-minimized. Even beyond that, I think developers can think about, “How do I use the expanded computational capabilities of Chainlink’s adapters to compute more and more advanced things in a trust minimized-way that doesn’t require me to disclose things to blockchains?”
The realm of services the Chainlink Network offers will continue to grow, so if you’re a developer and you want to build cutting-edge, truly world-changing applications, Chainlink is fundamentally here to help you. The Chainlink Network is here to help the world’s developers make trust-minimized decentralized applications that will be the new way that society interacts around various information. To me, it’s apparent that is where society is headed because of the systemic and continued failure of trust relationships with centralized institutions like social media, other communication systems, and financial systems. Fundamentally, our goal is to accelerate the transition to a truly decentralized and fair economic system.
