CCIP 1.5 Officially Launches on Mainnet
The Chainlink CCIP v1.5 upgrade is now live on mainnet for all developers, including the CCIP Token Manager.
We’re excited to introduce the CCIP v1.5 upgrade—a set of upgrades and improvements to Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), focused on massively scaling the number of tokens integrated with CCIP and making the protocol easier than ever for developers to use. The CCIP v1.5 upgrade is now live for all developers across all supported blockchain mainnets.
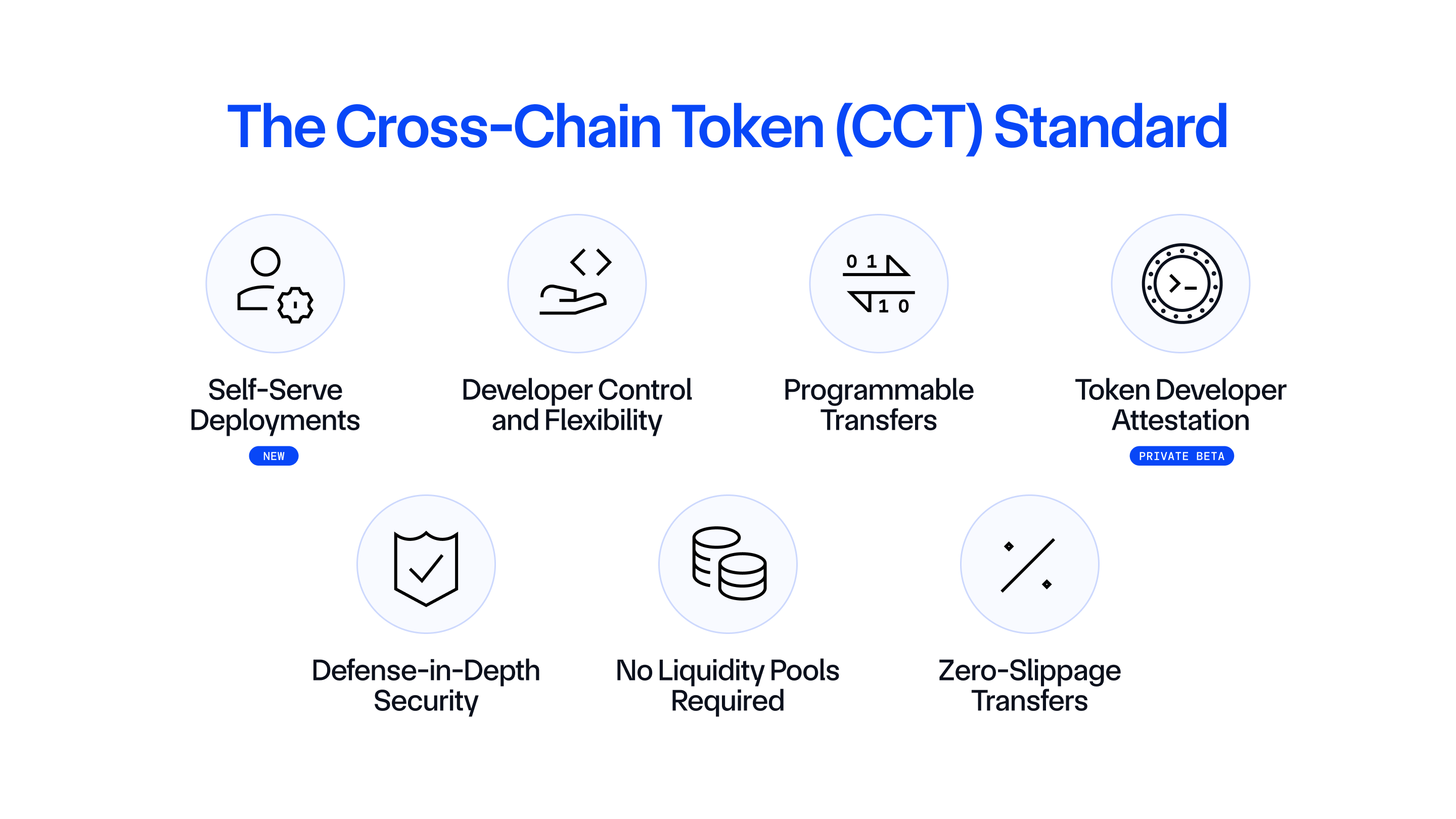
CCIP v1.5 introduces the Cross-Chain Token (CCT) standard, which enables token developers to integrate new and existing tokens with CCIP in a self-serve manner in minutes. CCTs are cross-chain native tokens secured by CCIP. CCTs support self-serve deployments, full control and ownership for developers, enhanced programmability, and zero-slippage transfers—all backed by CCIP’s industry-standard defense-in-depth security.
Notably, CCTs are token logic agnostic, meaning token developers can deploy pre-audited token pool contracts to turn any ERC20-compatible token into a CCT or deploy their own custom token pool contracts for bespoke token use cases. CCTs do not require token developers to inherit any CCIP-specific code within their token’s smart contract.
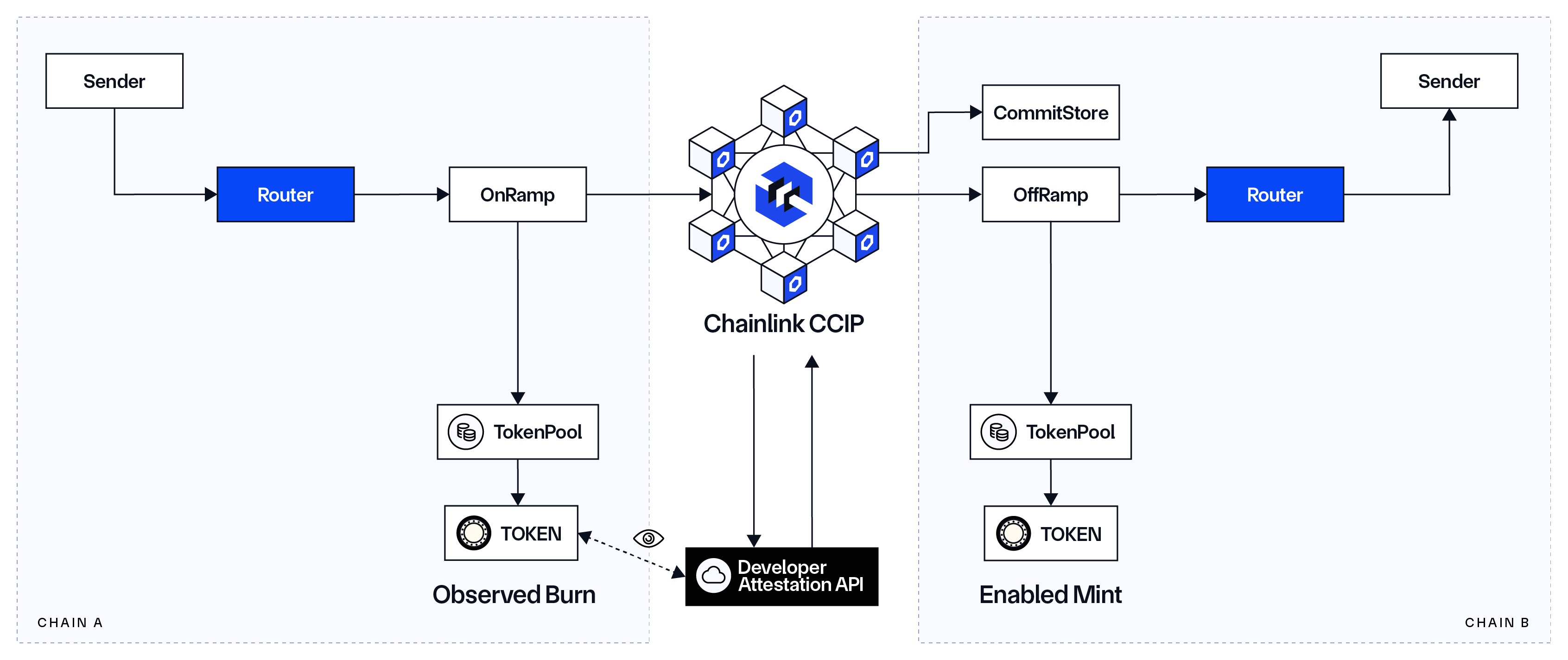
Furthermore, CCIP v1.5 introduces a new Token Developer Attestation feature that enables token developers to participate in an optional layer of verification for their CCTs by attesting to token burn or lock events on source chains before CCIP can mint or unlock tokens on destination chains. This feature was widely requested by developers of tokenized assets as a way to support their security model and assist with their compliance needs. The Token Developer Attestation feature is currently available in private beta.
The CCIP v1.5 upgrade also includes the CCIP Token Manager—an intuitive front-end web interface for the deployment of new and management of existing CCTs by their developers, including no-code guided deployments and configuration tools. The CCIP v1.5 upgrade also features a number of key developer experience improvements, including the new CCIP SDK, improvements to the CCIP Explorer, and additional security and privacy capabilities to further strengthen CCIP’s position as the most secure cross-chain infrastructure for Web3 and capital markets.
The Cross-Chain Token (CCT) Standard: Secure, Native Cross-Chain Transferability For Any Token
The CCT standard presents numerous key advantages for token developers seeking to make their token natively cross-chain interoperable.
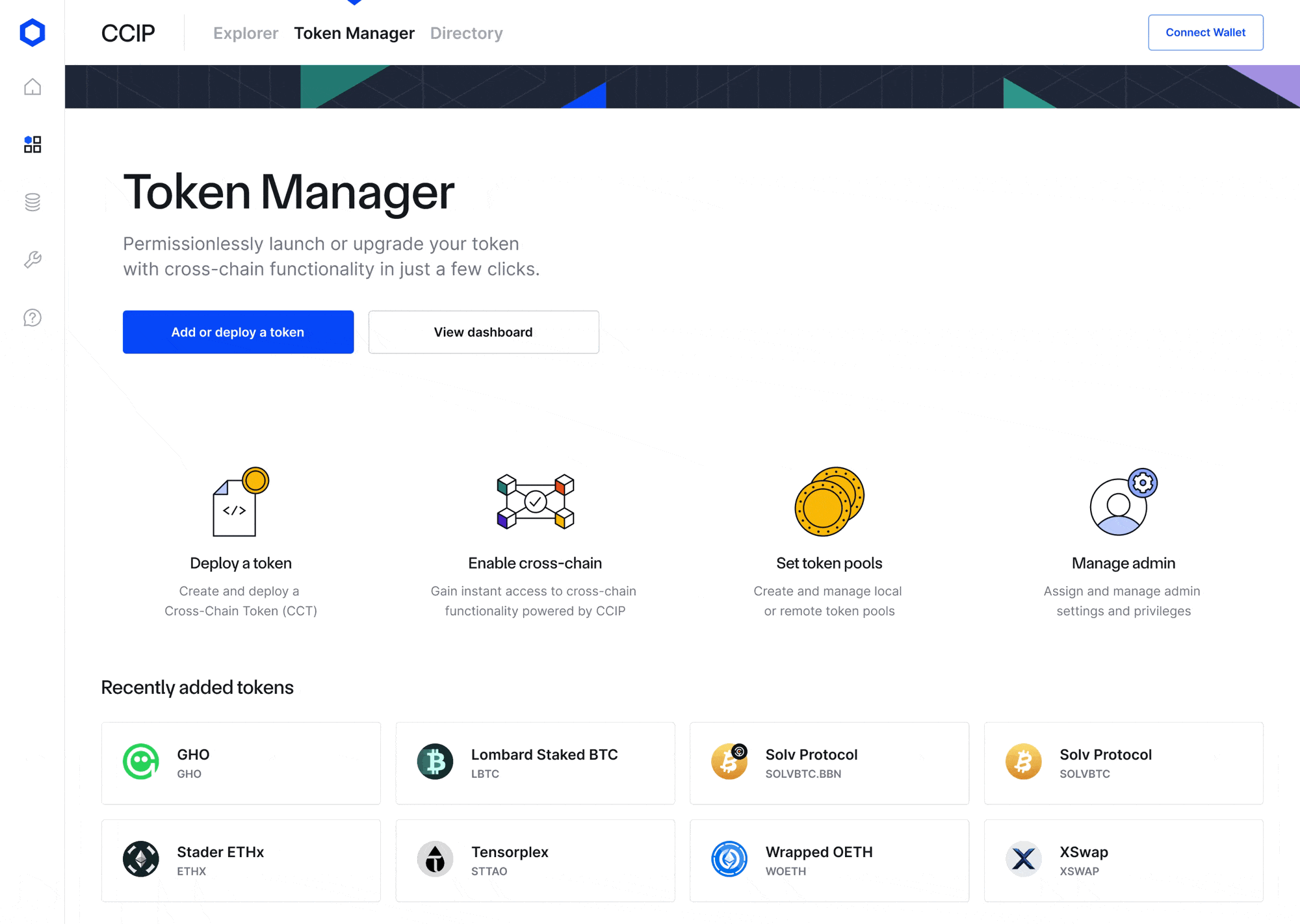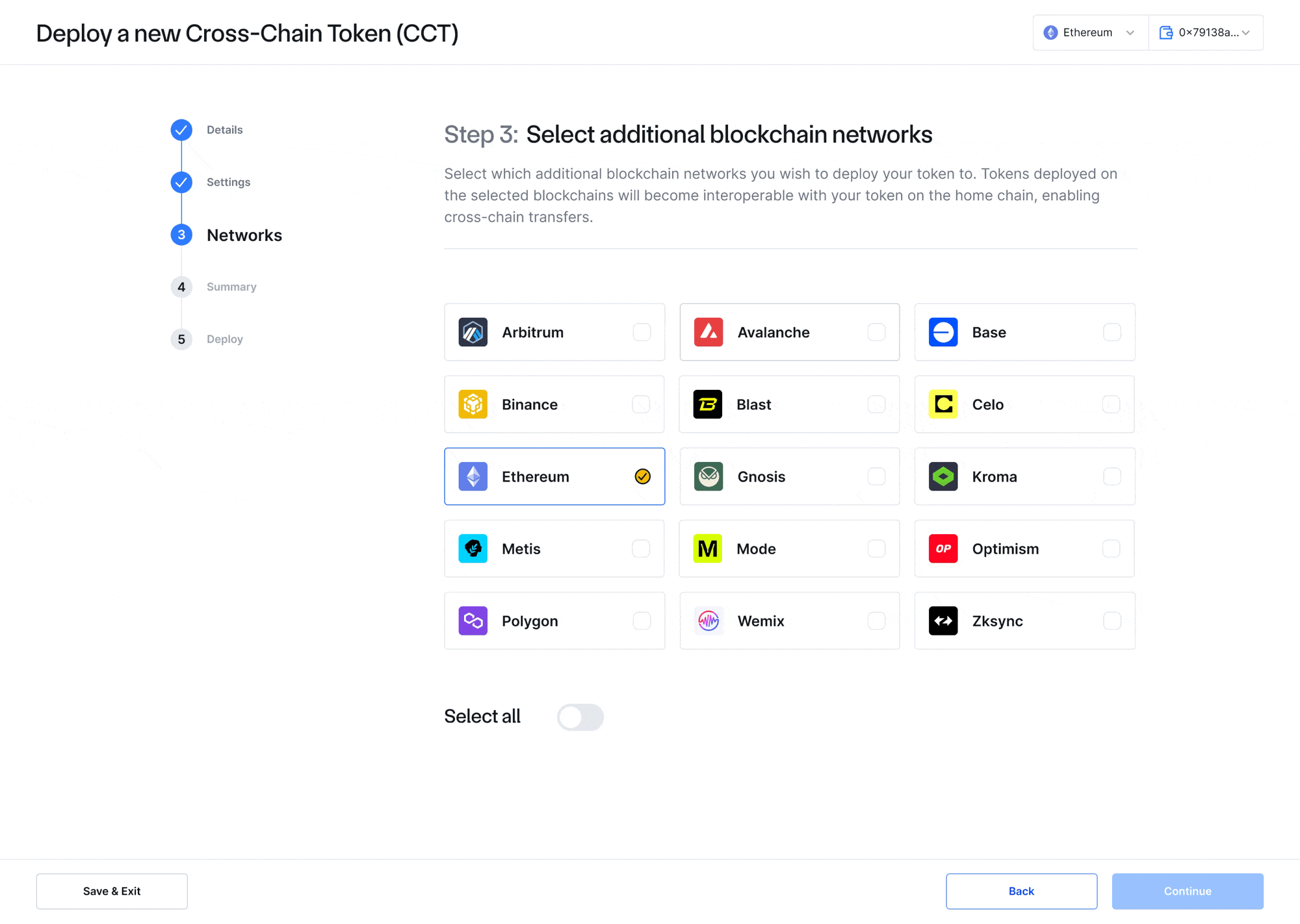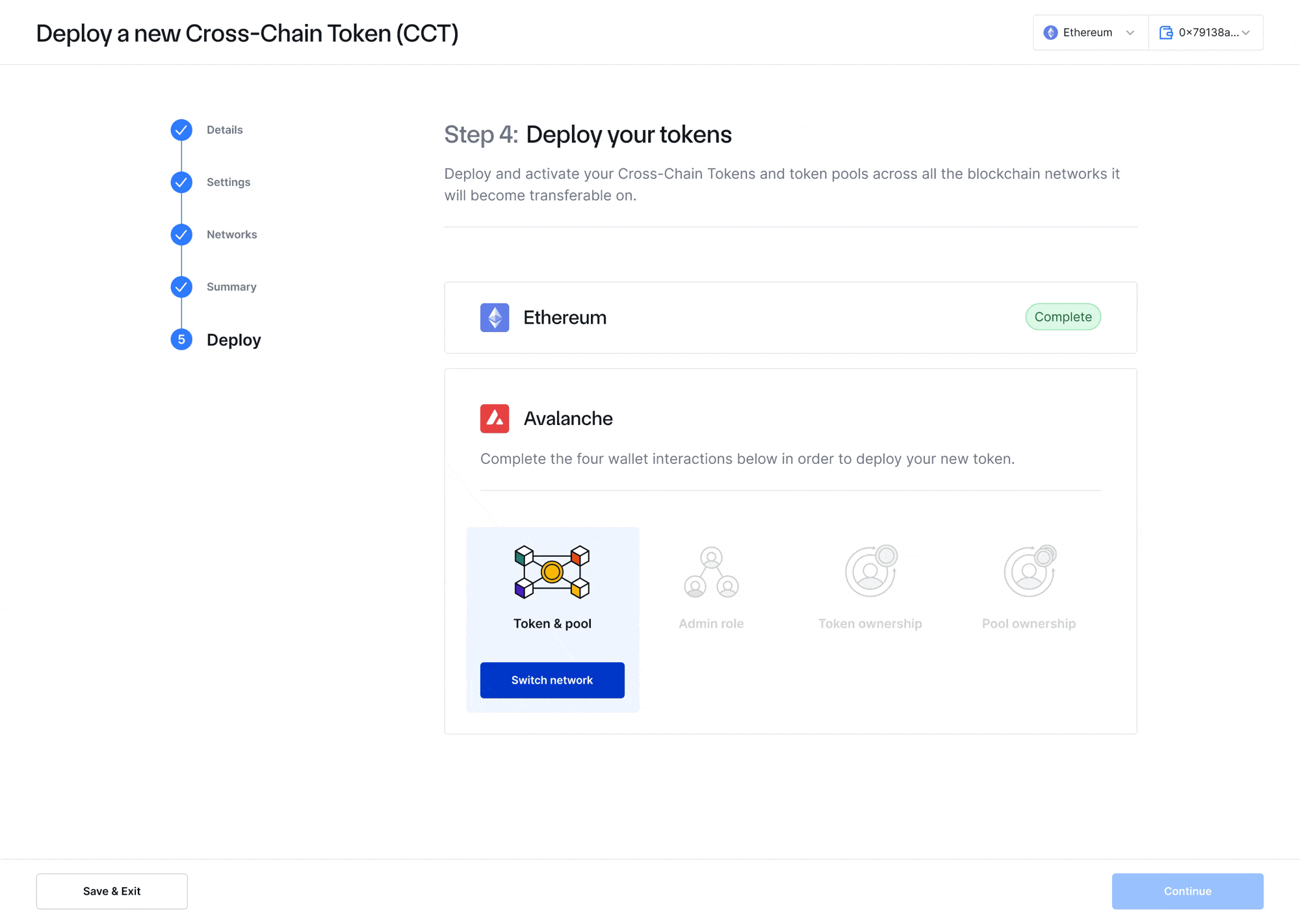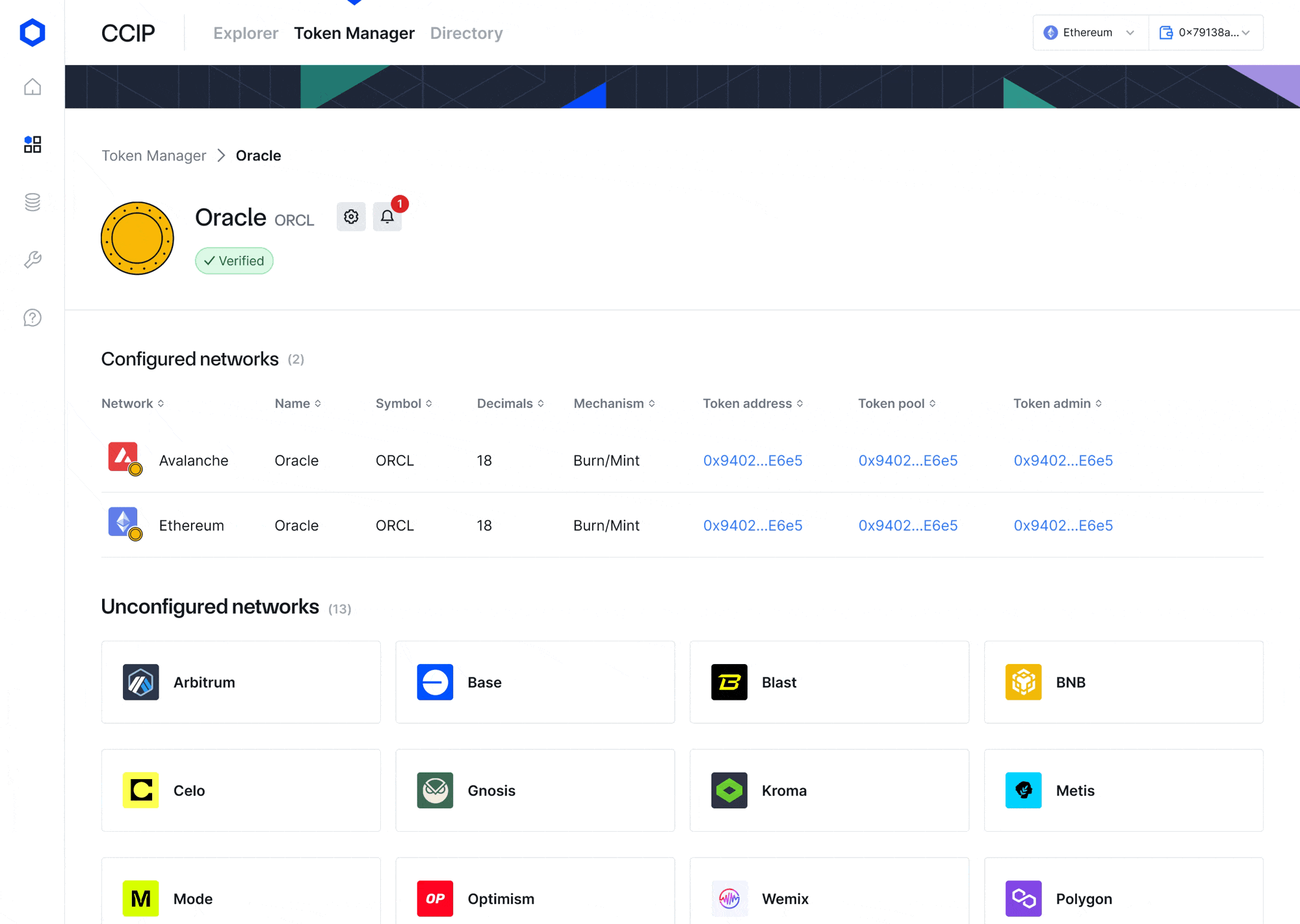
- Self-Serve and Permissionless—Token developers can launch a new CCT or make an existing token a CCT in a self-serve manner in minutes. When creating CCTs, CCIP contracts verify token contract ownership onchain to avoid fragmentation and help token developers remain in control of their tokens in an increasingly multi-chain world. If token ownership cannot be verified using onchain data, manual approval can be provided. Developers also have access to a number of resources that make the CCT creation process and ongoing management seamless, including a Token Manager, CCIP Explorer, CCIP Directory, and accompanying documentation (both tutorials and scripts).
- Developer Control and Flexibility—Token developers retain full ownership of their token contracts, CCIP token pools, and customized implementation logic, including rate limits across all blockchains. This ensures complete autonomy and flexibility when managing CCT deployments, without requiring vendor lock-in, hard-coded functions, or external dependencies that may limit future optionality or add risks to security. Notably, CCTs are token logic agnostic, meaning token developers can deploy pre-audited token pool contracts to turn any ERC20-compatible token into a CCT or deploy their own custom token pool contracts for custom token use cases.
CCTs do not require token developers to inherit any CCIP-specific code within their token’s smart contract.
- Programmable Token Transfers—CCIP enables the transfer of value (via CCTs) cross-chain along with data instructing the receiving smart contract on what to do with those CCTs once they arrive on the destination chain. Through CCIP’s Programmable Token Transfers, a complex set of actions involving multiple users, blockchains, and assets can be condensed down to a single atomic cross-chain instruction. CCTs also benefit from additional security functions in their CCIP token pools such as configurable rate limits and reliability features such as Smart Execution, which helps ensure reliable transaction execution on the destination chain regardless of blockchain network congestion.
- Token Developer Attestation—Token developers have the option of adding additional external verifiers to their CCTs, enabling token developers to participate in the verification process for transferring CCTs cross-chain by attesting to token burn or lock events on source chains before CCIP can mint or release tokens on destination chains. This feature was widely requested by developers of stablecoins, wrapped assets, staking derivatives, and developers of tokenized real-world assets (RWAs) as a way to support their security model and assist with their compliance needs, which may require more granular control over the authorization of cross-chain transfers.
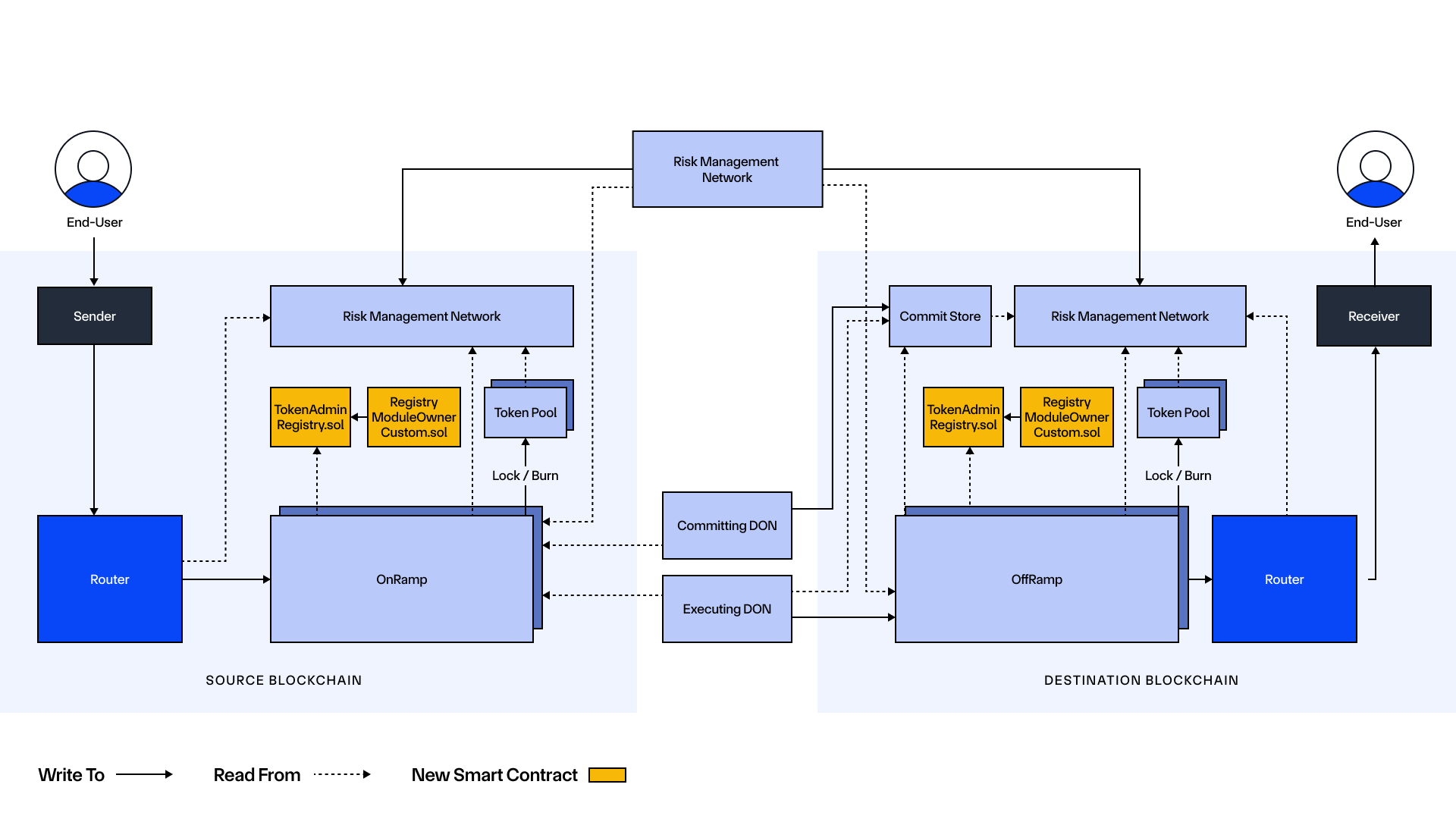
- Defense-in-Depth Security—CCTs are secured by Chainlink CCIP, which is powered by the same time-tested, battle-hardened Decentralized Oracle Network (DON) infrastructure that has enabled trillions in onchain transaction value since the start of 2022. Each CCIP transfer is validated by multiple DONs, including an independent Risk Management Network that continuously monitors and validates the behavior of CCIP—a pioneering advancement in cross-chain that builds upon established engineering principles (e.g., N-version programming).
- No Liquidity Pools Required—Leveraging burn and mint capabilities, token pools are able to operate without the need for liquidity. Compared to liquidity-based bridging solutions that require significant upfront capital to make their token cross-chain transferable, resulting in a diminished user experience, tokens that adopt the CCT standard are able to be instantly transferable without limitations on transfer size (within the configurable rate limits).
- Zero-Slippage Transfers—Token developers are provided access to pre-audited token pool contracts that enable zero-slippage cross-chain transfers of CCTs. The exact amount of tokens sent to the CCIP OnRamp on the source chain is always the exact amount of tokens received on the CCIP OffRamp on the destination chain.
A number of protocols have already adopted the CCT standard to make their native tokens cross-chain transferable via CCIP, including Aave’s decentralized stablecoin (GHO) and Solv Protocol’s wrapped/tokenized Bitcoin (SolvBTC). Furthermore, Lombard has already begun testing the Token Developer Attestation feature in private beta for their LBTC token.
Building and Managing CCIP-Powered dApps and CCTs Is Easier Than Ever
The CCIP v1.5 upgrade introduces a variety of new developer tools and web interfaces that make CCIP the optimal solution for developers building cross-chain.
- CCIP Token Manager—A new intuitive front-end web interface for token developers to seamlessly register, configure, and manage CCTs and token pools across multiple blockchain networks, including no-code, guided token deployments. The CCIP Token Manager serves as a complement to existing CLI methods and simplifies the process of deploying new CCTs or transforming existing tokens into a CCT. After deploying a CCT, CCIP-powered bridging applications such as Transporter, XSwap, and other interfaces can provide a front-end interface for users to transfer the token.
- CCIP SDK—A new software development kit that streamlines the process of integrating CCIP by allowing developers to use JavaScript to create a token transfer frontend dApp. It provides pre-built functionality that enables projects to integrate at a higher level of the stack, reducing the need for direct interaction with smart contracts, manual event watching, and error handling. The CCIP SDK UI components are built on top of Wagmi, a leading Web3 development framework for frontend developers, empowering developers to build with tools they already know and use. This new SDK is an additional option for developers building cross-chain with CCIP, complementing existing Chainlink ecosystem SDKs such as XSwap’s XPay.
- Refreshed CCIP Explorer—A new, unified design and improved navigation of the CCIP Explorer makes for a more seamless and intuitive developer experience. This includes the ability to enter any CCIP search term and get an expanded side drawer about the transaction details. The CCIP Directory also provides a simplified view of all supported networks and tokens, giving you instant access to any details related to a network lane or token.
Chainlink CCIP v1.5 allows developers to integrate their custom tokens across different chains while maintaining control of the underlying smart contracts. With this self-serve token pool setup, developers can write custom logic and build secure, interoperable blockchain projects.”—Patrick Collins, CEO at Cyfrin
Chainlink is partnering with Cyfrin Updraft to release a course that walks developers through how to build with CCIP v1.5. Web3 development platform thirdweb is also partnering with Chainlink to enable developers to create and deploy a Cross-Chain Token (CCT) from their Explore dashboard.
We’re excited to empower developers with native cross-chain token creation and transfers using Chainlink CCIP. We believe that the combination of thirdweb’s contract deployment flow and CCIP will accelerate adoption amongst developers.”—Cathal (Catty) Berragan, VP Marketing at thirdweb
Additional Security and Privacy Enhancements to CCIP
The CCIP v1.5 upgrade also introduces a number of additional upgrades to improve both the security and functionality of CCIP:
- Risk Management Network Enhancements—Introduction of finer-grained controls for the Risk Management Network’s anomaly detection, such as the ability to engage emergency halts (cursing) on a chain-by-chain basis. In practice, this means that if the Risk Management Network detects abnormal behavior with a specific chain (e.g., a deep block reorg), then lanes to/from that blockchain can be paused without pausing chain lanes between unrelated blockchains.
- Out of Order (OOO) Message Execution—Users can indicate that their message doesn’t need to be executed in nonce-order. This is particularly important on ZK-rollups, where a phenomenon known as “proof overflows” can make it impossible to include a transaction in the rollup chain. Proof overflows could allow a malicious actor to permanently render a cross-chain dApp on a ZK-rollup inoperable by blocking a nonce with an overflowing message. This potential attack vector is eliminated as part of the upgrade, ensuring CCIP can be safely deployed on ZK-rollups.
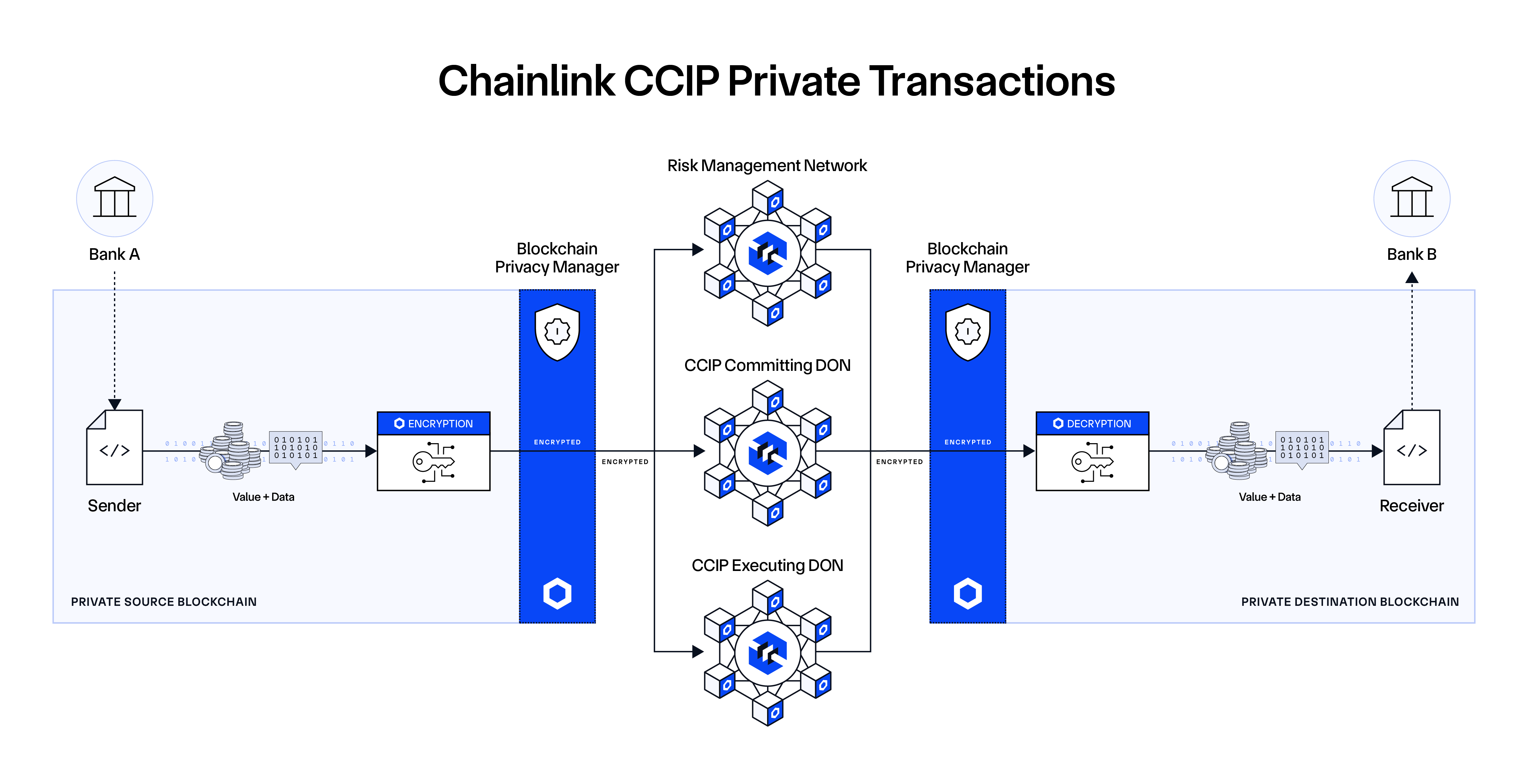
- CCIP Private Transactions—Chainlink introduced a new suite of privacy-preserving features that enable fully confidential transfers between private blockchain networks. CCIP Private Transactions are built upon the Blockchain Privacy Manager and use a novel onchain encryption protocol to preserve data confidentiality and data integrity.
CCIP As the Cross-Chain Standard Bridging DeFi and TradFi
The CCIP v1.5 upgrade marks a major upgrade in the CCIP developer experience, both for onboarding new/existing tokens to the CCT standard and quickly integrating CCIP into cross-chain applications. As a result, the growth of the cross-chain economy can further accelerate across DeFi and TradFi while still providing developers with secure-by-default infrastructure.
In parallel, we’re excited to share that we’ve already been working toward the release of the next upgrade of CCIP, which is currently going into audit and will further enhance the protocol’s scalability and integrability across blockchain environments. We look forward to sharing more info on CCIP’s continual improvements in the future.
Check out the CCIP developer documentation to start integrating CCIP into your cross-chain application. To learn more about Chainlink, visit chain.link, subscribe to the Chainlink newsletter, and follow Chainlink on Twitter and YouTube.
—
Disclaimer: This post is for informational purposes only and contains statements about the future, including anticipated product features, development, and timelines for the rollout of these features. These statements are only predictions and reflect current beliefs and expectations with respect to future events; they are based on assumptions and are subject to risk, uncertainties, and changes at any time. There can be no assurance that actual results will not differ materially from those expressed in these statements, although we believe them to be based on reasonable assumptions. All statements are valid only as of the date first posted. These statements may not reflect future developments due to user feedback or later events and we may not update this post in response. Chainlink CCIP is a messaging protocol which does not hold or transfer any assets. Please review the Chainlink Terms of Service, which provides important information and disclosures.
