How Chainlink Is Transforming the $30T Global Trade Industry
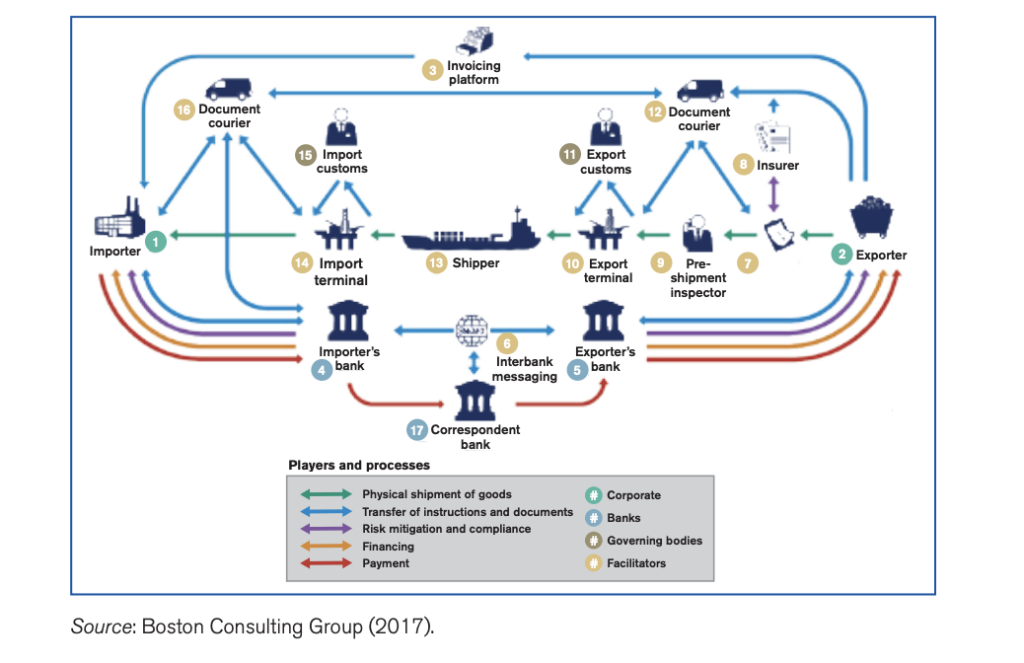
When Maersk tracked the paperwork and processes involved in sending a refrigerated container of avocados and roses from Kenya to the Netherlands, it found that over 100 people and 200 transactions were required. Moreover, of the 34 days the container spent in transit, 10 were spent waiting for documents to be processed.
Despite the many advances in blockchain and IoT technologies that have the potential to transform global trade, adoption has been slow. Holding back faster, digitized, and more efficient supply chains is the need to easily and securely connect supply chain systems with each other and access data from IoT devices.
Chainlink solves these interoperability and connectivity problems with its decentralized computing platform and is set to power a new era of global trade.
Seven Key Challenges in Global Trade
1. Interoperability
The inherently isolated nature of blockchains means they cannot connect with existing trade platforms or other blockchain-based applications in use across various companies and regions. A universal blockchain interoperability standard is needed to connect all supply chain systems and access real-world data.
2. Financing
Up to 80% of global trade is financed, according to the WTO, as buyers are usually only willing to pay once goods have been delivered. Whether it is through letters of credit or other supply chain finance instruments, the paper-heavy process and multiple parties involved typically lead to high costs, time-consuming procedures, and exposure to various risks.
3. Documentation
Paper-based processes increase administrative costs, are prone to errors, are vulnerable to fraud, and limit visibility. Despite advances in digital technologies, the industry still relies on many paper-based documents, such as packing lists, letters of credit, bills of lading, certificates of origin, export/import licenses, customs declarations, and more.
4. Coordination
Global trade relies on multiple players using separate processes and suffers from a lack of trust and coordination. For a single trade finance transaction, Boston Consulting Group found that more than 20 different entities and ~5,000 data interactions are involved in the process, with 85-90% of those interactions not adding any value. This problem is especially prevalent in emerging markets without access to the same financial services as developed economies.
5. Fraud
Counterfeit products and other malicious behavior, such as double financing, continue in global trade as the ecosystems lack the verification, tracking, and transparency needed to prevent fraud.
6. Errors
Missing cargo, duplicate payments, and inventory tracking mistakes are often almost impossible to detect in real-time. They are also challenging to remediate if they’re detected because it’s often unclear which journal entries correspond to which transactions, given the massive scale at which many supply chain companies operate.
7. Visibility
Orders, shipments, and payments cannot be easily tracked along the entire supply chain. They also often don’t sync up in backend systems, as a single order can be split across several shipments or multiple orders combined in one. While audits can help verify transactions and ensure contracts are fulfilled, they often lack sufficient detail to enhance decision-making and improve business operations.
How Chainlink Helps Solve Supply Chain Challenges
Blockchain technology can significantly improve global trade by enabling faster, more efficient, and verifiable delivery of goods, enhancing end-to-end traceability, improving coordination between partners, and enabling greater access to financing.
The Chainlink platform enables supply chains to realize the full benefits of blockchain and IoT technologies by connecting trade systems with each other and to real-world data in a reliable, secure, and decentralized manner.
Chainlink helps supply chains unlock:
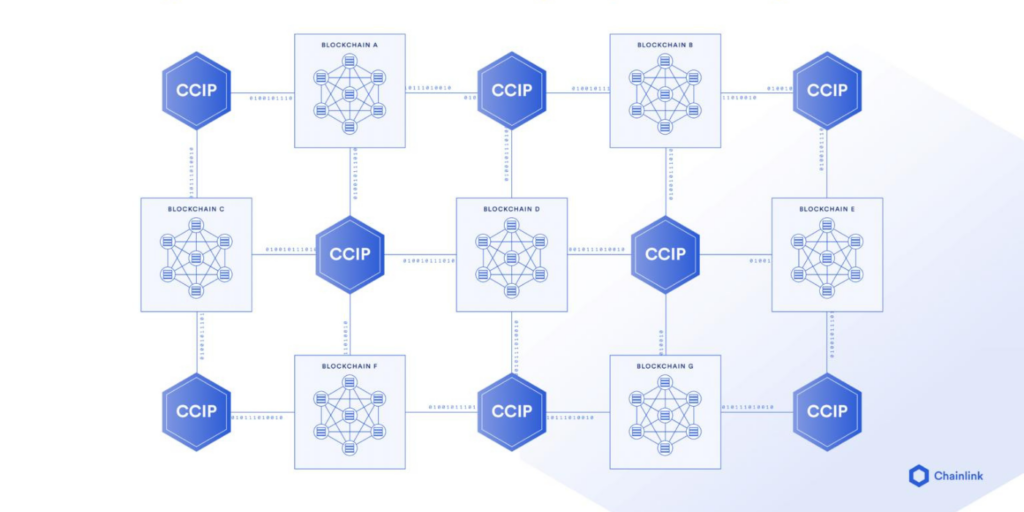
- Seamless interoperability—The Chainlink Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) provides a universal interoperability standard that enables the secure transfer of value and data between chains, and connection to existing platforms and systems.
- Onchain trade finance—Chainlink supports the onchain finance system with highly accurate market data, identity information, and proof of reserves, ultimately helping increase trade efficiency and expand global trade access across emerging markets.
- Digitization and automation—Reformatting previous paper-based documents as dynamic NFTs and utilizing Chainlink Automation and Functions enables digitized documents to be automatically updated as they move along the supply chain.
- Aligned ecosystem—A golden record on the blockchain enables multiple stakeholders to automate invoices, financing, payments, and more, reducing manual handling errors and saving on back-office administrative costs.
- Fraud protection—By enabling loads to be tracked and verified across the entire supply chain through the use of blockchain and IoT technologies, Chainlink can help provide end-to-end verification that enables the authenticity of goods to be established, reducing counterfeits and fraud.
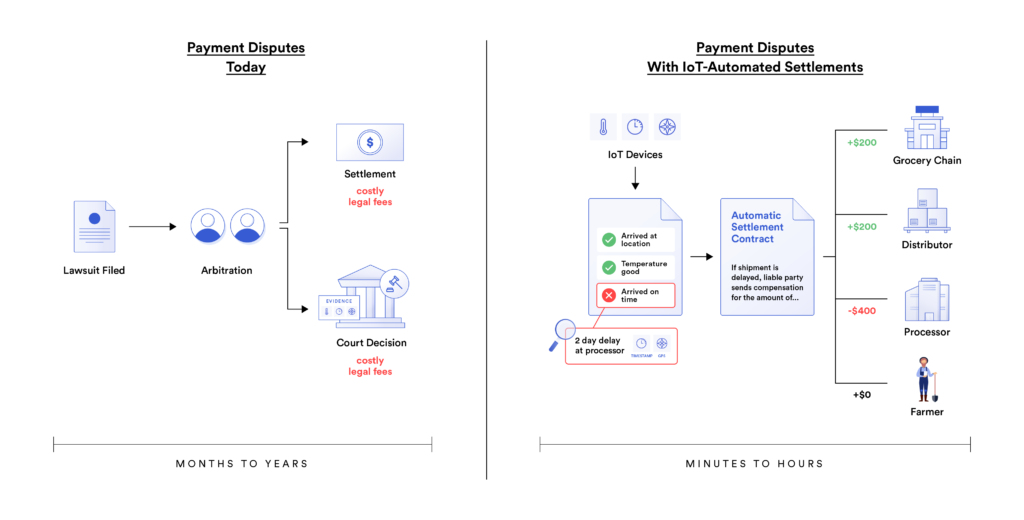
- Highly accurate data—Verifying shipment delivery and condition with various IoT, RFID, and other devices enables the documented status to reflect goods’ real-world condition, enabling faster business responses and helping to identify key issues in supply chains. For example, the temperature of a cargo container carrying fresh food could be monitored using an IoT device, and if the container exceeds a pre-specified temperature, it could trigger an onchain insurance smart contract and automatically release funds.
- End-to-end transparency—Instead of being limited to one-up/one-down visibility, blockchains can give participants greater visibility into all the necessary information while still protecting trade secrets and private information.
Chainlink and Vodafone DAB Transform Global Trade

Chainlink and Vodafone’s Digital Asset Broker (DAB) demonstrated the seamless exchange of trade documents across diverse platforms and blockchains using CCIP. This collaboration has the potential to enable applications in a supply chain to securely exchange data and tokens across public and private blockchains, and access data from IoT devices via the DAB platform. For example, an IoT device could detect that cargo has caught fire and automatically trigger an insurance process onchain. By securely connecting IoT data to blockchains, CCIP can unlock many exciting use cases for trade finance.
“Vodafone DAB and Chainlink are showing how their platforms can be combined to cut through this sea of incompatibility by bridging traditional markets with advanced decentralised platforms. This ensures seamless and secure exchanges of data and services across the global trade ecosystem, estimated to be worth over $30 trillion last year.”—Jorge Bento, CEO of Vodafone DAB
Unlocking the Economy of Things (EoT)
The Economy of Things (EoT) is the next generation of the Internet of Things (IoT). In the EoT, devices in the real world can not only send and receive information—they can transact. An EV can pay at a charging station, a fridge can purchase groceries, and a house can trigger its insurance contract.
Along with IoT devices, blockchains, smart contracts, and oracles are essential to unlocking the EoT. They provide a golden record, deterministic and programmable agreements, and connectivity to real-world information and other systems.
Enabled by Chainlink and Vodafone DAB, the EoT is set to completely redefine how supply chains operate. Instead of relying on paper-based processes, manual updates and audits, and inefficient financing—the entire supply chain will be automated, verifiable, and highly efficient end to end.
CCIP is not just for finance or global trade; it’s for the global economy. Regardless of whether it’s connected to an IoT device or a private bank chain, CCIP is becoming the universal standard that underpins the secure transfer of value and data across any blockchain-enabled application.
